Abstract
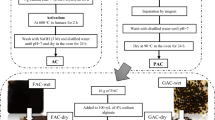
In order to improve the recovery of tungsten ores containing tin minerals, anisic hydroxamic acid (p-methoxy benzohydroxanic acid, PMOB) was synthesized and introduced as novel collector in the flotation of scheelite, wolframite and cassiterite. The flotation performance and adsorption mechanism were investigated by micro/batch flotation, zeta potential measurements and density functional theory (DFT). The micro flotation results showed that the recoveries of scheelite, wolframite and cassiterite using PMOB as collector are 97.45%, 95.77% and 90.08%, respectively, and the corresponding recoveries are 91.00%, 84.30% and 84.67% for benzohydroxamic acid (BHA). The batch flotation results revealed that the collector dosage could be reduced by about 45% for PMOB compared with BHA, in the case of similar flotation indicators. Zeta potential measurements indicated that PMOB could be adsorbed on the mineral surfaces by chemisorption. Moreover, density functional theory (DFT) calculation results showed that the substituent group −OCH3 endues PMOB stronger electron donation ability and hydrophobicity compared with benzohydroxamic acid (BHA), p-methyl benzohydroxamic acid (PMB) and p-hydroxyl benzohydroxamic acid (PHB).
摘要
为了提升钨锡矿物的浮选回收,本文研究了一种新型羟肟酸捕收剂——对甲氧基苯甲羟肟酸(茴香羟肟酸,PMOB)对白钨矿、黑钨矿和锡石的浮选性能。以茴香酸乙酯为原料与盐酸羟胺通过肟化反应制备PMOB,采用质谱与核磁共振光谱对产物结构进行表征。单矿物浮选试验结果表明,在适宜的浮选pH条件下,PMOB对白钨矿、黑钨矿和锡石的回收率分别为97.45%、95.77%和90.08%,而苯甲羟肟酸(BHA)对三者的回收率分别为91.00%、84.30% 和84.67%;根据黑白钨混合矿实际矿石浮选结果,获得相近的浮选指标时PMOB的用量比BHA降低约45%,浮选研究表明PMOB的捕收能力强于BHA。Zeta 电位测试研究证实,在浮选pH区间,PMOB的吸附导致三种矿物的表面电性发生不同程度的负移,PMOB在矿物表面发生了化学吸附。此外,采用密度泛函理论(DFT)方法研究了取代基—OCH3的电子效应,DFT计算结果表明,与苯甲羟肟酸、对甲基苯甲羟肟酸和对羟基苯甲羟肟酸相比,取代基团的引入提高了PMOB的给电子能力,增强了PMOB与矿物表面的结合能力,另一方面, 甲氧基同时也提高了PMOB的疏水性能,对其捕收性能的提升起到促进作用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GAO Zhi-yong, WANG Cong, SUN Wei, et al. Froth flotation of fluorite: A review [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 290: 102382. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102382.
GAO Yue-sheng, GAO Zhi-yong, SUN Wei, et al. Adsorption of a novel reagent scheme on scheelite and calcite causing an effective flotation separation [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 512: 39–46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.10.045.
WEI Zhao, SUN Wei, HAN Hai-sheng, et al. Enhanced electronic effect improves the collecting efficiency of benzohydroxamic acid for scheelite flotation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 152: 106308. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106308.
LIU Cheng, ZHANG Wen-cai, SONG Shao-xian, et al. Study on the activation mechanism of lead ions in wolframite flotation using benzyl hydroxamic acid as the collector [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 141: 105859. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.105859.
LU Yu-xi, WANG Shuai, ZHONG Hong. Study on the role of a hydroxamic acid derivative in wolframite flotation: Selective separation and adsorption mechanism [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 550: 149223. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149223.
SUN Lei, HU Yue-hua, SUN Wei. Effect and mechanism of octanol in cassiterite flotation using benzohydroxamic acid as collector [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(12): 3253–3257. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64458-8.
FENG Qi-cheng, ZHAO Wen-juan, WEN Shu-ming, et al. Activation mechanism of lead ions in cassiterite flotation with salicylhydroxamic acid as collector [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 178: 193–199. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.01.053.
SUN Qing, LU Yu-xi, WANG Shuai, et al. A novel surfactant 2- (benzylthio) -acetohydroxamic acid: Synthesis, flotation performance and adsorption mechanism to cassiterite, calcite and quartz [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 522: 146509. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146509.
LU Yu-xi, WANG Shuai, ZHONG Hong. Optimization of conventional hydroxamic acid for cassiterite flotation: Application of structural modification under principle of isomerism [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 167: 106901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.106901.
GIBSON C E, HANSULD R, KELEBEK S, et al. Behaviour of ilmenite as a gangue mineral in the benzohydroxamic flotation of a complex pyrochlore-bearing ore [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 109: 98–108. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.02.009.
CAO Miao, BU Hao, MENG Qing-bo, et al. Effect of surface modification by lead ions on flotation behavior of columbite-tantalite [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 611: 125827. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125827.
LI Mei, GAO Kai, ZHANG Dong-liang, et al. The influence of temperature on rare earth flotation with naphthyl hydroxamic acid [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2018, 36(1): 99–107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2017.07.004.
ABAKA-WOOD G B, ZANIN M, ADDAI-MENSAH J, et al. The upgrading of rare earth oxides from iron-oxide silicate rich tailings: Flotation performance using sodium oleate and hydroxamic acid as collectors [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2018, 29(12): 3163–3172. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2018.08.019.
Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. China Mineral Resources 2020 [R]. Peiking: Geological Publishing House, 2020.
