Abstract
Summary
Although the incidence of infection following vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty is rare, postoperative infection and cement augmentation in preexistent spondylitis can cause life-threatening complications in frail patients with notable comorbidities. In such cases, urgent culture and biopsy and the long-term use of proper antibiotics are necessary.
Purpose
Infection following vertebral augmentation with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) is rare. We aimed to analyze 11 cases of pyogenic spondylitis and spondylodiscitis that occurred after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty and to review similar cases in the literature.
Methods
All cases of postoperative spinal infections in our institution between January 2005 and November 2016 that primarily underwent percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty were retrospectively reviewed. Eleven patients (mean age 76.3 years) were included.
Results
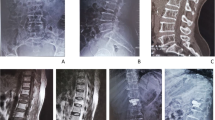
The incidence of infection following vertebroplasty/kyphoplasty was 0.36%. Postoperative infection occurred in 3 of 826 cases. All patients underwent combined surgical and antibiotic treatment because of neurologic deficit on the initial diagnosis of the infection or failure of prior medical treatment of the infection. The surgical procedure was thorough debridement of infected tissue and material including PMMA following anterior column reconstruction via anterior/posterior/combined approach in 10 patients and percutaneous pedicle screw fixation alone in 1 patient aged 96 years. The mean follow-up period was 21.1 months after the revision operation, excluding one patient who died 17 days after revision surgery. Ten patients recovered from infection.
Conclusions
Although the incidence of infection following vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty is rare, postoperative infection and cement augmentation in preexisting spondylitis can develop into a life-threatening complication in frail patients with notable comorbidities. In treating infected vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, immediate culture and biopsy and the long-term use of proper antibiotics are critical. Prompt surgical treatment should be considered in case of significant neurologic deficit, severe instability due to infected fracture, and resistance to antibiotics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kado DM, Duong T, Stone K, Ensrud K, Nevitt M, Greendale G, Cummings S, Group SoOFR (2003) Incident vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study. Osteoporos Int 14:589–594
Unit N, Chandra RV (2013) Vertebral augmentation: update on safety, efficacy, cost effectiveness and increased survival? Pain physician 16:309–320
Edidin A, Ong K, Lau E, Kurtz S (2013) Life expectancy following diagnosis of a vertebral compression fracture. Osteoporos Int 24:451–458
Gallbert P, Deramond H, Rosat P (1987) Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by pereutaneous acrylic vertebmplasty. Neurochirurgie 33:166–168
Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, Rose M, Sola-Martinez T, Enkaoua E (1996) Spinal metastases: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology 199:241–247
Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA (2001) New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:1511–1515
Rao RD, Singrakhia MD (2003) Painful osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Pathogenesis, evaluation, and roles of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in its management. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A:2010–2022
Papanastassiou ID, Phillips FM, Van Meirhaeghe J, Berenson JR, Andersson GB, Chung G, Small BJ, Aghayev K, Vrionis FD (2012) Comparing effects of kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, and non-surgical management in a systematic review of randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Eur Spine J 21:1826–1843
Nussbaum DA, Gailloud P, Murphy K (2004) A review of complications associated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty as reported to the Food and Drug Administration medical device related web site. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:1185–1192
Hulme PA, Krebs J, Ferguson SJ, Berlemann U (2006) Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine 31:1983–2001
Taylor RS, Fritzell P, Taylor RJ (2007) Balloon kyphoplasty in the management of vertebral compression fractures: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 16:1085–1100
Yu S-W, Chen W-J, Lin W-C, Chen Y-J, Tu Y-K (2004) Serious pyogenic spondylitis following vertebroplasty—a case report. Spine 29:E209–E211
Walker DH, Mummaneni P, Rodts GE Jr (2004) Infected vertebroplasty. Report of two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 17:E6
Mummaneni PV, Walker DH, Mizuno J, Rodts GE (2006) Infected vertebroplasty requiring 360° spinal reconstruction: long-term follow-up review: report of two cases. J Neurosurg Spine 5:86–89
Schmid KE, Boszczyk BM, Bierschneider M, Zarfl A, Robert B, Jaksche H (2005) Spondylitis following vertebroplasty: a case report. Eur Spine J 14:895–899
Bouvresse S, Chiras J, Bricaire F, Bossi P (2006) Pott’s disease occurring after percutaneous vertebroplasty: an unusual illustration of the principle of locus minoris resistentiae. J Infect 53:e251–e253
