Abstract
Objective
To observe the effects of different doses of Wenxiao Decoction (稳消方) on the expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in experimental atherosclerotic rabbits and to explore the mechanism by which it alleviates atherosclerosis.
Methods
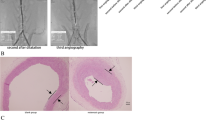
Sixty New Zealand rabbits were randomly divided into six groups: a blank group, a model group, a Simvastatin group, and high-, medium-, and low-dosage Wenxiao Decoction groups. Except for those in the blank group, all rabbits were fed with a high-cholesterol diet. Carotid atherosclerosis was established by balloon-induced carotid artery endothelium injury in conjunction with the high-cholesterol diet. After 8 weeks, all animals were euthanized to evaluate levels of IL-6 and ICAM-1 expressions (by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay) and of MCP-1 (by immunohistochemistry staining).
Results
The expressions of IL-6, ICAM-1, and MCP-1 were significantly increased in all groups except the blank group (P<0.05). However, the rabbits in the Wenxiao Decoction groups and the Simvastatin group showed significantly lower levels of IL-6, ICAM-1, and MCP-1 expression than those in the model group (P<0.05). The expressions of IL-6, ICAM-1, and MCP-1 in the highdosage Wenxiao Decoction group and the Simvastatin group were lower than those in the low-dosage Wenxiao Decoction group (P<0.05). The expression of MCP-1 in medium-dosage Wenxiao Decoction group was lower than that in the low-dosage group (P<0.05).
Conclusions
High, medium, and low doses of Wenxiao Decoction can inhibit the expressions of IL-6, ICAM-1, and MCP-1, which may prevent and stabilize atherosclerotic plaques. There may be a direct relationship between dosage and therapeutic efficacy of Wenxiao Decoction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross R. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 1999;340:115–126.
Tobias P, Curtiss LK. Thematic review series: the immune system and atherogenesis, paying the price for pathogen protection: toll receptors in atherogenesis. J Lipid Res 2005;46:404–411.
Frostegard J. Atherosclerosis in patients with autoimmune disorders. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005;25:1776–1785.
Shen H, Yi M, Li TS, Liu G, Wang YH, Feng LJ, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in atherosclerotic lesions and changes of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α, thromboxane B2 and tumor necrosis factor-α in serum. Chin Critic Care Med (Chin) 2002:14:226–229.
Ding SF, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Chen WQ, Chen YG, Li JF, et al. The role of atherosclerotic plaque stability and inflammation in the pathogenesis of acute coronary syndrome. Chin J Cardiol (Chin) 2006:34:512–514.
Hartford M, Wiklund O, Mattsson Hultén L, Pevers E, Person A, Herlitz J, et al. CRP, interleukin-6, secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 during the early phase of acute coronary syndromes and long-term follow-up. Int J Cardiol 2006:108:55–62.
Xu SY, Bian RX, Chen X, eds. Methodology of pharmacological experiment. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 1994:1049–1050.
ZhaoJ, Chi LX. Establishment of the carotid atherosclerosis model in rabbits. Chin J Cerebrovasc Dis (Chin) 2005;2:522–524.
Kanellakis P, Nestel P, Bobik A. Angioplasty-induced superoxide anions and neointimal hyperp lasia in the rabbit carotid artery: suppression by the isoflavone transtetra hydrodaidzein. Atherosclerosis 2004:176:63–72.
Yan S, Hao B. Current status of study on animal models of atherosclerosis. Shanxi Med J (Chin) 2008;37:731–733.
Ye BH, Guan YY, Lu HH, Yao Y, Liu YJ. Comparison among the carotid atherosclerotic rabbit models induced by balloon-injury with different size balloon plus high cholesteroldiet. J Nantong Univ (Med Sci, Chin) 2006;26:244–246.
Yin CM, Chu YP, Wu P. Pharmacodynamic test of active extract of Lumbricus. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (Chin) 2002;33:926–928.
Li JJ, Li YS, Fang CH, Hui RT, Yang YJ, Cheng JL, et al. Effects of simvastatin within two weeks on anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 in patients with unstable angina. Heart 2006:92:529–530.
Seino Y, Ikeda U, Ikeda M, Yamamoto K, Misawa Y, Hasegawa T, et al. Interleukin-6 gene transcripts are expressed in human atherosclerotic lesion. Cytokine 1994:26:141–145.
Sadowska AM, van Overveld FJ, Luyten C, Germonpré P, De Backer W A. Use of ICAM-1 antibodies and antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit transmigration of neutrophils. Inflamm Res 2004;53:143–149.
Asanori Aikawa, Peter Libby. The vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: pathohenesis and therapeutic approach. Cardio Vascul Pathol 2004;13:125–138.
Gerard C, Rollins B J. Chemokines and disease. Nat Immunol 2001:2:108–115.
Werle M, SclmaL U, Hanna K. MCP-1 induces activation of MAP kinases ERK, JNK and p38 MAPK in human endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 2002;56:284–292.
Hartung Dr, Petrov A, Haider N, Fujimoto S, Blankenberg F, Fujimoto A, et al. Radiolabeled monocyte chemotactic protein 1 for the detection of inflammation in experimental atherosclerosis. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1816–1821.
Hoogeveen RC, Morrison A, Boerwinkle E, Miles JS, Rhodes CE, Sharrett AR, et al. Plasma MCP-1 level and risk for peripheral arterial disease and incident coronary heart disease: atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Atherosclerosis 2005;183:301–307.
De Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Gibson CM, Antman EM, et al. Association between plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and long term clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2003;107:690–695.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a Research Grant from Health Bureau of Shanghai (No. 2008J003A)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, Qp., Liang, F., Li, Jp. et al. Effects of Wenxiao Decoction (稳消方) on the expression of interleukin-6, intercellular adhesion molecular-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in experimental atherosclerotic rabbits. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 20, 445–449 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1531-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-013-1531-6