Abstract
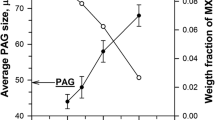
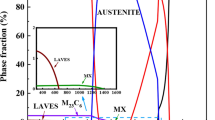
Two heats of 9 to 12 pct Cr ferritic/martensitic heat-resistant steels were prepared. One has an ultralow carbon content of 0.01 wt pct, whereas another heat has a normal carbon content of 0.09 wt pct. The effect of carbon content on microstructure and mechanical properties of 9 to 12 pct Cr ferritic/martensitic heat-resistant steels was studied. The results show that the ultralow-carbon steel contains bimodal, nanosized MX precipitates with high density in the matrix but few M23C6 carbide particles in the normalized-and-tempered state. The smaller nanosized MX precipitates have two kinds of typical morphology: One is cubic and another is rectangular. The cubic MX precipitate contains Nb, Ti, and V, whereas the rectangular one only contains Nb and V. The normal carbon steel has abundant M23C6 carbide particles along the grain and lath boundaries and much less density of nanosized MX precipitates after the same heat treatments. After long-term aging at 923 K (650 °C) for 10,000 hours, the stress rupture properties of the ultralow carbon content steel degrades more significantly. The strength degradation mechanism of the 9 to 12 pct Cr ferritic/martensitic heat-resistant steels is discussed in this article.








Similar content being viewed by others

References
K. Maruyama, K. Sawada, and J.-I. Koike: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 641–53.
M. Taneike, F. Abe, and K. Sawada: Nature, 2003, vol. 424, pp. 294–96.
F. Abe, M. Taneike, and K. Sawada: Int. J. Press. Vessels Piping, 2007, vol. 84, pp. 3–12.
F.S. Yin, W.S. Jung, and S.H. Chung: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 469–72.
F.S. Yin and W.S. Jung: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, p. 302–09.
H.K. Danielsen and J. Hald: CALPHAD, 2007, vol. 31, pp. 505–14.
C. Kocer, T. Abe, and A. Soon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 505, pp. 1–5.
F. Abe: Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 8, pp. 305–11.
R.O. Kaibyshev, V.N. Skorobogatykh, and I.A. Shchenkova: Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2010, vol. 52, nos. 3–4, p. 90–99.
K. Sawada, K. Suzuki, H. Kushima, M. Tabuchi, and K. Kimura: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 480, pp. 558–63.
K. Sawada, M. Taneike, K. Kimura, and F. Abe: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 1243–49.
Acknowledgments
Financial support is acknowledged from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong province (Grant Y2008F47), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 50771059), and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (Grant 2009AA03Z509).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 23, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, FS., Tian, LQ., Xue, B. et al. Effect of Carbon Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 9 to 12 pct Cr Ferritic/Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steels. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 2203–2209 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1092-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1092-x