Abstract
Objective
To explore the protective effect and the underlying mechanism of silibinin (SIB), one of the active compounds from Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn in endotoxemia.
Methods
Mouse peritoneal macrophage were isolated via intraperitoneally injection of BALB/c mice with thioglycolate medium. Cell viability was assessed using the cell counting kit-8, while cytotoxicity was determined through lactate dehydrogenase cytotoxicity assay. The protein expressions of interleukin (IL)-1 α, IL-1 β, and IL-18 were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Intracellular lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels were measured by employing both the limulus amoebocyte lysate assay and flow cytometry. Additionally, proximity ligation assay was employed for the LPS and caspase-11 interaction. Mice were divided into 4 groups: the control, LPS, high-dose-SIB (100 mg/kg), and low-dose-SIB (100 mg/kg) groups (n=8). Zebrafish were divided into 4 groups: the control, LPS, high-dose-SIB (200 εmol/L), and low-dose-SIB (100 εmol/L) groups (n=30 for survival experiment and n=10 for gene expression analysis). The expression of caspase-11, gasdermin D (GSDMD), and N-GSDMD was determined by Western blot and the expressions of caspy2, gsdmeb, and IL-1 β were detected using quantitative real-time PCR. Histopathological observation was performed through hematoxylineosin staining, and protein levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were quantified using the bicinchoninicacid protein assay.
Results
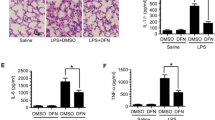
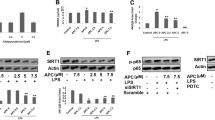
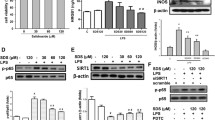
SIB noticeably decreased caspase-11 and GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis and suppressed the secretion of IL-1 α, IL-1 β, and IL-18 induced by LPS (P<0.05). Moreover, SIB inhibited the translocation of LPS into the cytoplasm and the binding of caspase-11 and intracellular LPS (P<0.05). SIB also attenuated the expression of caspase-11 and N-terminal fragments of GSDMD, inhibited the relative cytokines, prolonged the survival time, and up-regulated the survival rate in the endotoxemia models (P<0.05).
Conclusions
SIB can inhibit pyroptosis in the LPS-mediated endotoxemia model, at least in part, by inhibiting the caspase-11-mediated cleavage of GSDMD. Additionally, SIB inhibits the interaction of LPS and caspase-11 and inhibits the LPS-mediated up-regulation of caspase-11 expression, which relieves caspase-11-dependent cell pyroptosis and consequently attenuates LPS-mediated lethality.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Liu Z, Wang W, Luo J, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gan Z, et al. Anti-apoptotic role of Sanhuang Xiexin Decoction and anisodamine in endotoxemia. Front Pharmacol 2021;12:531325.
Munford RS. Endotoxemia-menace, marker, or mistake? J Leukoc Biol 2016;100:687–698.
Dickson K, Lehmann C. Inflammatory response to different toxins in experimental sepsis models. Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:4341.
Kuzmich NN, Sivak KV, Chubarev VN, Porozov YB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN, Peri F. TLR4 signaling pathway modulators as potential therapeutics in inflammation and sepsis. Vaccines 2017;5(4):34.
Pfalzgraff A, Weindl G. Intracellular lipopolysaccharide sensing as a potential therapeutic target for sepsis. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2019;40:187–197.
Yang JL, Zhao Y, Shao F. Non-canonical activation of inflammatory caspases by cytosolic LPS in innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 2015;32:78–83.
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Gao W, Ding J, Li P, et al. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature 2014;514:187–192.
Gao YL, Zhai JH, Chai YF. Recent advances in the molecular mechanisms underlying pyroptosis in sepsis. Mediat Inflamm 2018;2018:5823823.
Shi JJ, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi XY, Wang Y, Huang HW, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015;526:660–665.
Prasad RR, Paudel S, Raina K, Agarwal R. Silibinin and non-melanoma skin cancers. J Tradit Complement Med 2020;10:236–244.
You YT, He QX, Lu HQ, Zhou XH, Chen LQ, Liu HX, et al. Silibinin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest by activating drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in cervical cancer. Front Pharmacol 2020;11:271.
Jahanafrooz Z, Motamed N, Rinner B, Mokhtarzadeh A, Baradaran B. Silibinin to improve cancer therapeutic, as an apoptotic inducer, autophagy modulator, cell cycle inhibitor, and microRNAs regulator. Life Sci 2018;213:236–247.
Sun M, Zhao H, Jin Z, Lei W, Deng C, Yang W, et al. Silibinin protects against sepsis and septic myocardial injury in an NR1H3-dependent pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 2022;187:141–157.
Lim JO, Shin NR, Seo YS, Nam HH, Ko JW, Jung TY, et al. Silibinin attenuates silica dioxide nanoparticles-Induced inflammation by suppressing TXNIP/MAPKs/AP-1 signaling. Cells 2020;9:678.
Zheng R, Ma J, Wang D, Dong W, Wang S, Liu T, et al. Chemopreventive effects of silibinin on colitis-associated tumorigenesis by inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mediat Inflamm 2018;2018:1562010.