Olmos MA, González AS, Clemente JD, Tomé CV (2006) Infected vertebroplasty due to uncommon bacteria solved surgically: a rare and threatening life complication of a common procedure: report of a case and a review of the literature. Spine 31:E770–E773
Söyüncü Y, Özdemir H, Söyüncü S, Bigat Z, Gür S (2006) Posterior spinal epidural abscess: an unusual complication of vertebroplasty. Joint Bone Spine 73:753–755
Vats HS, McKiernan FE (2006) Infected vertebroplasty: case report and review of literature. Spine 31:E859–E862
Robinson Y, Tschöke SK, Stahel PF, Kayser R, Heyde CE (2008) Complications and safety aspects of kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective follow-up study in 102 consecutive patients. Patient safety in surgery 2:2
Kwak H-J, Lee J-K, Kim Y-S, Moon K-S, Joo S-P, Kim J-H, Kim S-H, Chang W-C (2008) Aortic aneurysm complicated with pyogenic spondylitis following vertebroplasty. J Clin Neurosci 15:89–93
Lin W-C, Lee C-H, Chen S-H, Lui C-C (2008) Unusual presentation of infected vertebroplasty with delayed cement dislodgment in an immunocompromised patient: case report and review of literature. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:231–235
Shin J-H, Ha K-Y, Kim K-W, Lee J-S, Joo M-W (2008) Surgical treatment for delayed pyogenic spondylitis after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
Syed MI, Avutu B, Shaikh A, Sparks H, Mohammed MI, Morar K (2009) Vertebral osteomyelitis following vertebroplasty: is acne a potential contraindication and are prophylactic antibiotics mandatory prior to vertebroplasty? Pain physician 12:E285–E290
Ivo R, Sobottke R, Seifert H, Ortmann M, Eysel P (2010) Tuberculous spondylitis and paravertebral abscess formation after kyphoplasty: a case report. Spine 35:E559–E563
Ha K-Y, Kim K-W, Kim Y-H, Oh I-S, Park S-W (2010) Revision surgery after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Clinics in orthopedic surgery 2:203–208
Buttermann GR, Mullin WJ (2011) Percutaneous vertebral body cement augmentation for back pain related to occult osteomyelitis/diskitis. Orthopedics 34:e788–e792
Kim HJ, Shin DA, Cho KG, Chung SS (2012) Late onset tuberculous spondylitis following kyphoplasty: a case report and review of the literature. Korean Journal of Spine 9:28–31
Santbergen B, Vriens P, De Lange W, Van Kasteren M (2013) Combined infection of vertebroplasty and aortic graft after intravesical BCG treatment. BMJ Case Reports 2013:bcr2012008161
Lee J-S, Choi S-M, Kim K-W (2013) Triparesis caused by gas-containing extensive epidural abscess secondary to Aeromonas hydrophila infection of a thoracic vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine J 13:e9–e14
Kang JH, Kim H-S, Kim SW (2013) Tuberculous spondylitis after percutaneous vertebroplasty: misdiagnosis or complication? Korean Journal of Spine 10:97–100
Abdelrahman H, Siam AE, Shawky A, Ezzati A, Boehm H (2013) Infection after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. A series of nine cases and review of literature. Spine J 13:1809–1817
Kim K-Y, Hur J, Jo W, Hong J, Cho O-H, Kang DH, Kim S, Bae I-G (2015) Infectious spondylitis with bacteremia caused by Roseomonas mucosa in an immunocompetent patient. Infection & chemotherapy 47:194–196
Zou MX, Wang XB, Li J, Lv GH, Deng YW (2015) Spinal tuberculosis of the lumbar spine after percutaneous vertebral augmentation (vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty). Spine J 15:e1–e6
Ge C-Y, He L-M, Zheng Y-H, Liu T-J, Guo H, He B-R, Qian L-X, Zhao Y-T, Yang J-S, Hao D-J (2016) Tuberculous spondylitis following kyphoplasty: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine 95:e2940
Pola E, Autore G, Pambianco V, Formica VM, Colangelo D, Nasto LA (2016) A particular case of pyogenic spondylodiscitis misdiagnosed as a vertebral fragility fracture and erroneously treated with balloon kyphoplasty. Spine J 16:e659–e662
Giger A, Yusuf E, Manuel O, Clerc O, Trampuz A (2016) Polymicrobial vertebral osteomyelitis after oesophageal biopsy: a case report. BMC Infect Dis 16:141
Anselmetti GC, Marcia S, Saba L, Muto M, Bonaldi G, Carpeggiani P, Marini S, Manca A, Masala S (2012) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: multi-centric results from EVEREST experience in large cohort of patients. Eur J Radiol 81:4083–4086
Chen Y-J, Chen H-Y, Hsu H-C (2014) Re: Infection after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. A series of nine cases and review of literature. Spine J 13:1809–1817 The spine journal: official journal of the North American Spine Society 14:1366
Kallmes DF, Jensen ME (2003) Percutaneous vertebroplasty. Radiology 229:27–36
Shapiro SA (1991) Cranioplasty, vertebral body replacement, and spinal fusion with tobramycin-impregnated methylmethacrylate. Neurosurgery 28:789–791
Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME, Deramond H (2001) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:373–381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JW., Park, SM., Lee, H.J. et al. Infection following percutaneous vertebral augmentation with polymethylmethacrylate. Arch Osteoporos 13, 47 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-018-0468-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-018-0468-y