Abstract
Objective
To examine the effect of the zedoary essential component-eluting stent (ZES) on a porcine coronary neointimal formation.
Methods
ZES, sirolimus-eluting stents (SES), and bare metal stents (BMS) were randomly implanted in three different major epicardial vessels in 36 balloon-injured pigs. Coronary angiography, optical coherence tomography, and histomorphological analysis were used to determine antihyperplasia effects.
Results
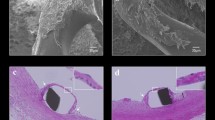
ZES and SES had a significantly larger lumen diameter and area, and reduced diameter and area of stenosis in arteries at 30 and 90 days compared with arteries implanted with BMS (P<0.01). Histomorphometric analysis showed moderate inflammatory responses, such as infiltration of mononuclear cells, lymphocytes, and multinucleated giant cells in some arteries with SES compared with ZES (P<0.05). Injury scores were not different among the three groups at 30 and 90 days. The endothelialization score in the SES group was 2.69±0.42 at 30 days and 2.83±0.39 at 90 days compared with the ZES and BMS groups (both were 3.00±0.00 at either 30 or 90 days, P<0.05). Well developed endothelium was observed in the ZES group, while incomplete endothelium and inflammatory cells were observed with stent struts partly naked at the vessel lumen in the SES group.
Conclusion
The ZES inhibits neointimal hyperplasia with good endothelia coverage in the porcine balloon injury coronary model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook S, Ladich E, Nakazawa G, Eshtehardi P, Neidhart M, Vogel R, et al. Correlation of intravascular ultrasound findings with histopathological analysis of thrombus aspirates in patients with very late drug-eluting stent thrombosis. Circulation 2009;120:391–399.
Jensen LO, Tilsted HH, Thayssen P, Kaltoft A, Maeng M, Lassen JF, et al. Paclitaxel and sirolimus eluting stents versus bare metal stents: long-term risk of stent thrombosis and other outcomes. From the Western Denmark Heart Registry. EuroIntervention 2010;5:898–905.
Zhou H, Beevers CS, Huang S. The targets of curcumin. Curr Drug targets 2011;12:332–347.
Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Sung B, Ahn KS, Murakami A, Sethi G, et al. Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, tetrahydrocurcumin and turmerones differentially regulate anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative responses through a ROS-independent mechanism. Carcinogenesis 2007;28:1765–1773.
Commission on life Sciences National Resenrch Council, ed. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals institute of laboratory animal resources. Washington D.C.: National academy Press; 1996:21–55.
Schwartz RS, Huber KC, Murphy JG, Edwards WD, Camrud AR, Vlietstra RE, et al. Restenosis and the proportional neointimal response to coronary artery injury: results in a porcine model. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992;19:267–274.
Suzuki T, Kopia G, Hayashi S, Bailey LR, Llanos G, Wilensky R, et al. Stent-based delivery of sirolimus reduces neointimal formation in a porcine coronary model. Circulation 2001;104:1183–1193.
Suzuki Y, Ikeno F, Koizumi T, Tio F, Yeung AC, Yock PG, et al. In vivo comparison between optical coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound for detecting small degrees of in-stent neointima after stent implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol Interv 2008;1:168–173.
Chen W, Lu Y, Gao M, Wu J, Wang A, Shi R. Anti-angiogenesis effect of essential oil from Curcuma zedoaria in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol 2011:133;220–226.
Beevers CS, Li F, Liu L, Huang S. Curcumin inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated signaling pathways in cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2006:119;757–764.
Chen A, Zheng S. Curcumin inhibits connective tissue growth factor gene expression in activated hepatic stellate cells in vitro by blocking NF-kappa B and ERK signalling. Br J Pharmacol 2008:153;557–567.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappa B signaling. Cell 2008;132:344–362.
Hayden MS, West AP, Ghosh S. NF-kappa B and the immune response. Oncogene 2006:25;6758–6780.
Singh S, Aggarwal BB. Activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B is suppressed by curcumin (diferuloylmethane). J Biol Chem 1995:270;24995–5000.
Aggarwal S, Takada Y, Singh S, Myers JN, Aggarwal BB. Inhibition of growth and survival of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by curcumin via modulation of nuclear factor-kappa B signaling. Int J Cancer 2004;111:679–692.
Inoue T, Node K. Molecular basis of restenosis and novel issues of drug-eluting stents. Circulation J 2009;73:615–621.
Prakash P, Misra A, Surin WR, Jain M, Bhatta RS, Pal P, et al. Anti-platelet effects of Curcuma oil in experimental models of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion and thrombosis. Thromb Res 2011;127:111–118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81072931) and National Health Fund (No. CMH200701110)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Fh., Liu, Jg., Wang, X. et al. Long-term effect of stent coating with zedoary essential components on neointimal formation in the porcine coronary artery. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 19, 771–776 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1596-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1596-2