Abstract
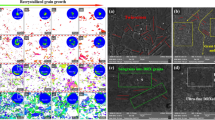
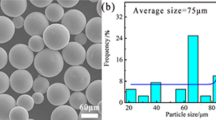
Electropulsing induced texture evolution in the primary recrystallization of a Fe-3 pct Si alloy strip was studied using the electron backscattered diffraction technique. The results revealed that the electropulsing strengthened considerably the recrystallization of a cold-rolled Fe-3Si alloy strip. Various textures with high-energy storages, such as α (100)〈110〉, γ (111)〈110〉, γ (111)〈112〉, and G-texture (110)〈001〉, formed after several seconds of electropulsing treatment (EPT), depending on the intensity of electropulsing. The athermal effect of electropulsing is 319 times stronger than the thermal effect of electropulsing for the formation of the G texture. The mechanism of electopulsing induced texture evolution is discussed from the point of view of Gibbs free energy and dislocation dynamics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.H. Heo: Mater. Lett., 2005, vol. 59, pp. 2827–31.
C. Gheorghies and A. Doniga: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2009, vol. 16 (4), pp. 78–83.
D.N. Lee Intern and H.T. Jeong: Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 1219–23.
J.T. Park and J.A. Szpunar: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 3037–51.
Y.H. Zhu, S. To, W.B. Lee, X.M. Liu, Y.B. Jiang, and G.Y. Tang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 501, pp. 125–32.
S. To, Y.H. Zhu, W.B. Lee, G.Y. Tang, X.M. Liu, and Y.B. Jiang: Mater. Trans., 2009, vol. 50 (12), pp. 2772–77.
Y.H. Zhu, S. To, X.M. Liu, and G.L. Hu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 1933–40.
Y.H. Zhu, S. To, W.B. Lee, X.M. Liu, Y.B. Jiang, and G.Y. Tang: J. Mater. Res., 2009. vol. 4, pp. 2661–66.
S. To, Y.H. Zhu, W.B. Lee, X.M. Liu, Y.B. Jiang, and G.Y. Tang: Appl. Phys. A, 2009, vol. 96, pp. 939–44.
Z.H. Xu, G.Y. Tang, F. Ding, S.Q. Tian, and H.Y. Tian: Appl. Phys. A, 2007, vol. 88, pp. 429–33.
V.V. Stolyarov: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 503, pp. 18–20.
V.E. Gromov, Y. Ivanov, F.E.V. Kozlov, E.Y. Suchkova, S.V. Konovalov, and V.A. Rybyanets: Proc. Electromagnetic Fields Effect on the Structure and Characteristics of Materials, Novokuznetsk, Russia, D. Yury, V.D. Baranov, V.E. Gromov, and T.G. Tang, eds., 2009, pp. 209–24.
Y. Hayakawa, J.A. Szpunar, G. Palumbo, and P. Lin: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1996, vol. 160, pp. 143–44.
G. Hu, Y.H. Zhu, C.H. Shek, and G.Y. Tang: J. Mater. Res., 2011, vol. 26 (7), in press.
Y. Dolinsky and T. Elperin: Phys. Rev. B, 1993, vol. 42, pp. 14778–14785.
Acknowledgment
The authors express their thanks to Mr. Franke Y.F. Chan, The Electron Microscope Unit, The Hong Kong University, for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted February 22, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, G., Tang, G., Zhu, Y. et al. Electropulsing Induced Texture Evolution in the Recrystallization of Fe-3 Pct Si Alloy Strip. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 3484–3490 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0770-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0770-4