Abstract
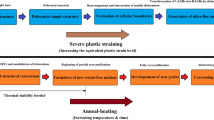
Recent efforts have focused on the development of novel manufacturing processes capable of producing microstructures dominated by sub-micron grains. For structural applications, grain refinement has been shown to enhance mechanical properties such as strength, fatigue resistance, and fracture toughness. Through control of the thermo-mechanical processing parameters, dynamic recrystallization mechanisms were used to produce microstructures consisting of sub-micron grains in 9310 steel. Starting with initial bainitic grain sizes of 40 to 50 μm, various levels of grain refinement were observed following hot deformation of 9310 steel samples at temperatures and strain rates ranging from 755 K to 922 K (482 °C and 649 °C) and 1 to 0.001/s, respectively. The resulting deformation microstructures were characterized using scanning electron microscopy and electron backscatter diffraction techniques to quantify the extent of carbide coarsening and grain refinement occurring during deformation. Microstructural models based on the Zener–Holloman parameter were developed and modified to include the effect of the ferrite/carbide interactions within the system. These models were shown to effectively correlate microstructural attributes to the thermal mechanical processing parameters.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Davis, Davis & Associates: ASM Specialty Handbook - Carbon and Alloy Steels, ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 1996.
W.D. Klopp: Aerospace Structural Metals Handbook, E 9310 (Code 1209), Purdue Research Foundation, West Lafayette, 1999.
U.J. De Souza and M.F. Amateau: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 183–93.
R. Song, D. Ponge, D. Raabe, J. G. Speer, and D. K. Matlock: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 441 (1), pp. 1–17.
R. Z. Valiev, R. K. Islamgaliev, and I. V. Alexandrov: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2000, vol. 45 (2), pp. 103–89.
Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, N. Tsuji, and T. Sakai: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47 (2), pp. 579–83.
K. Muszka, L. Madej, and J. Majta: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 574, pp. 68–74.
Z. Hegedüs, J. Gubicza, M. Kawasaki, N. Q. Chinh, J. L. Lábár, and T. G. Langdon: J. Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 48, pp. 4637–45.
Y. Iwahashi, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, and T. G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46 (9), pp. 3317–31.
R. Z. Valiev and T. G. Langdon: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2006, vol. 51 (7), pp. 881–981.
B. Cherukuri, T. S. Nedkova, and R. Srinivasan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 410, pp. 394–97.
A. K. Padap, G. P. Chaudhari, S. K. Nath, and V. Pancholi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 527 (1), pp. 110–17.
A. Azushima, R. Kopp, A. Korhonen, D.Y. Yang, F. Micari, G.D. Lahoti, P. Groche, J. Yanagimoto, N. Tsuji, A. Rosochowski, and A. Yanagida: CIRP Annals – Manuf. Tech., 2008, vol. 57, pp. 716–35.
Y. Estrin and A. Vinogradov: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 782–817.
S. F. Medina and C. A. Hernandez: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44 (1), pp. 165–71.
I. N. Kunitskaya, Ya. I. Spektor, and V. E. Olshanetskii: Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2012, vol. 53 (9–10), pp. 498–502.
G.F. Vander Voort: Atlas of Time-Temperature Diagrams for Irons and Steels, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1991, pp. 466.
G. Glover and C. M. Sellars: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4 (3), pp. 765–75.
R.D. Doherty, D.A. Hughes, F.J. Humphreys, J.J. Jonas, D. Juul Jensen, M.E. Kassner, W.E. King, T.R. McNelley, H.J. McQueen, and A.D. Rollett (1997) Mater. Sci. Eng. A, vol. 238 (2), pp. 219–74.
D. Snyder, E. Y. Chen, C. C. Chen, and S. Tin: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44A, pp. 479–93.
N. Tsuji, Y. Matsubara, and Y. Saito: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 477–84.
S.V.S. Murty, S. Torizuka, K. Nagai, T. Kitai, and Y. Kogo: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 763–68.
J. Baczynski and J.J. Jonas: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 447–62.
N.R. Tao, Z.B. Wang, W.P. Tong, M.L. Sui, J. Lu, and K. Lu: Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 4603–16.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly (1995) Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Elsevier Science Ltd., Amsterdam.
P. Cotterill and P.R. Mould (1976) Recrystallization and Grain Growth in Metals, Halsted Press, New York.
D.S. Weaver and S.L. Semiatin: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 1044–47.
S.L. Semiatin, D.S. Weaver, P. N. Fagin, M. G. Glavicic, R. L. Goetz, N. D. Frey, R. C. Kramb, and M. M. Antony: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 679–93.
M. Jackson, R. Dashwood, L. Christodoulou, and H. Flower: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 1317–27.
Y. Ivanisenko, W. Lojkowski, R.Z. Valiev, and H.-J. Fecht: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 5555–70.
V.G. Gavriljuk (2003) J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 345:81-89.
H. Shen, Z. Li, B. Günther, A.V. Korznikov, and R.Z. Valiev: Nanostruct. Mater., 1995, vol. 6, pp. 385–88.
A.V. Korznikov, O. Dimitrov, G.F. Korznikova, J.P. Dallas, A. Quivy, R.Z. Valiev and A. Mukherjee: Nanostruct. Mater., 1999, vol. 11 (1), pp. 17–23.
G. Shen, J. Rollins, and D. Furrer: Superalloys 1996, R.D. Kissinger, D.J Deye, D.L. Anton, A.D. Cetel, M.V. Nathal, T.M. Pollock, and D.A. Woodford, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1996, pp. 613–20.
S.A. Transvalor: FORGE 2011 Recrystallization During Metal Forming Operation, Transvalor S.A., Mougins, 2003.
C. Murgau, R. Pederson, and L.E. Lindgren: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2012, vol. 20, 055006 (23pp).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge financial support provided by Army Aviation Technology Directorate STTR Phase I and II Contract# W911W6-11-C-0055 and W911W6-10-C-0063 managed by Clay Ames.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 30, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozmel, T., Chen, E.Y., Chen, C.C. et al. Kinetics of Sub-Micron Grain Size Refinement in 9310 Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 2590–2600 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2212-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2212-6