Tan CH, Xu XR, Shang YQ, Fu XL, Xia GH, Yang H. A novel approach for the efficient extraction of silybin from milk thistle fruits. Pharmacogn Mag 2014;10:536–540.
Vanaja SK, Russo AJ, Behl B, Banerjee I, Yankova M, Deshmukh SD, et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles mediate cytosolic localization of LPS and caspase-11 activation. Cell 2016;165:1106–1119.
Lu Z, Liu S, Ou J, Cao H, Shi L, Liu D, et al. Forsythoside A inhibits adhesion and migration of monocytes to type II alveolar epithelial cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through upregulating miR-124. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2020;407:115252.
Lu Z, Cao H, Liu D, Zheng Y, Tian C, Liu S, et al. Optimal combination of anti-inflammatory components from Chinese medicinal formula Liang-Ge-San. J Ethnopharmacol 2021;269:113747.
Heck TG, Scomazzon SP, Nunes PR, Scholer CM, da Silva GS, Bittencourt A, et al. Acute exercise boosts cell proliferation and the heat shock response in lymphocytes: correlation with cytokine production and extracellular-to-intracellular HSP70 ratio. Cell Stress Chaperones 2017;22:271–291.
Yang H, Lu Z, Huo C, Chen Y, Cao H, Xie P, et al. Liang-Ge-San, a classic traditional chinese medicine formula, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through up-regulating miR-21. Front Pharmacol 2019;10:1332.
Gabarin RS, Li M, Zimmel PA, Marshall JC, Li Y, Zhang H. Intracellular and extracellular lipopolysaccharide signaling in sepsis: avenues for novel therapeutic strategies. J Innate Immun 2021;13:323–332.
Kayagaki N, Wong MT, Stowe IB, Ramani SR, Gonzalez LC, Akashi-Takamura S, et al. Noncanonical inflammasome activation by intracellular LPS independent of TLR4. Science 2013;341:1246–1249.
Downs KP, Nguyen H, Dorfleutner A, Stehlik C. An overview of the non-canonical inflammasome. Mol Asp Med 2020;76:100924.
Kim BR, Seo HS, Ku JM, Kim GJ, Jeon CY, Park JH, et al. Silibinin inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines through inhibition of NF-kappa B signaling pathway in HMC-1 human mast cells. Inflamm Res 2013;62:941–950.
Gao Y, Theng SS, Mah WC, Lee CGL. Silibinin down-regulates FAT10 and modulate TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma-induced chromosomal instability and apoptosis sensitivity. Biol Open 2015;4:961–969.
Tong WW, Zhang C, Hong T, Liu DH, Wang C, Li J, et al. Silibinin alleviates inflammation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and has a therapeutic effect on arthritis in rats. Sci Rep 2018;8:3241.
Gugliandolo E, Crupi R, Biondi V, Licata P, Cuzzocrea S, Passantino A. Protective effect of silibinin on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in equine peripheral blood mononuclear cells, an in vitro study. Animals 2020;10:2022.
Park JW, Shin NR, Shin IS, Kwon OK, Kim JS, Oh SR, et al. Silibinin inhibits neutrophilic inflammation and mucus secretion induced by cigarette smoke via suppression of ERK-SP1 pathway. Phytother Res 2016;30:1926–1936.
Wang Z, Gu ZY, Hou Q, Chen WJ, Mu D, Zhang YX, et al. Zebrafish GSDMEb cleavage-gated pyroptosis drives septic acute kidney injury in vivo. J Immunol 2020;204:1929–1942.
Yang DH, Zheng X, Chen SW, Wang Z, Xu WT, Tan JC, et al. Sensing of cytosolic LPS through caspy2 pyrin domain mediates noncanonical inflammasome activation zebrafish. Nat Commun 2018;9:3052.
Deng MH, Tang YT, Li WB, Wang XY, Zhang R, Zhang XY, et al. The endotoxin delivery protein HMGB1 mediates caspase-11-dependent lethality in sepsis. Immunity 2018;49:740–753.
Tsaroucha AK, Valsami G, Kostomitsopoulos N, Lambropoulou M, Anagnostopoulos C, Christodoulou E, et al. Silibinin effect on Fas/FasL, HMGB1, and CD45 expressions in a rat model subjected to liver ischemia-reperfusion Injury. J Invest Surg 2018;31:491–502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ou JY and Liu SH designed and conducted the experiment. Paper drafting and a portion of the in vivo experiment were carried out by Ou JY, Liu SH, Tang DK, Shi LZ, and Chen YY. Yan LJ, Huang JY, and You YT were responsible for data curation and visualization. Zou LF, You YT, Quan JY, and Yu LZ handled data curation, formal analysis, and methodology. Lu ZB provided supervision, research guidance, and reviewed the draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Supported by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2023A1515011106), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (No. 2023A04J1826)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, Jy., Liu, Sh., Tang, Dk. et al. Protective Effect of Silibinin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endotoxemia by Inhibiting Caspase-11-Dependent Cell Pyroptosis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3656-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3656-1