Abstract
Objective
To explore the change of intestinal microecology in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome (pSS) and correlation with disease activity, and also discuss the therapy effect of Yangyin Yiqi Huoxue Recipe (养阴益气活血方, YYHD).
Methods
Sixteen pSS patients were enrolled in the present study, who received 3-month treatment of YYHR, 200 mL orally twice daily. Their pre-and post-test ESSDAI scores, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels were measured respectively. The 16SrDNA metagenomic sequencing was used to detect and analyze the abundance and diversity of intestinal bacteria flora and the proportion of bacteria at the levels of phylum, family, and genus, in comparision with those of 6 healthy subjects in the control group.
Results
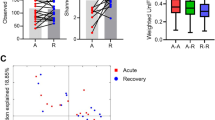
The abundance and diversity of intestinal bacteria flora in pSS patients were lower than those of healthy subjects (P<0.05). After the treatment with YYHD, patients’ ESSDAI score and levels of IgG and ESR have decreased significantly (P<0.05). At the phylum level, the proportions of Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria and Proteobacteria have reduced sharply, while the proportions of Bacteroidetes, Teneriquetes and Candidate-division-TM7 have increased significantly by treatment (all P<0.05). At the classification level, such treatment has caused a significant decrease in the proportions of Bacteroidaceae, Ruminococcaceae, Veillonellaceae, and Enterobacteriacea (all P<0.05), but a significant increase in the proportion of Lachnospiraceae (P<0.05). At the genus level, the treatment has significantly decreased the proportions of Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides, Escherichia-Shigella, Faecalibacterium and Prevotella (all P<0.05), but significantly increased the proportion of Clostridia (P<0.05), close to the levels of healthy subjects (P>0.05).
Conclusions
There exists an imbalance of intestinal microecology in pSS patients, which can be improved through the treatment with YYHD. Besides, such treatment can also improve the disease activity and adjust the diversity of intestinal bacteria flora, the composition and the abundance of intestinal flora.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chou A, Gonzales JA, Daniels TE, Criswell LA, Shiboski SC, Shiboski CH. Health-related quality of life and depression among participants in the Sjögren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance registry. RMD Open 2017;3:e000495.
Nezos A, Mavragani CP. Contribution of genetic factors to Sjögren’s syndrome and Sjögren’s syndrome related lymphoma genesis. Immunol Res 2015:754825.
Wang Y, Guo F. The progress in the treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome with traditional Chinese medicine. Nei Mongol J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2017;36:131–133.
Wu GL, Wu NY, Li TY, Fan YS, Yu GY, Lu WW. Effect of Chinese herbal medicine for nourishing yin, supplementing qi, and activating blood on the reproductive endocrine and immune networks in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Chin J Integr Med 2015;21:778–783.
Wu GL, Li TY, Fan YS, Yu GY, Chen J. Effect of Chinese herbal medicine for nourishing yin, supplementing qi, and activating blood on the Th1/Th2 immune balance in peripheral blood in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Chin J Integr Med 2013;19:696–700.
Van der Meulen TA, Harmsen H, Bootsma H, Spijkervet F, Kroese F, Vissink A. The microbiome-systemic diseases connection. Oral Dis 2016;22:719–734.
De Luca F, Shoenfeld Y. The microbiome in autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 2018;19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.13158.
Shiboski CH, Shiboski SC, Seror R, Criswell LA, Labetoulle M, Lietman TM, et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for primary Sjogren’s syndrome: a consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:9–16.
Ministry of Health, P.R.C. The research guidelines for new drugs of traditional Chinese medicine;1995:188.
Seror R, Ravaud P, Bowman SJ, Baron G, Tzioufas A, Theander E, et al. EULAR Sjogren’s syndrome disease activity index: development of a consenses systemic disease activity index for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1103–1109.
Edgar RC. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 2013;10:996–998.
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009;75:7537–7541.
White JR, Nagarajan N, Pop M. Statistical methods for detecting differentially abundant features in clinical metagenomic samples. PLoS Comput Biol 2009;5: e1000352.
Li Y, Zhang FC. Disease assessment system for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Chin J Rheumatol (Chin) 2016;20:138–140.
Xu D, Zhao Y. Disease activity index and damage index in Sjogren’s syndrome. Pract Hosp Clin J (Chin) 2016;12:22–26.
Wang L, Zhang W, Li MT, Zhao Y. Correlation of memory B cell and B cell activation factor with clinical indicators in primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients and their first-degree relatives. Med J Peking Union Med Coll Hosp (Chin) 2010;1:132–136.
Mavragani CP. Mechanisms and new strategies for primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Annu Rev Med 2017;14:331–343.
Huang SJ, Wa Z, Zhong M. Research progress in the pathogeny and pathogenesis of Sjogren’s syndrome. Chin J Pract Stomatol (Chin) 2017;10:497–481.
Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Ando M, Kamada N, Nagano Y, Narushima S, et al. Th17 cell induction by adhesion of microbes to intestinal epithelial cells. Cell 2015;163:367–380.
Chassaing B, Aitken JD, Gewirtz AT, Vijay-Kumar M. Gut microbiota drives metabolic disease in immunologically altered mice. Adv Immunol 2012;116:93–112.
Koboziev I, Reinoso Webb C, Furr KL, Grisham MB. Role of the enteric microbiota in intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med 2013;68C:122–133.
Chen DD, Gu SH, Zhang JN, Bao FK, Tang YQ, Wu XL. Effect of intestinal microbes on the immune system and the latest research methods. Chin J Appl Environ Biol (Chin) 2013;19:542–546.
Armougom F, Bittar N, Stremler JM, Rolain C, Robert JC, Dubus J, et al. Microbial diversity in the sputum of a cystic fibrosis patient studied with 16SrDNA pyrosequencing. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2009;28:1151–1154.
Zeng P, He XL, Ma WK, Hou L. Advances in TCM diagnosis and treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome. J Guiyang Coll Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2016;38:98–101.
Wu GL, Li TY, Lu WW, Yu GY, Fan YS. Effect of Chinese herbal medicine for the Nourishing yin, Strengthening qi and Activating blood Decoction on Fas/FasL and their mRNA in submandibular glands of NOD mice with Sjogren’s syndrome. Chin J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2013;38:4148–4151.
Wu GL, Pu XH, Li TY, Yu GY, Lu WW, Fan YS. Effect of Yangyin Yiqi Huoxue Decoction on immune balance of Th1/Th2 in serum and submaxillary glands of NOD mice with Sjogren’s syndrome. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2013;33:1653–1657.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wu GL and Li TY carried out the studies, participated in collecting data, and drafted the manuscript. Lu HF and Wang Q carried out intestinal microecological detection. Chen YL and Cao H collected cases and examined specimens. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors declare that they have no any conflict of interests.
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81473604) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (No. LY19H270013)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Gl., Lu, Hf., Chen, Yl. et al. Changes of Intestinal Microecology in Patients with Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome after Therapy of Yangyin Yiqi Huoxue Recipe (养阴益气活血方). Chin. J. Integr. Med. 25, 654–662 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-2939-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-2939-4