Abstract
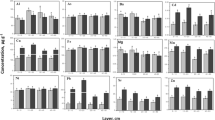
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) has become a powerful tool for providing reliable analytical results in many laboratories around the word. In this study, the mixture of HF and HNO3 acids in high-temperature and high-pressure closed-vessel digestion technique were used to decompose some Chinese reference materials, and thirty seven elements were determined by ICP-MS. Most of the results for Chinese soil reference materials were found to be in reasonable agreement with the reference values, except Cs, Ta, Li, Ge, Zn, Nd, Tb and Ta whose values need to be revised. Their precisions were typically lower than 5% RSD. However, the Precisions of Chinese clay reference materials, especially for GBW03102 and GBW03102a, were significantly different with reference values, probably reflecting the existence of a coarser-grained fraction (>70 μm) in samples, and the formation of fluorides in Al-rich samples during sample decomposition by using the mixture of HF and HNO3 acids. Moreover, thirty-seven trace elements covering the mass range from Li to U in four Chinese clay reference materials were firstly provided with good precision and accuracy in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu Zhaochu, Gao Shan, Liu Yongsheng, Hu Shenghong, Zhao Laishi, Li Yanxiang, and Wang Qi (2010) NH4F assisted high pressure digestion of geological samples for multi-element analysis by ICP-MS [J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry. 25, 408–413.
Hu Shenghong, Chen Aifang, and Lin Shoulin (2000) ICP-MS analitical research into 40 trace and ultra-trafic elements in geological samples [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences. 25, 186–190 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jenner G.A., Longerich H.P., Jackson S.E., and Fryer B.J. (1990) ICP-MS A powerful tool for high-precision trace-element analysis in Earth sciences: Evidence from analysis of selected U.S.G.S. reference samples [J]. Chemical Geology. 83,133–148.
Li Bing and Yang Hongxia (2003) Applications of ctively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in earth science [J]. Earth Science Frontier. 10, 367–378 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Bing and Yi Ming (1995) Advances in inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis. 4, 254–273 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Ye, Liu Xiaoming, Hu Zhaochu, Diwu Chunrong, Yuan Honglin, and Gao Shan (2007) Evaluation of accuracy and long-term stability of determination of 37 trace elements in geological samples by ICP-MS [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica. 5, 1203–1210 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Ying, Liu Haichen, and Li Xianhua (1996) Simultaneous and precise determination of 40 trace elements in rock samples using ICP-MS [J]. Geochimica. 25, 552–558 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Qi Liang, Hu Jing, and Gregoire D.C. (2000) Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry [J]. Talanta. 51, 507–513.
Rollinson H. (1993) Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presention, Interpretation [M]. Longman Scientific & Technical, London.
Rudnick R.L. and Gao Shan (2003) Composition of the continental crust [M]. In Treatise on Geochemistry (eds. Heinrich D.H. and Karl K.T.). pp.1–64. Pergamon, Oxford
Takei H., Yokoyama T., Makishima A., and Nakamura E. (2001) Formation and suppression of AlF3 during HF digestion of rock samples in Teflon bomb for precise trace element analyses by ICP-MS and ID-TIMS [J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy (Series B), 77B, 13–17.
Wang Yimin (2003) Practical Handbook of Reference Materials for Geoanalysis [M]. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
Zhang Wen, Hu Zhaochu, Liu Yongsheng, Chen Haihong, Gao Shan, and Richard M. Gaschnig (2012) Total rock dissolution using ammonium bifluoride (NH4HF2) in screw-top teflon vials: A new development in open-vessel digestion [J]. Analytical Chemistry. 84, 10686–10693.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Diwu, C., Zhao, Y. et al. Determination of trace and rare-earth elements in Chinese soil and clay reference materials by ICP-MS. Chin. J. Geochem. 33, 95–102 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0663-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0663-5