Abstract
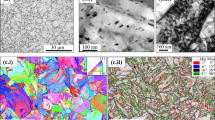
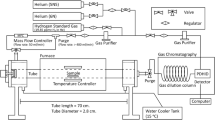
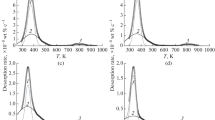
Nanoprecipitation-hardened martensitic bearing steels (100Cr6) and carbide-free nanobainitic steels (superbainite) are examined. The nature of the hydrogen traps present in both is determined via the melt extraction and thermal desorption analysis techniques. It is demonstrated that 100Cr6 can admit large amounts of hydrogen, which is loosely bound to dislocations around room temperature; however, with the precipitation of fine coherent vanadium carbide traps, hydrogen can be immobilized. In the case of carbide-free nanostructured bainite, retained austenite/bainite interfaces act as hydrogen traps, while concomitantly retained austenite limits hydrogen absorption. In nanostructured steels where active hydrogen traps are present, it is shown that the total hydrogen absorbed is proportional to the trapped hydrogen, indicating that melt extraction may be employed to quantify trapping capacity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreone C, Murut A, (1990) . Metall. Trans. A 24:1453–1458
Barrow ATW, Kang JH, Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo PEJ (2012). Acta Mater. 60: 2805–2815
Barrow ATW, Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo PEJ (2011) Acta Mater. 59:7155–7167
W.Y. Choo and J.Y. Lee: J. Mater. Sci., 1982a, vol. 17, pp. 1930–38.
W.Y. Choo and J.Y. Lee: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 135–40.
Craig BD, Krauss G (1980) . Metall Trans A 11A: 1799–1808
D. Eliezer and T. Boellinghaus: Proc. 2008 Int. Hydrogen Conf. ASM Int, 2008, pp. 438–48
D. Enomoto and M. Hirakami: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 1–10.
Ferreira PJ, Robertson IM, Birnbaum HK (1999) . Acta. Mater.. 47:2991–2998
S. Frappart, A. Oudriss, X. Feaugas, J. Creus, J. Bouhattate, F. Thébault, L. Delattre, and H. Marchebois: Scripta Mater., 2011, vol. 65, pp. 859–62
C. Garcia-Mateo and F.G. Caballero: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 1736–40.
C. Garcia-Mateo and F.G. Caballero, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1238–43
W.W. Gerberich and T.J. Foecke: in Hydrogen Efects on Materials, N.R. Moody and A.W. Thompson, eds., TMS, Warendale, PA, 1990, pp. 687–701.
W.W. Gerberich, R.A. Oriani, M. Lii, X. Chen, and T. Foecke: Philos. Mag. A, 1991, vol. 63, pp. 363–76
Hagihara K, Takai Y, HiraiS K (2012) . ISIJ. Int.. 52:298–306
Hong JY, Lee GW (1983) . J Mater 18:271–277.
K. Horikawaa, N. Andoa, H. Kobayashia, and W. Urushiharab: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012 , pp. 495–503.
Kino N, Otani K (2003) . Soc Auto Eng 24:289–294
Lee SM, Lee J (1986) . Surf Coat Tech 28:301–314
Li J, Oriani R, Darken L (1966) Zeitschrift fur Physikalische Chemie Neue Folge 49:271–290
N. Luzginova: Ph.D. Thesis. Delft University of Technology, 2008.
Maroef I, Olson DL, Eberhart M, Edwards GR, (2002) Int. Mater Rev 47:191–223
Marsh PG, Gerberich WW (1994) Acta. Metall Mater 42:613–619
Michler T, Balogh MP (2010) Int. J Hydrogen Energ 35: 9746–9754
Nagumo M (2004) Mater. Sci Tech 20:940–950
M. Nagumo and M. Nakamura: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 339–47
M. Nagumo, H. Shimura, T. Chaya, H. Hayashi, and I. Ochiai: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 348, pp. 192–200.
Nagumo M, Yagi T, Saitoh H (2000) Acta. Mater.. Aust.. 48: 943–951.
Park A, Maroef YD, Landau A (2002) Weld. J. Law. Econ. Organ. 27S: 27–35
Pérez-Escobar D, Depover T, Duprez L, Verbeken K, Verhaege M (2012a) Acta. Mater.. Aust.. 60:2593–2605
Pérez-Escobar D, Depover T, Wallaert E, Duprez L, Verhaege M, Verbeken K (2012b) Corros. Sci.. Agric.. 65:199–208
Pérez-Escobar D, Verbeken K, Duprez L, Verhaege M (2012c) Mater. Sci Eng A 551:50–58
G.M. Pressouyre: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 1571–73
Robertson IM (1999) Eng. Fract Mech 64: 649–637
Scott PM (1985) Corros. Sci.. Agric.. 583:8–9
Szost BA, Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo PEJ (2013) Scripta. Mater.. Aust.. 68:467–470
Szost BA, Vegter RH, Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo PEJ (2013) Mater. Des.. Codes. Crypt.. 43:499–506
Tabata T, Birnbaum HK (1984) Scripta. Metall Mater 18: 18–231
Takahashi K, Kawakami K (2010) Scripta. Mater.. Aust.. 63: 261–264
Takai K, Shoda H, Suzuki H, Nagumo M (2008) Acta. Mater.. Aust.. 56:5158–5167
Takasawa K, Ishigaki R, Wada Y, Kayano R (2010) ISIJ. IEEP. 50: 1496–1502
H. Uyama: in Wind Turbine Tribology Seminar, R. Errichello, S. Sheng, J. Keller, and A. Greco, eds., NSK Corporation, Bloomfield, CO, 2011, pp.14–16.
T. Wei and F.G. Hara: in Effects of Hydrogen in Metals, P. Sofronis, B. Somerday, and R. Jones, eds., ASM International, Novelty, OH, 2009, pp. 456–63.
Yamasaki S, Bhadeshia HKDH (2006) Proc. R Soc A 462:2315–2330
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the SKF Engineering & Research Centre and financed by SKF AB. The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Prof. A.L. Greer for the provision of laboratory facilities at the University of Cambridge and Mohammed Faid for his kind help with the TDA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 20, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szost, B.A., Vegter, R.H. & Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Hydrogen-Trapping Mechanisms in Nanostructured Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 44, 4542–4550 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1795-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1795-7