Abstract
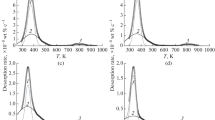
In the current study, ferritic steels containing NbC or NbN precipitates were investigated. The materials were subjected to various heat treatments, giving rise to different precipitate size distributions as determined by transmission electron microscopy. Both NbC and NbN precipitates act as hydrogen traps. The steels were hydrogen charged both electrochemically and/or from the gaseous hydrogen source, followed by multiple thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS) measurements. Electrochemical charging gave rise to a low-temperature peak [323 K to 523 K (50 °C to 250 °C)], originating from the hydrogen trapped near grain boundaries, with activation energy ranging between 24 and 33 kJ/mol, and at small NbC (39 to 48 kJ/mol) or NbN precipitates (23 to 24 kJ/mol). Gaseous charging caused a high-temperature TDS peak [723 K to 923 K (450 °C to 650 °C)], which was attributed to the presence of incoherent precipitates. The activation energy for NbC precipitates, charged in a hydrogen atmosphere, ranged between 63 and 68 kJ/mol and between 100 and 143 kJ/mol for NbN precipitates.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Duprez, K. Verbeken, and M. Verhaege: Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf., 1st ed., ASM International, Wyoming, WY, 2008, pp. 62–69.
T. Depover, D. Pérez Escobar, E. Wallaert, Z. Zermout, and K. Verbeken: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.12.190.
H. Asahi, D. Hirakami and S. Yamasaki: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 527-533.
B. Malard, B. Remy, C. Scott, A. Deschamps, J. Chene, T. Dieudonne and M. H. Mathon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 536, pp. 110-116.
T. Asaoka, G. Lapasset, M. Aucouturier and P. Lacombe: Corros. NACE, 1978, vol. 34, pp. 39-47.
G. M. Pressouyre and I. M. Bernstein: Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9, pp. 1571-1580.
M. A. V. Devanathan and Z. Stachurski: Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1962, vol. 270, pp. 90-102.
H. G. Lee and J. Y. Lee: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 131-136.
F. G. Wei, T. Hara and K. Tsuzaki: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35, pp. 587-597.
D. Pérez Escobar, E. Wallaert, L. Duprez, A. Atrens, and K. Verbeken: Met. Mater. Int., 2013, vol. 19, pp. 741–48.
F. G. Wei and K. Tsuzaki: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 331-353.
J. Takahashi, K. Kawakami, Y. Kobayashi and T. Tarui: Scr. Mater., 2010, vol. 63, pp. 261-264.
M. Ohnuma, J. I. Suzuki, F. G. Wei and K. Tsuzaki: Scr. Mater., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 142-145.
F. Wei and K. Tsuzaki: Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf., 1st ed., ASM International, Wyoming, WY, 2008, pp. 456–63.
F. Wei, T. Hara, and K. Tsuzaki: Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf., 1st ed., ASM International, Wyoming, WY, 2008, pp. 448–55.
D. Pérez Escobar, L. Miñambres, L. Duprez, K. Verbeken, and M. Verhaege: Corros. Sci., 2011, vol. 53, pp. 3166–76.
D. Pérez Escobar, L. Duprez, A. Atrens, and K. Verbeken: J. Nucl. Mater., 2014, DOI:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.07.006.
D. Pérez Escobar, L. Duprez, K. Verbeken, and M. Verhaege: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 551, pp. 50–58.
S. Lee and J. Lee: Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 181-187.
J. Y. Lee and S. M. Lee: Surf. Coat. Technol., 1986, vol. 28, pp. 301-314.
J. Lee and J. Lee: Met. Sci., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 426-432.
H. E. Kissinger: Anal. Chem., 1957, vol. 29, pp. 1702-1706.
W. Choo and J. Lee: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 135-140.
A. Kumnick and H. Jonhson: Acta Metall., 1980, vol. 28, pp. 33-39.
D. Pérez Escobar, T. Depover, L. Duprez, K. Verbeken, and M. Verhaege: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 2593–2605.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Special Research Fund (BOF), Ghent University (BOF10/ZAP/121), and the Agency for Innovation by Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT) for support (Project nr SB111205). The authors also acknowledge the technicians and staff working at the hydrogen laboratory at OCAS (ArcelorMittal Global R&D Gent) and the technical staff from the Department Materials Science and Engineering, Ghent University, for their help with the experiments and sample preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 6, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallaert, E., Depover, T., Arafin, M. et al. Thermal Desorption Spectroscopy Evaluation of the Hydrogen-Trapping Capacity of NbC and NbN Precipitates. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 2412–2420 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2181-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2181-1