Abstract
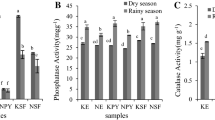
The authors presented the enzyme characteristics of catalase, sucrase, urease and alkaline phosphatase under agroforestry systems in northern Jiangsu Province. The results show that soil enzyme activities reduce gradually from top to bottom layer of the soil profile, and the fluctuations of catalase and urease are smaller than those of sucrase and alkaline phosphatase. Soil enzyme activities differe significantly in different samples, and the order is arranged as poplar-crop intercropping segment (A, D) > paulownia-crop intercropping segment (B, C) > CK. Furthermore, soil enzyme activities increase with intercropping age. On the other hand, in the same plot, there are closer relationships between enzymes in the soil samples. Catalase, alkaline phosphatase and urease are negatively related, while alkaline phosphatase and urease are positively related (except in samples B and C). In addition, the enzyme activities have a close relationship with the fertilizers. Catalase is positively correlated with the soil pH value (r=0.854, 0.804, 0.078 and 0.082, respectively), and is negatively correlated with total N (r=−0.201, −0.529, −0.221 and −0.821, respectively), total P (r=−0.143, −0.213, −0.362 and −0.751, respectively) and available P (r=−0.339, −0.351, −0.576, and −0.676, respectively). Sucrase, urease and alkaline phosphatase are negatively correlated with the pH value, while positively correlated with the other fertilizers (r ≈ 1). The authors suggest that enzyme activity will be a great potential as an indicator of soil quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Dai W, Bai H Y. 1995. Correlation between catalase activity and its kinetic characteristic and some soil properties. Journal of Beijing Forestry University. 17 (1): 37–40
Dai W, Chen X D. 1995. Correlation of enzyme activities with some soil properties in Beijing low mountain area. Journal of Hebei Forestry College. 10 (1): 13–18
Guan S Y, Shen G Q. 1984. Enzyme activities in main soil in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica. 21 (4): 368–381
Guan S Y. 1986. Soil enzyme and study methods of soil enzyme. Beijing: Agriculture Publication House
Guan S Y. 1989. Studies on the factors influencing soil enzyme activities. Acta Pedologica Sinica. 26 (1): 72–78
He W X, Lai H X, Wu Y J et al. 2001. Study no soil enzyme activities effected by fertilizing cultivation. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric Life Sic). 27 (3): 265–268
He W X, Zhu M E. 1997. Study on relation between urease and fertility of soil in Shanxi Province. Acta Pedologica Sinica. 34 (1): 42–52
Hu H B, Zhang J C. 2001. Study on soil enzyme activity of main forest types in rock coastal area. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University. 25 (4): 21–25
Huang S W. 1981. Enzyme activity and fertilizer of soil. Bulletin of Soil. 12 (4): 37–39
Li Y. 1981. Study of enzyme activity and fertilizer of soil. Bulletin of Soil. 20 (4): 190–193
Lu Q, Yang H X. 1997. Effect of radiation transmission on crop yield and quality. Acta Ecological Sinica. 17 (1): 36–43
Ministry of Forestry. 1998. Forestry development in the northern plains region. Afforestation Bureau Work Report, Beijing, China
Ong C K, Corlett J E. 1991. Above and belowground interactions in agroforestry systems. Forest Ecology and Management. 45: 45–57
Shun C L, Tong C R. 2001. Study on volume, soil microbes and enzyme activities in different porpus types. Forest Research. 3 (14): 336–339
Yin R, He Q. 1997. The spatial and temporal effects of paulownia intercropping the case of northern China. Agroforestry Systems. 37: 91–109
Zhou L K, Zhang Z M, Cao C M. 1983. On the role of the totality of soil enzyme activities in the evaluation of the level of soil fertility. Acta Pedologica Sinica. 20 (4): 413–418
Zhu Z, Cai M T, Wang S J et al. 1991. Agroforestry systems in China. Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing and IDRC, Canada. 216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, F., Chen, P. Soil enzyme activities under agroforestry systems in northern Jiangsu Province. For. Stud. China 6, 21–26 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-004-0015-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-004-0015-3