Abstract
The kinetics of the recrystallization of pure copper was investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The associated microstructural change was characterized by electron backscatter diffraction imaging (EBSD), by analyzing deformed specimens before recrystallization and specimens after partial recrystallization and after completed recrystallization. The experimental results acquired by the two methods were compared with each other and discussed in the context of the available body of literature results. The observed kinetics deviate from Johnson–Mehl–Avrami–Kolmogorov (JMAK)-like behavior. The observed grain-area distribution is unusually broad and skewed toward large grains. Comparison with mesoscopic, geometric simulations showed that previously proposed (simple) models fail to correctly describe the microstructure resulting from recrystallization, although they can successfully model the recrystallization kinetics. It was concluded that the experimental results on both the kinetics and the microstructure can be reconciled employing a recrystallization model incorporating ongoing (i.e., beyond time t = 0) nucleation and accounting for the inhomogeneous nature of the deformed material.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
It must be recognized that nucleation in recrystallization is not the outcome of a fluctuation phenomenon as in heterogeneous phase transformations. Instead, the “nuclei” are already present in the deformed material (as subgrains[3]) and can become “activated” subject to instability criteria.[3–5] Nevertheless, the moment a (sub-) grain starts to grow is denoted "nucleation."
This refers to recrystallization that occurs during annealing after deformation and not (dynamically) during deformation.
The growth exponent n can also be determined from isochronally (i.e., with constant heating rate) conducted experiments. To this end, an appropriately adapted variant of the JMAK equation has to be applied and then n is the negative of the slope of the straight line possibly observed in a plot of \(\ln(-\ln(1-f))\) vs \(\ln \Upphi\) (with \(\Upphi\) as the heating rate). Refer to Section 9.6.15.5 in Ref. 13.
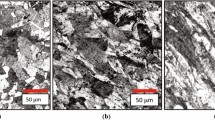
The image quality is a measure of the quality of the backscatter electron diffraction pattern of the material corresponding to one pixel.
It is also possible to use the average orientation spread in a grain to distinguish between recrystallized and unrecrystallized parts of the specimen. In the present study, both methods have been shown to lead to the same results.
If the misorientation between two pixels is smaller than 5°, the pixels are considered to belong to the same grain.
References
W.G. Burgers: Rekristallisation, Verformter Zustand und Erholung, Akademische Verlags-Gesellschaft, Leipzig, Germany, 1941.
P. Cotterill and P.R. Mould: Recrystallization and Grain Growth in Metals, Surrey University Press, London, 1976.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004.
Y. Bréchet and G. Martin: Comptes Rendus Phys., 2006, vol. 7, 959–76.
R.D. Doherty: in Solid to Solid Phase Transformations in Inorganic Materials, J.M. Howe, D.E. Laughlin, J.K. Lee, U. Dahmen, and W.A. Soffa, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2005, vol. 1, pp. 553−64.
P. Krüger and E. Woldt: Acta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 2933–42.
T.O. Sætre, O. Hunderi, and E. Nes: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 981–87.
H.S. Zurob, Y. Bréchet, and J. Dunlop: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 2983–3990.
A. Brahme, J.M. Fridy, H. Weiland, and A.D. Rollett: Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2009, vol. 17, p. 015005.
E. Fjeldberg and K. Marthinsen: Comp. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 48, pp. 267–91.
Y.B. Chun, S.L. Semiatin, and S.K. Hwang: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 6373–89.
F. Liu, F. Sommer, C. Bos, and E.J. Mittemeijer: Int. Mater. Rev., 2007, vol. 52, pp. 193–212.
E.J. Mittemeijer: Fundamentals of Materials Science, Springer, Heidelberg, Germany, 2010.
R. Bauer, E. Bischoff, and E.J. Mittemeijer: Int. J. Mater. Res., 2011, vol. 102, pp. 1027–41.
R.A. Vandermeer and D. Juul Jensen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 2227–35.
D. Juul Jensen: Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 11, pp. 4117–29.
R.A. Vandermeer and D. Juul Jensen: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2004, vols. 467–470, pp. 193–96.
