Abstract
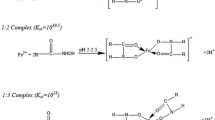
Bauxite resources are widely spread in the earth. However, the effective utilization of this mineral is still under infant. The conventional collector for diaspore mineral is oleic acid. It has three main drawbacks which are highly insoluble, large dosages in bauxite flotation, and low selectivity, which hinder its application in industry. In this research, octylic hydroxamic acid was synthesized, and its collecting ability toward two major minerals in bauxite-diaspore and kaolinite was investigated. The collecting power of various reagents for diaspore are shown as follows: oleic acid<octylic hydroxamic acid; while the collecting power for kaolinite was like this: octylic hydroxamic acid<oleic acid. It is shown that octylic hydroxamic acid has the capability of high collectivity and good selectivity. The optimum pH was determined to be 8–9. Zeta potential test revealed that the anionic collectors-octylic hydroxamic acid and oleic acid had been adsorbed on the surface of diaspore and kaolinite, meanwhile the adsorption for diaspore was more remarkable. By the adsorptive capability and IR tests, the adsorption of octylic hydroxamic acid on diaspore was determined to be a process of chemical absorption, which was greater than that of oleic acid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao Li and Anh V. Nguyen (2010) Developing a physically consistent model for gibbsite leaching kinetics [J]. Hydrometallurgy. 104, 86–98.
Hu Yuehua (2003) Progress in flotation de-silica [J]. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 13, 656–662.
Jiang Yuren, Zhao Binnan, Zhou Xiaohong, and Zhou Liyi (2010) Flotation of diaspore and aluminosilicate minerals applying novel carboxyl hydroxamic acids as collector [J]. Hydrometallurgy. 104, 112–118.
Lin I.J., Malts N., and Shindler Y. (1998) The complex chemical treatment of alumina-silica-containing materials [J]. J. Mater. Synth. Process. 6, 27–35.
Matjie R.H. and Engelbrecht R. (2007) Selective removal of dissolved silicon and aluminium ions from gas liquor by hydrometallurgical methods [J]. Hydrometallurgy. 85, 172–182.
Mu Wenning and Zhai Yuchun (2010) Desiliconization kinetics of nickeliferous laterite ores in molten sodium hydroxide system [J]. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 20, 330–335.
Pontikes Y.C. Rathossi P. Nikolopoulos, Angelopoulos G.N., Jayaseelan D.D., and Lee W.E. (2009) Effect of firing temperature and atmosphere on sintering of ceramics made from Bayer process bauxite residue [J]. Ceram. Int. 35, 401–407.
Smith Peter (2009) The processing of high-silica bauxites—Review of existing and potential processes [J]. Hydrometallurgy. 98, 162–176.
Wahnsiedler W.E. (1985) The Kinetics of Bauxite Digestion in the Bayer Process [C]. pp.145–182. TMS Light Met. Comm., Processdings of 114th Annu. Meet., New York.
Wang Yuhua, Hu Yuehua, and Liu Xiaowen (2003). Flotation de-silicating from diasporic-bauxite with cetyl trimethylammonium bromide [J]. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol (Engl. ed.). 10, 324–328.
Xia Liuyin, Zhong Hong, and Liu Guangyi (2010) Flotation techniques for separation of diaspore from bauxite uing Gemini collector and starch depressant [J]. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 20, 495–501.
Xia Liuyin, Zhong Hong, Liu Guangyi, Huang Zhiqiang, and Chang Qingwei (2009) Flotation separation of the aluminosilicates from diaspore by a Gemini cationic collector [J]. Int. J. Miner. Process. 92, 74–83.
Li Yi, Hong Yetang, Wang Duojun, and Zhu Yongxuan (2010) Effect of red mud on the mobility of heavy metals in mining-contaminated soils [J]. Chin. J. Geochem. 29, 191–196.
Zhang Y.H., Wei D.Z., Zeng K.W., Ren A.J., Zheng G.B., Liu S.H., and Chen D.Z. (2008) Application and development of depressant BK501 in the desilication from bauxite by reverse floatation [J]. Proc. Int. Miner. Process. Congr. 1, 1563–1567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Qin, W., Peng, T. et al. Flotation mechanism of octylic hydroxamic acid on diaspore. Chin. J. Geochem. 32, 191–194 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-013-0621-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-013-0621-7