Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of hydro-alcoholic extract of Launaea acanthodes, a blood glucose lowering plant in folk medicine of Iran, on the structure of seminiferous tubules and serum gonadotropin and testosterone levels in hyperglycemic rats.
Methods
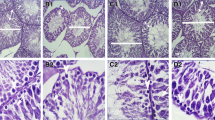
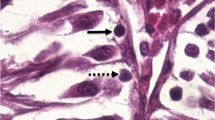
Twenty-four Wistar rats were randomly allocated into 4 groups (n=6): control, streptozotocin (STZ), STZ + insulin [STZ + Ins, 5 IU/(kg•day)], and STZ + Launaea acanthodes extract [STZ + Ext, 150 mg/(kg•day)]. Blood samples were collected at the 2nd and 4th weeks for detection of testosterone, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) with enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA), and the right testes of rats were removed at the 7th week for the evaluation of diameter and wall thickness of seminiferous tubules and number of Leydig cells using unbiased stereological techniques.
Results
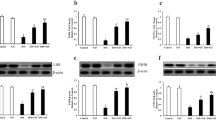
In comparison with the control group, at the 2nd week FSH (0.45 vs 0.03, 0.02, 0.02 IU/L in STZ, STZ + Ins and STZ + Ext groups, respectively) and LH (1.02 vs 0.37, 0.2, 0.29 IU/L) showed significant decreases (all P<0.05) and testosterone (4.2 vs 8.37, 7.78, 11.8 ng/mL) showed a remarkable increase (all P<0.05). The levels of these hormones became closer in the STZ + Ext and the STZ + Ins groups to the control at the 4th week. A significant decrease in diameter and wall thickness of seminiferous tubules and number of Leydig cells were observed in the STZ group as compared with the control (P<0.01).
Conclusions
Administration of Launaea extract demonstrated a beneficial impact on the protection of testis from pathogenic and degenerative effects of hyperglycemia which may be partly due to its potential antioxidative effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daneman D. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2006;367:847–858.
Hans S, Jonathan S, Paul Z. Guidelines for the detection of diabetes mellitus-diagnostic criteria and rationale for screening. Clin Biochem Rev 2003;24:77–80.
Karimidokht Shahrbabaki A, Oryan SH, Parivar K. Anticonvulsant activity of ethanolic extract and aqueous fraction of Launaea acanthodes gum in comparison with diazepam in mice. J Qazvin Univ Med Sci Health Servic 2009;13:15–20.
Behnam-Rassouli M, Ghayour M, Ghayour N, Ejtehadi MM. Investigating the effects of hydro-alcoholic extract of Launaea acanthodes on the serum levels of glucose, insulin, lipids and lipoproteins in stereptozotocin-induced type ? diabetic rats. Arak Med Univ J 2012;14(6):48–56.
Jalali M, Behnam-Rasouli M, Tehranipour M, Ghayour N, Khayatzadeh J, Jannati H. Study of the effects of hyperglycemia and Launaea acanthodes extract administration on disorders of liver function in rats. Physiol Parmacol 2012;15:562–571.
Ghaderian SM, Baker AJM. Geobotanical and biogeochemical reconnaissance of the ultramafics of Central Iran. J Geochem Explorat 2007;2:34–42.
Piazza L, Bertini S, Milany J. Extraction and structural characterization of the polysaccharide fraction of Launaea acanthodes gum. Carbohydr Polym 2010;9:449–454.
Stereo DC. The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the dissector. J Microscopy 1984;1:127–136.
Ozdemir O, Akalin PP, Baspinar N, Hatipoglu F. Pathological changes in the acute phase of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Bull Veterin Instit Pulawy 2009;53:783–790.
Palmeira CM, Santos DL, Seica R, Moreno AJ, Santos MS. Enhanced mitochondrial testicular antioxidant capacity in Goto-Kakizaki diabetic rats: role of coenzyme Q. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2001;281:1023–1028.
Jiang GY, Practical diabetes. 1st ed. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House;1996:295.
