Abstract
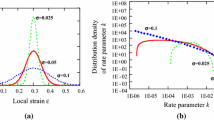
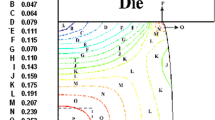
Recrystallization in an inhomogeneously predeformed material (a cold-drawn cylindrical rod) is described by an analytical model and simulated with the Monte-Carlo technique. For this purpose, an equation for the nucleation rate during recrystallization as a function of local deformation has been derived. The analytical model considering the derived nucleation equation is capable of predicting the progress of the recrystallization front as observed in experiments with Titanium Grade 2. The Monte-Carlo model has been developed on the basis of the analytical model. Different functions for the local deformation were introduced, and recrystallization and subsequent grain growth were simulated. With the aid of simulation, the formation of both a grain size gradient and large elongated grains in the region of critical deformation can be understood. The graded microstructure is a consequence of the combined effect of inhomogeneous nucleation and anisotropic growth of the recrystallizing grains. Experimental grain size gradients were reproduced quantitatively by the present simulations. Agreement was also found for the grain elongation that forms during the recrystallization and grain growth stages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Elsevier Science, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1995, pp. 3–8(a), 186–205(b), and pp. 418–423(c).
B. Radhakrishnan, G.B. Sarma, and T. Zacharia: Acta Metall. Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 4415–33.
R.L. Goetz and V. Seetharaman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 2307–21.
W.J. Zhang, U. Lorenz, and F. Appel: Acta Metall. Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 2803–13.
M.P. Anderson, D.J. Srolovitz, P.S. Sahni, and G.S. Grest: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 783–92.
D.J. Srolovitz, G.S. Grest, M.P. Anderson, and A.D. Rollett: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 1833–42.
C. Müller, S. Pascuzzi, and P. Neuhäusel: Prakt. Metallogr., 1997, vol. 34, pp. 606–16.
C. Müller and H.E. Exner: Z. Metallkd., 1998, vol. 89, pp. 338–42.
K. Lange: Umformtechnik, Springer, Berlin, 1974, vol. 2.
U. Zwicker: Titan und Titanlegierungen, Springer, Berlin, 1974, p. 139.
J. Gil Sevillano, P. van Houtte, and E. Aernoudt: Progr. Mater. Sci., 1980, vol. 25, pp. 69–81.
H.E. Exner and H.P. Hougardy: Quantitative Image Analysis of Microstructures, DGM Informationsgesellschaft, Oberursel, Germany, 1988, pp. 30–32.
X. Song and G. Liu: Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 1691–96.
C. Müller: Technical University of Darmstadt, Darmstadt, unpublished research, 1997.
S. Pascuzzi: “Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Titanium Grade 2, Studienarbeit,” Darmstadt University of Technology, Darmstadt, 1997, p. A2, (in German)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Rettenmayr, M., Müller, C. et al. Modeling of recrystallization after inhomogeneous deformation. Metall Mater Trans A 32, 2199–2206 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0195-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-001-0195-6