Abstract
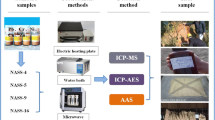
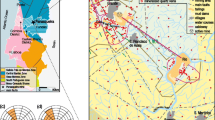
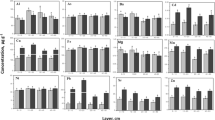
In this study, we determined the concentrations of heavy metals in the agricultural soils of Kafr El-Zayat city using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). The LA-ICP-MS performance was firstly evaluated by analyzing appropriate reference materials and comparing the concentration values found to those of the reference values. LA-ICP-MS was then applied to examine the content of 21 elements (Mg, Al, Si, Ca, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Rb, Sr, Mo, Sn, Ba, Pb, Th, and U) in 16 collected agricultural soil samples from Egypt. The soil quality was assessed by calculating the contamination factor (CF), enrichment factor (EF), and the geo-accumulation index (Igeo) of the measured heavy metals. The average concentrations of V, Cr, Co, Ni, and Cu were higher than the average worldwide background concentrations and exceeded the Canadian soil quality guidelines with values of 162.8, 113.3, 42.2, 88.1, and 70.6 μg/g, respectively. Multivariate analysis was applied to investigate the correlation and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils. Cluster analysis indicated the clustering of heavy metals into three groups: Cr and Mo; Fe and Mn; and V, Ni, Co, Cu, Zn, and Pb. The results of principal component analysis (PCA) agreed with those of the cluster analysis and yielded three components that explained 81.13% of the total variance. The contamination factor (CF) of soils from all sampling sites showed moderate contamination.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adimalla N, Qian H, Wang H (2019) Assessment of heavy metal (HM) contamination in agricultural soil lands in northern Telangana, India: an approach of spatial distribution and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ Monit Assess 191:246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7408-1
Al Naggar Y, Naiem E, Mona M et al (2014) Metals in agricultural soils and plants in Egypt. Toxicol Environ Chem 96:730–742. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2014.984496
Al-Wabel MI, Sallam AEAS, Usman ARA et al (2017) Trace metal levels, sources, and ecological risk assessment in a densely agricultural area from Saudi Arabia. Environ Monit Assess 189:252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5919-1
Aslam Farooq W, Tawfik W, Al-Mutairi FN, Alahmed ZA (2013) Qualitative analysis and plasma characteristics of soil from a desert area using LIBS technique. J Opt Soc Korea 17:548–558. https://doi.org/10.3807/JOSK.2013.17.6.548
Bacon JR, Butler OT, Cairns WRL, Cook JM, Davidson CM, Cavoura O, Mertz-Kraus R (2020) Atomic spectrometry update-a review of advances in environmental analysis. J Anal At Spectrom 35:9–53. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ja90060h
Bánfalvi G (2011) Heavy metals, trace elements and their cellular effects. In: Banfalvi G (ed) Cellular Effects of Heavy Metals. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 3–28
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (2007) Soqi_Calculator_E_1. https://www.ccme.ca/en/resources/canadian_environmental_quality_guidelines/calculators.html. Accessed 26 Mar 2020
CCME (2007) Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health, Update 7.0 September 2007. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment
El-Bady MSM (2016) Distributions and variations of the heavy metals with depth and grain size fractions in the cultivated soils, a case study in middle Nile Delta, Egypt. Int J ChemTech Res 9:97–110
Farooq WA, Rasool KG, Tawfik W, Aldawood AS (2015) Application of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy in early detection of red palm weevil: (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) infestation in date palm. Plasma Sci Technol 17:948–952. https://doi.org/10.1088/1009-0630/17/11/11
Farooq WA, Al-Johani AS, Alsalhi MS et al (2020) Analysis of polystyrene and polycarbonate used in manufacturing of water and food containers using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. J Mol Struct 1201:127152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127152
Frentiu T, Ponta M, Mihaltan A et al (2009) Qualitative assessment of heavy metals sources in pitcoal/biomass briquettes combustion using multivariate statistical analysis. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 11:697–704
Fryer BJ, Jackson SE, Longerich HP (1995) The design, operation, and role of the laser-ablation microprobe coupled with an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (LAM-ICP-MS) in the earth sciences. Can Mineral 33:303–312
Gałuszka A, Migaszewski Z (2011) Geochemical background - an environmental perspective. Mineralogia 42:7–17. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10002-011-0002-y
Guerra MF, Sarthre C-O, Gondonneau A, Barrandon J-N (1999) Precious metals and provenance enquiries using LA-ICP-MS. J Archaeol Sci 26:1101–1110. https://doi.org/10.1006/jasc.1999.0405
Guillong M, Günther D (2002) Effect of particle size distribution on ICP-induced elemental fractionation in laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 17:831–837. https://doi.org/10.1039/b202988j
