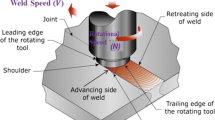
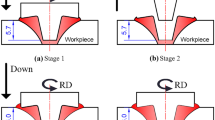
Abstract
The main difficulty in the formulation of any model for friction stir welding (FSW) is due to the high coupling between thermal and mechanical phenomena. In the analytical models present in the literature, the fundamental unknown parameter, under the assumption of sticking between the tool/matrix interface, is the yield shear stress, which is temperature dependent. For this reason, any fully analytical model is unable to predict the temperatures for conditions not supported by measurements of the heat input. In this work a semianalytical thermal model for FSW is proposed. The formulation of heat flow during the welding process is based on generic solutions of the differential equation for heat conduction in a solid body, formulated for a point heat source with constant linear velocity. The heat generation was considered as a function of the tool-matrix interface temperature, which is calculated by means of a numerical routine written in Matlab code. Comparison with the experimental measurements taken from the literature shows that the results from the present semianalytical model are in good agreement with the test data.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Matlab is a trademark of The MathWorks, Natick, MA.
Abbreviations
- ρ :
-
density, g/m3
- c p :
-
specific heat capacity, J/(g·°C)
- k :
-
thermal conductivity, W/(m·°C)
- α :
-
diffusion coefficient, m2/s
- Q int :
-
volumetric heat source due to plastic dissipation, W/m3
- Q :
-
heat generation due to frictional and plastic dissipation, W
- Q workpiece :
-
heat absorbed by the workpiece, W
- T :
-
temperature, °C
- T 0 :
-
initial temperature, °C
- T M :
-
melting temperature, °C
- q :
-
heat flux, W/m2
- v :
-
welding speed, m/s
- r :
-
radial distance from the tool center, m
- H :
-
plate thickness, m
- η :
-
thermal efficiency of the process
- q total :
-
heat flux due to plastic and frictional dissipation, W/m2
- q plastic :
-
local “surface plastic heat flux,” W/m2
- q friction :
-
local surface heat flux, W/m2
- ω :
-
tool angular rotation speed, rad/s
- δ :
-
contact state variable
- τyield :
-
yield shear stress, Pa
- τfriction :
-
friction shear stress, Pa
- τ0 :
-
fitting parameter, Pa
- A :
-
tool surface into contact with the workpiece, m2
- T* :
-
tool/matrix interface temperature, °C
- β :
-
tool shoulder cone angle, deg
- R sh :
-
tool shoulder radius, m
- R p :
-
tool pin radius, m
- H p :
-
tool pin height, m
- R* :
-
model parameter (radial distance from the tool center at which the temperature T* is calculated), m
References
R. Nandan, T. DebRoy, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2008, vol. 53, pp. 980–1023.
S. Lim, S. Kim, C.-G. Lee, and S. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 1977–80.
Y. Uematsu, Y. Tozaki, K. Tokaji, and M. Nakamura: Strength Mater., 2008, vol. 40, pp. 138–41.
D. Storjohann, O.M. Barabash, S.S. Babu, S.A. David, P.S. Sklad, and E.E. Bloom: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 3237–47.
P. Cavaliere, E. Cerri, L. Marzoli, and J. Dos Santos: Appl. Comp. Mater., 2004, vol. 11, pp 246–58.
P. Dong, F. Lu, J.K. Hong, and Z. Cao: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2001, vol. 6, pp. 281–87.
P. Ulysse: Mach. Tool. Manufact., 2002, vol. 42, pp. 1549–57.
P.A. Colegrove and H.R. Shercliff: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2004, vol. 9, pp. 483–92.
G. Buffa, J. Hua, R. Shivpuri, and L. Fratini: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 419, pp. 389–96.
H. Schmidt and J. Hattel: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2005, vol. 13, pp. 77–93.
L. Fourment and S. Guerdoux: Int. J. Mater. Form Suppl., 2008, vol. 1, pp. 1287–90.
Y.J. Chao, X. Qi, and W. Tang: Trans. ASME, 2003, vol. 125, pp 138–45.
X.K. Zhu and Y.J. Chao: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, vol. 146, pp. 263–72.
Z. Zhang: J. Mater. Sci., 2008, vol. 43, pp. 5867–77.
M.Z.H. Khandkar, J.A. Khan, and A.P. Reynolds: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2003, vol. 8, pp. 165–74.
M.J Russell and H.R Shercliff: 1st Int. Symp. on Friction Stir Welding, Thousand Oaks, CA, 1999.
H. Schmidt, J. Hattel, and J. Wert: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2004, vol. 12, pp. 143–57.
H.B. Schmidt and J.H. Hattel: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 332–37.
P. Vilaca, L. Quintino, and J.F. dos Santos: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2005, vol. 169, pp. 452–65.
P. Vilaca, L. Quintino, J.F. dos Santos, R. Zettler, and S. Sheikhi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 445, pp. 501–08.
S. Perivilli, J. Peddieson, and J. Cui: J. Heat Transfer, 2008, vol. 130, pp 1–9.
B.M. Darras and M.K. Khraisheh: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2008, vol. 17, pp. 168–77.
D. Rosenthal: Weld. J. Res. Supp., 1941, vol. 20, pp. 220–34.
D. Rosenthal and H. Shamerber: Weld. J. Res. Supp., 1938, vol. 17, pp. 2–8.
∅. Grong: Metallurgical Modelling of Welding, 2nd ed., Materials Modelling Series, H.K.D.H Bhadeshia, ed., The Institute of Materials, London, 1997, pp. 24–90.
Metals Handbook, vol. 2, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, 10th ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1990, pp. 774–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 7, 2009.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0170-1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferro, P., Bonollo, F. A Semianalytical Thermal Model for Fiction Stir Welding. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 440–449 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0104-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0104-y