Gholam-Hosseini B, Khaki A, Ahmadi-Ashtiani HR, Rezazadeh S, Rastegar H, Fathiazad F, et al. Treatment effects of onion on spermatogenesis in streptozotocininduced diabetic rat. J Med Plants 2009;8:153–161.
Steger RW, Rabe MB. The effect of diabetes mellitus on endocrine and reproductive function. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1997;214:1–11.
Benitez A, Perez Diaz J. Effect of streptozotocin-diabetes and insulin treatment on regulation of Leydig cell function in the rat. Horm Metab Res 1985;17:5–7.
Altay B, Cetinkalp S, Doganavsargil B, Hekimgil M, Semerci B. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic effects on spermatogenesis with proliferative cell nuclear antigen immunostaining of adult rat testis. Fertil Steril 2003;80:828–831.
Wolff SP, Jiang ZY, Hunt JV. Protein glycation and oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus and ageing. Free Radic Biol Med 1991;10:339–352.
Leaming AB, Mathur RS, Levine JH. Increased plasma testosterone in streptozotocin-diabetic female rats. Endocrinology 1982;111:1329–1333.
Bryson JM, Baxter RC. Adrenal involvement in the diabetes-induced loss of growth hormone and prolactin receptors in the livers of female rats. EASD 1999;4:17–25.
Hassan G, Abdel Moneium T. Structural changes in the testes of streptozotocin-Induced diabetic rats. Suez Canal Univ Med J 2001;4:17–25.
Cameron DF, Murray FT, Drylie MF. Interstitial compartment pathology and spermatogenic disruption in testes from impotent diabetic men. Anat Rec 1985;213:53–62.
Shahreari Sh, Khaki A, Ahmadi-Ashtiani HR, Rezazadeh Sh, Hajiaghaei R. Effects of Danae racemosa on testosterone hormone in experimental diabetic rats. J Med Plants 2010;9:114–119.
Cai L, Chen S, Evans T, Deng DX, Mukherjee K, Chakrabarti S. Apoptotic germ-cell death and testicular damage in experimental diabetes: prevention by endothelin antagonism. Urol Res 2000;28:342–347.
Foglia VG, Rosner JM, Ramos M, Lema BE, Cattaneo de Paralta Ram. Sexual disturbances in the male diabetic rat. Horm Metab Res 1969;1:72–77.
Paz G, Homonnai ZT. Leydig cell function in streptozotocininduced diabetic rats. Experientia 1979;35:1412–1413.
Pietta PG. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J Nat Prod 2000;63:1035–1042.
Meenakshi S, Manicka-Gnanambigai D, Tamil-mozhi S, Arumugam M, Balasubramanian T. Total flavanoid and in vitro antioxidant activity of two seaweeds of rameshwaram coast. Glob J Pharmacol 2009;3:59–62.
Bors W, Michel C, Stettmaier K. Antioxidant effects of flavonoids. Biofactors 1997;6:399–402.
Khaki A, Nouri M, Fathiazad F, Ahmadi Ashtiani HR, Rastgar H, Rezazadeh S. Protective effects of quercetin on spermatogenesis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. J Med Plants 2009;8:57–64.
Khaki A, Fathiazad F, Nouri M, Maleki NA, Khamnei HJ, Ahmadi P. Beneficial effects of quercetin on sperm parameters in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male rats. Phytother Res 2010;24:1258–1291.
Khaki A, Fathiazad F, Nouri M, Khaki AA, Ghanbari Z, Ghanbari M, et al. Anti-oxidative effects of citro flavonoids on spermatogenesis in rat. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 2011;5:721–725.
Prabhakar PK, Doble M. Mechanisms of action of natural products used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Chin J Integr Med 2011;17:563–574.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Grant from the Office of Research Affairs of Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran (No. 3/17085)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, A., Behnam-Rassouli, M., Momeni, Z. et al. Effects of hydro-alcoholic extract of Launaea acanthodes on serum gonadotropin and testosterone levels and the structure of seminiferous tubules in hyperglycemic rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 22, 207–213 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2315-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2315-y