Hattendorf B, Latkoczy C, Günther D (2003) Laser ablation-ICPMS. Anal Chem 75:341 A–347 A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac031283r
Hoffmann E, Lüdke C, Stephanowitz H (1996) Application of laser-ICP-MS in environmental analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 355:900–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s0021663550900
Jantzi SC, Almirall JR (2011) Characterization and forensic analysis of soil samples using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Anal Bioanal Chem 400:3341–3351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4869-7
Jantzi SC, Almirall JR (2015) Elemental analysis of soils using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) with multivariate discrimination: tape mounting as an alternative to pellets for small forensic trans. Appl Spectrosc 68:963–974. https://doi.org/10.1366/13-07351
Jantzi SC, Dutton CL, Saha A, Masikini R, Almirall JR (2019) Novel “filter pellet” sample preparation strategy for quantitative LA-ICP-MS analysis of filter-bound sediments: a “green chemistry” alternative to sediment fingerprinting in Tanzania’s Ruvu River basin. J Soils Sediments 19:478–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2076-2
Jochum KP, Nohl U, Herwig K, Lammel E, Stoll B, Hofmann AW (2005) GeoReM: a new geochemical database for reference materials and isotopic standards. Geostand Geoanal Res 29:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-908X.2005.tb00904.x
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, London
Khalifa M, Gad A (2018) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in agricultural soil of southwestern Nile Delta, Egypt. Soil Sediment Contam 27:619–642. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2018.1498445
Kroslakova I, Günther D (2007) Elemental fractionation in laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry: evidence for mass load induced matrix effects in the ICP during ablation of a silicate glass. J Anal At Spectrom 22:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1039/b606522h
Lagas P, Loch JPG, Bom CM, Gerringa LJA (1984) The behavior of barium in a landfill and the underlying soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 22:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00163093
Limbeck A, Galler P, Bonta M, Bauer G, Nischkauer W, Vanhaecke F (2015) Recent advances in quantitative LA-ICP-MS analysis: challenges and solutions in the life sciences and environmental chemistry ABC Highlights: Authored by Rising Stars and Top Experts. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:6593–6617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8858-0
Longerich HP, Jackson SE, Günther D (1996) Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric transient signal data acquisition and analyte concentration calculation. J Anal At Spectrom 11:899–904
Malcolm HM, Wood M, Kingdom U (2004) IPCS Concise International Chemical Assessment Documents. Manganese and its compounds: environmental aspects. IPCS Concise Int Chem Assess Doc 1–37
Mankoula AF, Tawfik W, Gagnon JE, Fryer BJ, el-Mekawy F, Shaheen ME (2021) ICMMS-2: assessment of heavy metals content in the agricultural soils of Kafr El-Zayat Egypt using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. Egypt J Chem 64:1167–1177. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2021.55867.3185
Mao XL, Ciocan AC, Borisov OV, Russo RE (1998) Laser ablation processes investigated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Appl Surf Sci 127–129:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(97)00787-3
Moenke-blankenburg L, Schumann T, Nolte J (1994) Direct solid soil analysis by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry *. J Anal At Spectrom 9:1059–1062
Mortvedt JJ (1995) Heavy metal contaminants in inorganic and organic fertilizers. Fertil Res 43:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00747683
Mousavi SR, Shahsavari M, Rezaei M (2011) A general overview on manganese (Mn) importance for crops production. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 5:1799–1803
Musil P, Otruba V, Kanický V, Mermet J-M (2000) Determination of elements in agricultural soils using IR laser ablation inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 55:1747–1758. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0584-8547(00)00280-9
Pan L b, Ma J, Wang X l, Hou H (2016) Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: levels, sources and spatial distribution. Chemosphere 148:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.049
Petrotou A, Skordas K, Papastergios G, Filippidis A (2012) Factors affecting the distribution of potentially toxic elements in surface soils around an industrialized area of northwestern Greece. Environ Earth Sci 65:823–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1127-4
Pisonero J, Günther D (2008) Femtosecond laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: fundamentals and capabilities for depth profiling analysis. Mass Spectrom Rev 27:609–623. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.20180
