Abstract
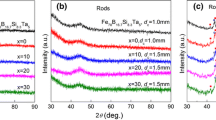
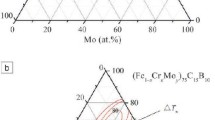
The effects of alloying elements on the thermal stability, glass-forming ability (GFA), corrosion resistance, and magnetic and mechanical properties of a soft magnetic Fe75P10C10B5 metallic glass with a low glass transition temperature (T g) of 723 K (450°C) were investigated. The addition of Mo, Ni, and Co significantly increased the stabilization of supercooled liquid, GFA, and corrosion resistance in the H2SO4 solution. The maximum critical diameter (d c) of 4 mm for glass formation was obtained for the Fe55Co10Ni5Mo5P10C10B5 alloy, which shows the largest supercooled liquid region (ΔT x ) of 89 K (89 °C). The substitution of Cr for Mo further enhanced the corrosion resistance of the Fe55Co10Ni5Mo5P10C10B5, while the ΔT x and d c decreased. The (Fe, Ni, Co)70(Mo, Cr)5P10C10B5 bulk metallic glasses showed low T g of 711 K to 735 K (438 °C to 462 °C), wide ΔT x of 67 K to 89 K, high saturation magnetization of 0.79 to 0.93 T, low coercive force of 2.36 to 6.61 A m−1, high compressive yield strength of 3271 to 3370 MPa, and plastic strain of 0.8 to 2.3 pct. In addition, the mechanism for enhancing stability of supercooled liquid was discussed in terms of the precipitated phases during crystallization.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Inoue and N. Nishiyama: MRS Bull., 2007, vol. 32, pp. 651–58.
J. Schroers: Adv. Mater., 2010, vol. 22, pp. 1566–97.
Y. Saotome, K. Itoh, T. Zhang, and A. Inoue: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 1541–45.
Q. Jing, R.P. Liu, G.J. Shao, and W.K. Wang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 359 pp. 402–04.
G. Kumar, H.X. Tang, and J. Schroers: Nature, 2009, vol. 457, pp. 868–72.
W. Zhang, H. Guo, M.W. Chen, Y. Saotome, C.L. Qin, and A. Inoue: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 61, pp. 744–47.
Y. Kawamura, T. Nakamura, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1999, vol. 40, pp. 794–803.
A. Inoue, Y. Shinohara, and J.S. Gook: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1995, vol. 36, pp. 1427–1433.
C. Suryanarayana, and A. Inoue: Int. Mater. Rev., 2013, vol. 58, pp. 131–66.
T. Zhang, F.J. Liu, S.J. Pang, and R. Li: Mater. Trans., 2007, vol. 48, pp. 1157–60.
D.H. Xu, G. Duan, and W.L. Johnson: Phys. Rev. Lett., 2004, vol. 92, pp. 245504–507.
W.H. Wang: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 52, pp. 540–96.
B.L. Shen, M. Akiba, and A. Inoue: J. Appl. Phys., 2006, vol. 100, pp. 043523-1-5.
S.J. Pang, T. Zhang, K. Asami, and A. Inoue: J. Mater. Res., 2002, vol. 17, pp. 701–4.
D. Turnbull: Contempt. Phys., 1969, vol. 10, pp. 473–88.
Z.P. Lu, and C.T. Liu: Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 3501–12.
J. Schroers: JOM, 2005, vol. 57, pp. 35–9.
E. McCafferty: Corros. Sci., 2005, vol. 47, pp. 3202–15.
Z.L. Long, Y. Shao, X.H. Deng, Z.C. Zhang, Y. Jiang, P. Zhang, B.L. Shen, and A. Inoue: Intermetallics, 2007, vol. 15, pp. 1453–58.
H.S. Chen: Rep. Prog. Phys., 1980, vol. 43, pp. 353–32.
X.J. Gu, S.J. Poon, G.J. Shiflet, and M. Widom: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, vol. 92, pp. 161910–12.
A. Takeuchi, and A. Inoue: Mater. Trans. JIM, 2000, vol. 41, pp. 1372–78.
B.L. Shen, M. Akiba, and A. Inoue: Phys. Rev. B, 2006, vol. 73, pp. 104204–209.
A. Inoue, and B.L. Shen: Adv. Mater., 2004, vol. 16, pp. 2189–92.
M. Imafuku, C.F. Li, M. Matsushita, and A. Inoue: Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2002, vol. 41, pp. 219–21.
Japan Institute of Metals: Metals Databook, Maruzen, Tokyo, 1983, p. 8.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51271043, 51171034, and 51201024), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China [Grant Nos. DUT11RC(3)29, and DUT11RC(3)70], and Research and Development Project on Advanced Metallic Glasses, Inorganic Materials and Joining Technology from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 30, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Jia, X., Zhang, W. et al. Effects of Alloying Elements on the Thermal Stability and Corrosion Resistance of an Fe-based Metallic Glass with Low Glass Transition Temperature. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 2393–2398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2071-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2071-6