Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of total flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry on the proliferation, cell cycle, and expressions of p21Ras and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene in erythroleukemia cell line K562.
Methods
The effect of total flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry on K562 cell line survival was determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium (MTT) reduction assay. The time- and dose-dependent manner was also observed. The cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed with flow cytometry (FCM). The immunocytochemistry method was applied to quantitatively analyze the effects of flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry on changes p21Ras and PCNA gene expressions.
Results
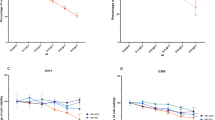
Flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry (20–100 μg/mL) significantly inhibited the proliferation of K562 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. After K562 cells were cultured for 48 h, total flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry had no significant effect on the apoptosis of K562 cells but showed significantly inhibition (P<0.01), indicating that total flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry could induce K562 cells arrested at G0/G1 and G2/M phases. Compared with the control group, p21Ras and PCNA gene expressions were decreased significantly in K562 cells treated with total flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry (40 and 80 μg/mL, respectively) for 48 h.
Conclusion
The inhibitory effect on proliferation of K562 cells was observed in the groups treated with flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry, which might be related to cells arresting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melo J, Toczyski D. A unified view of the DNA-damage checkpoint. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2002;14:237–245.
Jian JC, Wu ZH. Effects of traditional Chinese medicine on nonspecific immunity and disease resistance of large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea (Richardson). Aquaculture 2003;218:1–9.
Hikino H. Constituents and physiological actions of Astragalus and Hedysarum. J Tradit Sino-Jpn Med 1982;3:46–51.
Zhao J, Yu QT, Li P, Zhou P, Zhang YJ, Wang W. Determination of nine active components in Radix Hedysari and Radix Astragali using capillary HPLC with diode array detection and MS detection. J Sep Sci 2008;31:255–261.
Liu Y, Chen HB, Zhao YY, Wang B, Zhang QY, Zhang L, et al. Quantification and stability studies on the flavonoids of Radix hedysari. J Agric Food Chem 2006;54:6634–6639.
Liu Y, Zhao YY, Chen HB, Wang B, Zhang QY. Structure elucidation and complete NMR spectral assignme triterpenoid saponins from Radix Hedysari. Fitoterapia 2009;80:127–129.
Cheng XD, Yue H, Zhao YQ, Wang YJ. Clinical significance of expression of p21 and p53 proteins and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in pancreatic cancer. Hepatibiliary Pancreatic Dis Int 2002;1:302–305.
Huang TJ, Wang ZZ, Fang GG, Liu ZH. Expression of p53 protein and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in human gestation trophoblastic disease. Chin J Cancer Res (Chin) 2004;16:147–149.
Wang W, Wang L. Research progress of flavonoid compound. J Shenyang Med Coll (Chin) 2002;4:115–119.
Yang CJ, Wang CS, Hung JY, Huang HW, Chia YC, Wang PH, et al. Pyrogallol induces G2-M arrest in human lung cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in an animal model. Lung Cancer 2009;66:162–168.
Zhang XZ, Yin AH, Liu JH, Zhu XY, He M, Ding Q, et al. Sodium valproate induces cycle arrest, apoptosis and elevates P21RASWAF1 mRNA expression in chronic myeloid leukemia cell line K562. Chin J Pathophysiol (Chin) 2008;24:1726–1729.
Jin HM, Wang JZ, eds. Pathophysiology. 6th ed. Beijing: People’s Health Publishing House; 2006:116–129.
Tsujita M, Batista WL, Ogata FT, Stern A, Monteiro HP, Arai RJ. The nitric oxide-sensitive p21Ras-ERK pathway mediates S-nitrosoglutathione-induced apoptosis. Biochem Bioph Res Comm 2008:369;1001–1006.
Xia SH, Chen ZH, Forman LW, Faller DV. PKCδ survival signaling in cells containing an activated p21Ras protein requires PDK1. Cell Signal 2009;21:502–508.
Korshunov A, Golanov A, Sycheva R. Immunohistochemical markers for prognosis of cerebral glioblastomas. Neurooncol 2002;58:217–236.
Vaque JP, Navascues J, Shiio Y, Laiho M, Ajenjo N, Mauleon I, et al. Myc antagonizes Ras-mediated growth arrest in leukemia cells through the inhibition of the Ras-ERK-p21Cip1 pathway. J Biol Chem 2005;280:1112–1122.
Zhang YC, Zhou SD, Kong QY, Liu H. Expression of p21ras and cyclin D1 and their relationships in human lung cancer tissues. Acta Acad Med Xuzhou (Chin) 2003;23:395–398.
Lou JL, Lin HS, Qiu QY. Effect of procyanidin on cell cycle in murine lewis lung carcinoma. Chin J Cancer Res (Chin) 2004;16:220–224.
Knowles LM, Milner JA. Diallyl disulfide inhibits p34cdc2 kinase activity through changes in complex formation and phospho2rylation. Carcinogenesis 2000;21:1129–1134.
Charrier-Savournin FB, Chateau MT, Gire V, Sedivy J, Piette J, Dulic V. p21ras-mediated nuclear retention of cyclinB1-Cdk1 in response to genotoxic stress. Mol Biol Cell 2004;15:3965–3976.
Peng ZG, Song SJ. The anti-leukemia effect of flavonoids. Foreign Med Sci: Blood Transfusion Hematol (Chin) 2004;27:159–162.
Feng XQ, You Y, Xiao J, Zou P. Thapsigargin-induced apoptosis of K562 cells and its mechanism. Chin J Exp Hematol (Chin) 2006;14:25–30.
Chin S, Hughes MP, Coley HM, Labeed FH. Rapid assessment of early biophysical changes in K562 cells during apoptosis determined using dielectrophoresis. Int J Nanomed 2006;1:333–337.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation for Middle-Aged and Young Scientist of Gansu Province (No. YS031-A21-015)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yl., Luo, Yl., Chen, C. et al. The influence of the total flavonoids of Hedysarum polybotry on the proliferation, cell cycle, and expressions of p21Ras and proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene in erythroleukemia cell line K562. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 385–390 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0952-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0952-3