Saetveit NJ, Bajic SJ, Baldwin DP, Houk RS (2008) Influence of particle size on fractionation with nanosecond and femtosecond laser ablation in brass by online differential mobility analysis and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 23:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/b709995a
Senesi GS, Dell’Aglio M, Gaudiuso R, de Giacomo A, Zaccone C, de Pascale O, Miano TM, Capitelli M (2009) Heavy metal concentrations in soils as determined by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), with special emphasis on chromium. Environ Res 109:413–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2009.02.005
Shaheen M, Fryer BJ (2010) Improving the analytical capabilities of femtosecond laser ablation multicollector ICP-MS for high precision Pb isotopic analysis: the role of hydrogen and nitrogen. J Anal At Spectrom 25:1006–1013. https://doi.org/10.1039/c003879b
Shaheen M, Gagnon JE, Yang Z, Fryer BJ (2008) Evaluation of the analytical performance of femtosecond laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry at 785 nm with glass reference materials. J Anal At Spectrom 23:1610–1621. https://doi.org/10.1039/b809880h
Shaheen ME, Gagnon JE, Fryer BJ (2012) Femtosecond (fs) lasers coupled with modern ICP-MS instruments provide new and improved potential for in situ elemental and isotopic analyses in the geosciences. Chem Geol 330–331:260–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.09.016
Shaheen ME, Gagnon JE, Fryer BJ (2015) Elemental fractionation in 785 nm picosecond and femtosecond laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 107:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2015.02.010
Shaheen ME, Gagnon JE, Fryer BJ (2016) Excimer laser ablation of aluminum: influence of spot size on ablation rate. Laser Phys 26:116102. https://doi.org/10.1088/1054-660X/26/11/116102
Shaheen ME, Gagnon JE, Fryer BJ, Polat A (2017) A simple and rapid method for preparing a diversity of powdered materials for analysis by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom 421:104–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2017.05.013
Shaheen ME, Gagnon JE, Fryer BJ (2021) Experimental studies on ablation characteristics of alumina after irradiation with a 193-nm ArF excimer laser. Eur Phys J Plus 136:119. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01132-5
Shivakumar D, Srikantaswamy S, Sreenivasa S, Kiran BM (2012) Speciation and geochemical behaviour of heavy metals in industrial area soil of Mysore City, India. J Environ Prot 3:1384–1392. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2012.310157
Shokr MS, El Baroudy AA, Fullen MA et al (2016) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the middle Nile delta of Egypt. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 4:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.10.003
Simon L (2014) Potentially harmful elements in agricultural soils. In: PHEs, environment and human health. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 85–150
Song H, Hu K, An Y, Chen C, Li G (2018) Spatial distribution and source apportionment of the heavy metals in the agricultural soil in a regional scale. J Soils Sediments 18:852–862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1795-0
Suyanto H, Lie TJ, Kurniawan KH, Kagawa K, Tjia MO (2017) Practical soil analysis by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy employing subtarget supported micro mesh as a powder sample holder. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 137:59–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2017.09.013
Tawfik W, Farooq WA, Al-Mutairi FN, Alahmed ZA (2015) Monitoring of inorganic elements in desert soil using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Lasers Eng 32:129–140
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72:175–192
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank JC Barrette and Sharon Lackie, Great Lakes Institute for Environmental Research, University of Windsor, Canada, for helping with LA-ICP-MS and EDS analysis. We thank Drs. Osama Hemeda, Ahmed Farouk, Ahmed Heneish, and Hany El-Ghrabawy, Physics Department, Faculty of Sciences, Tanta University, Egypt, for helping with sample preparation.
Funding
This work was partially funded by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Cultural Affairs and Missions Sector, and Tanta University, Egypt. Chemical analysis was supported by NSERC Discovery Grant to Brian J Fryer and Joel Gagnon and CFI to Joel E Gagnon, University of Windsor, Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MES performed the experimental work, interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript. WT reviewed the manuscript. AFM collected the soil samples and participated in data interpretation. JEG and BJF supported the experimental analysis using LA-ICP-MS and SEM instruments in their labs. FEM reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaheen, M.E., Tawfik, W., Mankoula, A.F. et al. Determination of heavy metal content and pollution indices in the agricultural soils using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 36039–36052 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13215-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13215-y