Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the chemical composition and pharmacological potential of hydro distillate from Salix caprea inflorescence.
Methods
Fresh flowers were subjected to conventional hydrodistillation. Antioxidant activity was assessed as free radical scavenging capacity (RSC) towards 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazil (DPPH) radicals. Anti inflammatory activity was examined by human red blood cell (HRBC) membrane stabilization method. Qualitative and Quantitative analysis of hexane extract of aromatic water was performed by gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MS).
Results
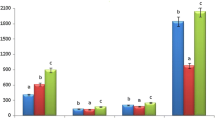
A total of 19 constituents representing (99.2%) of the aromatic water were identified; Hexahydrofarnesylacetone (38.3%), 2-butyl-octanol (24.0%), 2.hexyl-1-octanol (8.6%) were the main components. Results suggest that the hydro distillate possess significant antioxidant and anti-inflammtory properties.
Conclusions
The aromatic water's composition and its pharmacological evaluations has been reported in our results for this unique and endemic species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moohammadnor M, Tursun X, Qiong Ling M, Sultan A, Eshbakova K. Flavonoids from Salix caprea. Chem nat prod 2010;46:673–674.
Ajaz A, Wajahat AS, Seema A, Mohammad Y, Dinesh K. A short chemical review on Salix caprea commonly known as Goat willow. In J Res Phytochem Pharmacol 2011;1:17–20.
Nasudari AA, Kompantsev VA, Oganesyan ET, Shinkarenko AL. Luteolin 7-glucoside from Salix caprea. Khimioter Prirodn Soedin 1972;3:392–393.
Thapliyal RP. Bahugana RP Fatty acids and flavonoids of Salix Lindlevana. Int J Pharmacog 1993;31:165–166.
Karl E, Malterud, Torgunn E, Bremnes AF, Turid M, Eva K, et al. Flavonoids from the wood of Salix caprea as inhibitors of wood-destroying Fungi. J Nat Prod 1985;48:559–563.
Gorobets AB, Bandyukova VA, Shapirom DK. Flavonoid composition of pollen of Salix caprea and S. Alba. Khim Prir Soedin 1982;6:781–782.
Sagareishvili TG, Alaniya MD, Kemerelidze EP. Phenols in leaves of Salix caprea. Khimioter Prirodn Soedin 1990;1:119–120.
Bodas R, López S, Fernández M, García-González R, Wallace RJ, González JS. Phytogenic additives to decrease in vitro ruminal methanogenesis. Nutritional and foraging ecology of sheep and goats. Zaragoza: CIHEAM/ FAO/NAGREF 2009;85:279–283.
Gandhidasan R, Thamaraichelvan A, Baburaj S. Anti inflammatory action of Lannea coromandelica by HRBC membrane stabilization. Fitoterapia 1991;62:81–83.
Young IS, Woodside JV. Antioxidants in health and disease. J Clin Pathol 2001;54:176–186.
Miller NJ, Rice-Evans CA. The relative contributions of ascorbic acid and phenolic antioxidants to the total antioxidants to the activity of orange and apple fruit juices and black currant drink. Food Chem 1997;60:331–337.
Lucas SM, Rothwell NJ, Gibson RM. The role of inflammation in CNS injury and disease. Br J Pharmacol 2006;147:232–240.
Ajaz A, Wajahat AS, Seema A, Dinesh K, Vijender K, Mohammad Y. In-vitro anti inflammatory activity of Salix caprea Linn. (goat willow) by HRBC membrane stabilization method. Pharm Res 2011;4:1067–1068.
Wajaht AS, Ajaz A. Antioxidant potential and GC analysis of extracts and isolated fractions from the flowers of Salix caprea. J Pharm Res 2012;5:1284–1286.
Conti ME, Saccares S, Cubadda F, Cavallina R, Tenoglio CA, Ciprotti L. II Miele nel Lazio: Indagine sul contenuto in metallic in trace e radionuclide. Rivisita di Scienza dell Alimentazione 1998;2:107–109.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge that Dr. M.A Qurishi, Department of chemistry, University of Kashmir provide the valuable guidance to carry out experiments. We would also like to thanks Dr. Tariq Ahmad Bhat, SMPU, RRIUM for authentication of the plant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, A., Akbar, S. & Shah, W.A. Chemical composition and pharmacological potential of aromatic water from Salix caprea inflorescence. Chin. J. Integr. Med. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2781-5
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2781-5