D.P. Field, L.T. Bradford, M.M. Nowell, and T.M. Lillo: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 4233–41.
F. Scholz and E. Woldt: Proc. 19th Riso Symp. on Materials Science, J.V. Carstensen, T. Leffers, T. Lorentzen, O.B. Pedersen, B.F. Sorensen, and G. Winther, eds., Risø National Laboratory, Roskilde, Denmark, 1998.
E. Woldt: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 2465–73.
E. Woldt and D. Juul Jensen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, vol. 26A, pp. 1717–24.
N. Hansen, T. Leffers, and J.K. Kjems: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, pp. 1523–33.
A.M. Wusatowska-Sarnek, H. Miura, and T. Sakai: Mater. Trans. JIM, 2001, vol. 42, pp. 2452–59.
L. Blaz and P. Kwapisinski: Arch. Metall. Mater., 2009, vol. 54, pp. 161–70.
Y. Amouyal, S.V. Divinski, L. Klinger, and E. Rabkin: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 5500–13.
D.P. Field, M.M. Nowell, P. Triverdi, S.I. Wright, and T.M. Lillo: Solid State Phenom., 2005, vol. 105, pp. 157–62.
B. Hutchinson, S. Jonsson, and L. Ryde: Scripta Metall., 1989, vol. 23, pp. 671–86.
M.J. Luton, R.A. Petrovic, and J.J. Jonas: Acta Metall., 1980, vol. 28, pp. 729–43.
G. Benchabane, Z. Boumerzoug, I. Thibon, and T. Gloriant: Mater. Charact., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 1425–28.
F. Häßner: in Thermal Analysis in Metallurgy, R.D. Shull and A. Joshi, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 233–57.
M.J. Starinka and A.M. Zahra: Thermochim. Acta, 1997, vol. 298, pp. 179–89.
K. Marthinsen, O. Lohne, and E. Nes: Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 135–45.
T. Furu, K. Marthinsen, and E. Nes: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1990, vol. 6, pp. 1093–1102.
A.D. Rollett, D.J. Srolovitz, R.D. Doherty, and M.P. Anderson: Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 627–39.
F. Häßner and K. Sztwiertina: Scripta Metall., 1992, vol. 27, pp. 1545–50.
G. Bäro and H. Gleiter: Z. Metallk., 1972, vol. 63, pp. 661–63.
A. Berger, P.J. Wilbrandt, F. Ernst, U. Klement, and P. Haasen: Progr. Mater. Sci., 1998, vol. 32, pp. 1–95.
F.J. Humphreys: J. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 36, pp. 3833–54.
E.E. Underwood: Quantitative Stereology, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Reading, MA, 1970.
E.A. Jägle and E.J. Mittemeijer: Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2010, vol. 18, p. 065010.
E.J. Mittemeijer: J. Mater. Sci., 1992, vol. 27, pp. 3977–87.
R.A. Vandermeer and D. Juul Jensen: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, 2083–94.
U.F. Kocks, C.N. Tomé, and H.R. Wenk: Texture and Anisotropy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1998.
M. Miodownik, A.W. Godfrey, E.A. Holm, and D.A. Hughes: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, p. 2661.
J.K. Mackenzie: Biometrika, 1958, vol. 45, pp. 229–40.
J.W. Cahn: Acta Metall., 1956, vol. 4, pp. 449–59.
E.A. Jägle and E.J. Mittemeijer: Solid State Phenom., 2011, vols. 172–174, pp. 1128–33.
E.A. Jägle and E.J. Mittemeijer: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59, pp. 5775–86.
G. Gottstein and L.S. Shvindlerman: Grain Boundary Migration in Metals, 2nd ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2010.
E.A. Jägle and E.J. Mittemeijer: Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (formerly Max Planck Institute for Metals Research), Stuttgart, Germany, unpublished research, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 26, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jägle, E.A., Mittemeijer, E.J. The Kinetics of and the Microstructure Induced by the Recrystallization of Copper. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 1117–1131 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0959-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0959-6