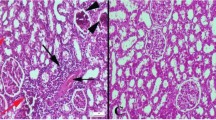
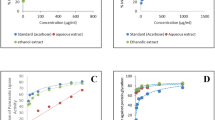
Abstract
Objective
To test the effect of Banxia Xiexin Decoction (半夏泻心汤, BXD) on the contraction and relaxation of gastric smooth muscle (SM) in diabetic gastroparesis (DGP) model rats, and to explore the mechanism of BXD in the prevention and treatment of DGP through experiments of signal pathway both in vivo and in vitro.
Methods
Sixty Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 6 groups according to a random number table: control group, model group, high-, medium- and low-dose BXD groups (9.2, 4.6 and 1.8 g/(kg·d), respectively), and domperidone group (10 mg/(kg·d)), 10 rats per group. DGP model was established initially by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ), and was confirmed by recording gastric emptying, intestinal transport velocity and gastric myoelectric activity of rats after 2 months. Each group was treated with a corresponding drug for 4 weeks. The mRNA and protein expressions of phospholipase C (PLC), inositol triphosphate (IP3), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) dependent protein kinase G (PKG) were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot, respectively, while nitric oxide (NO) and cGMP expressions were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Gastric tissues were obtained from rats for primary cell culture preparation. Gastric SM cells were treated with 0.8 µmol/L of STZ or STZ plus 1,000, 500 and 200 µg/mL of BXD or STZ plus 2.5 µmol/mL of domperidone for 24, 48, 72 or 96 h, respectively. The length of gastric SM cells and intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) before and after BXD treatment was measured.
Results
Compared with the model group, high- and medium-dose BXD and domperidone significantly increased the expressions of PLC, IP3, NO, nNOS, cGMP and PKG in rat’s gastric tissue (P<0.01). Gastric SM cells treated with BXD showed a time- and dose-dependent increase in cell viability (P<0.01). The treatment with high- and medium-dose BXD and domperidone inhibited the increase in gastric SM cells length and increased [Ca2+]i compared with the model cells (P<0.01).
Conclusions
Treatment with high- and medium-dose BXD significantly attenuated STZ-induced experimental DGP in rats. The therapeutic effect of BXD on DGP rats might be associated with the PLC-IP3-Ca2+/NO-cGMP-PKG signal pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luo D, Liu S. Abnormal mechanism of gastric motility in DGP. Gastroenterol 2007;12:372–374.
Zhang XZ, Zhang MH, Fang XS, Cui XS. Mechanism of AMPK-mediated apoptosis of rat gastric smooth muscle cells under high glucose condition. Biosci Rep 2019;39:1–2.
Makhlouf GM, Murthy KS. Signal transduction in gastrointestinal SM. Cell Signal 1997;9:269–276.
Grider JR, Murthy KS. Autoinhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in gut SM by nitric oxide. Regul Pept 2008;151:75–79.
Tang TH. Banxia Xiexin Decoction in the treatment of diabetic gastroparesis in 50 cases. Sichuan Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;19:35.
Zhou YP. Banxia Xiexin Decoction in treating 32 cases of postoperative gastroparesis syndrome in gastric cancer. New Chin Med (Chin) 2014;46:154–155.
Zhou L. Banxia Xiexin Decoction in the treatment of gastrectomy after gastrectomy in 20 cases. Chin Med (Chin) 2004;19:5–6.
Zhu LY, Gu X. Modified Banxia Xiexin Decoction in the treatment of functional dyspepsia and its effect on plasma motilin. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;42:36–37.
Li XF, Song GR, Yan BC, Zhao YM. Effect of Banxia Xiexin Decoction on gastric motility of intractable non-ulcerative dyspepsia. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 1994;14:36–37.
Pan JH, Feng DM, Jiang LJ. Banxia Xiexin Decoction in the treatment of 120 cases of gastrointestinal disorders. Natl Med Forum (Chin) 1997;12:10.
Wang JE, Liu TT, Huang XS, Zhang FH, Chen JL, Zeng YQ. Effect of Banxia Xiexin Decoction on the expression of GLUT-4 and GSK-3 in the insulin resistance of diabetic gastroparesis rats. Pharm Clin Chin Mate Med (Chin) 2015;31:1–3.
Xu M, Wang J, Chen JL, Huang XS, Qiu GL, Zhou XF. Effect of Banxia Xiexin Decoction on insulin resistance in diabetic gastroparesis rats. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2015;56:1502–1505.
Lin G, Zhang J, Li L, Zou Z, Chen C, Xue L. Effect of electroacupuncture on gastric interstitial cells of Cajal in a rat model of diabetic gastroparesis. Exp Ther Med 2016;11:2489–2494.
Guo XJ, Zou YH, Wu L, Liu XQ. Factors affecting the diabetic models induced by streptozocin in SD and Wistar rats. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin 2008;16:301–305.
Broad J, Takahashi N, Tajimi M, Sudo M, Góralczyk A, Parampalli U. A motilin receptor agonist causing long-lasting facilitation of human gastric cholinergically-mediated contractions. J Pharmacol Sci 2016;130:60–65.
Mahavadi S, Nalli A, Al-Shboul O, Murthy KS. Inhibition of MLC20 phosphorylation downstream of Ca2+ and RhoA: a novel mechanism involving phosphorylation of myosin phosphatase interacting protein (M-RIP) by PKG and stimulation of MLC phosphatase activity. Cell Biochem Biophys 2014;68:1–8.
Murthy KS. Contractile agonists attenuate cGMP levels by stimulating phosphorylation of cGMP-specific PDE5; an effect mediated by RhoA/PKC-dependent inhibition of protein phosphatase 1. Br J Pharmacol 2008;153:1214–1224.
Pereira L, Bare DJ, Galice S, Shannon TR, Bers DM. β-Adrenergic induced SR Ca2+ leak is mediated by an Epac-NOS pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2017;108:8–16.
Chen G, Yang Y, Liu ML, Teng ZY, Ye J, Xu YH. Banxia Xiexin Decoction protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2015;166:149–156.
Shang YY, Huang TS, Xiao DH. Advances in theory and clinical research of traditional Chinese medicine in diabetic gastroparesis. Chin J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2013;26:75–77.
Shi GM, Fan LY. Banxia Xiexin Decoction in the treatment of functional gastric retention in 84 cases. Bright Chin Med (Chin) 2009;24:2107.
Zhao MF. Application of Banxia Xiexin Decoction and its mechanism of action. Jiangsu Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2005;26:45–49.
Zhang Q, Liang XC. Effects of mitochondrial dysfunction via AMPK/PGC-1 α signal pathway on pathogenic mechanism of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the protective effects of Chinese medicine. Chin J Integr Med 2019;25:386–394.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wang B, Zeng KW and Hong ZF conducted the animal experiments. Ti GX, Wang LY and Lu P conducted the cell experiments. Liu Z conducted the data statistics.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81503553)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zeng, Kw., Hong, Zf. et al. Banxia Xiexin Decoction (半夏泻心汤) Treats Diabetic Gastroparesis through PLC-IP3-Ca2+/NO-cGMP-PKG Signal Pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26, 833–838 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-020-3077-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-020-3077-8