U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral commodity summaries [R]. Washington: U.S. Geological Survey, 2021.
NI Chen-quan, LIU Chang, FANG Xing-zhong, et al. A novel collector with wide pH adaptability and high selectivity towards flotation separation of scheelite from calcite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 158: 106606. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106606.
WANG Xu, JIA Wen-hao, YANG Cong-ren, et al. Innovative application of sodium tripolyphosphate for the flotation separation of scheelite from calcite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 170: 106981. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.106981.
REN Hui-chuan, LI Jiang-tao, TANG Zhong-yang, et al. Sustainable and efficient extracting of tin and tungsten from wolframite-scheelite mixed ore with high tin content [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 269: 122282. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122282.
HUANG Hai-wei, QIU Ting-sheng, REN Si-li, et al. Research on flotation mechanism of wolframite activated by Pb(II) in neutral solution [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 530: 147036. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147036.
LI Ai-min, WEI Zhao, HAN Hai-sheng, et al. Production practice of a new mixed flotation process for wolframite and scheelite based on complex collector in Xingluokeng tungsten mine [J]. Metal Mine, 2021(6): 73–79.
TAN Xin, ZHANG Hua, WANG Jin-fu, et al. Molecular design of a new hydroxamic acid collector for scheelite flotation separation [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019 (6): 1331–1340. (in Chinese)
WEI Zhao, SUN Wei, HAN Hai-sheng, et al. Improving the flotation efficiency of Pb-BHA complexes using an electron-donating group [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 234: 116461. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2021.116461.
YU Xin-yang, WANG Li-ping, HU Lin-qi, et al. Nipalgin hydroximic acid as well as its preparation method and application in tungsten ore flotation: China, CN108503562A[P]. 2018-09-07.
YU Xin-yang, WANG Li-ping, HU Lin-qi, et al. Nicotinic hydroxamic acid as well as its preparation method and application: China, CN107694763B[P]. 2020-02-07.
YU Xin-yang, WANG Li-ping, HU Lin-qi, et al. 2-Furoic hydroxamic acid as well as its preparation method and application: China, CN107638957B [P]. 2020-02-07. (in Chinese)
LI Fang-xu, ZHOU Xiao-tong, ZHAO Gang, et al. A novel decyl-salicyl hydroxamic acid flotation collector: Its synthesis and flotation separation of malachite against quartz [J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 374: 522–526. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.07.068.
YU Xin-yang, ZHANG Rui-rui, ZENG Yu-hui, et al. The effect and mechanism of cinnamic hydroxamic acid as a collector in flotation separation of malachite and calcite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 164: 106847. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.106847.
ZHAO Gang, ZHONG Hong, QIU Xian-yang, et al. The DFT study of cyclohexyl hydroxamic acid as a collector in scheelite flotation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 49: 54–60. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2013.04.025.
ZHAO Gang, DAI Ting, WANG Shuai, ZHONG Hong. Study on a novel hydroxamic acid as the collector of rhodochrosite [J]. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing, 2018, 54(2): 428–439. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5277/ppmp1830.
FRISCH M J, TRUCKS G W, SCHLEGEL H B, et al. Fox, Gaussian 09 (Revision A. 1) [M]. Wallingford CT: Gaussian, Inc., 2009.
SARVARAMINI A, AZIZI D, LARACHI F. Hydroxamic acid interactions with solvated cerium hydroxides in the flotation of monazite and bastnäsite—Experiments and DFT study [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 387: 986–995. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.044.
VERMA D K, AL FANTAZI A, VERMA C, et al. Experimental and computational studies on hydroxamic acids as environmental friendly chelating corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in aqueous acidic medium [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 314: 113651. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113651.
ELSHARKAWY E R, ALMALKI F, BEN HADDA T, et al. DFT calculations and POM analyses of cytotoxicity of some flavonoids from aerial parts of Cupressus sempervirens: Docking and identification of pharmacophore sites [J]. Bioorganic Chemistry, 2020, 100: 103850. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103850.
CHEN Yan-fei, TANG Xue-kun. Selective flotation separation of smithsonite from calcite by application of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid as depressant [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 512: 145663. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145663.
SUN Qing, MA Xin, LU Yu-xi, et al. Insights into the selective adsorption mechanism of a multifunctional thioether-containing hydroxamic acid on separation of wolframite from fluorite [J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 380: 421–429. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.11.014.
JIN Sai-zhen, ZHANG Peng-yu, OU Le-ming, et al. Flotation of cassiterite using alkyl hydroxamates with different carbon chain lengths: A theoretical and experimental study [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 170: 107025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.107025.
TIAN Meng-jie, ZHANG Chen-yang, HAN Hai-sheng, et al. Novel insights into adsorption mechanism of benzohydroxamic acid on lead (II) -activated cassiterite surface: An integrated experimental and computational study [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 122: 327–338. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.04.012.
WANG Pei-pei, QIN Wen-qing, REN Liu-yi, et al. Solution chemistry and utilization of alkyl hydroxamic acid in flotation of fine cassiterite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(6): 1789–1796. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62662-X.
WANG Xu, JIAO Fen, QIN Wen-qing, et al. Sulfonated brown coal: A novel depressant for the selective flotation of scheelite from calcite [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, 602: 125006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125006.
FARASAT M, SHOJAEI S H R, GOLZAN M M, et al. Theoretical study of the potential energy surface and electric dipole moment of aniline [J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2016, 1108: 341–346. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.12.044.
GHOSE A K, CRIPPEN G M. Atomic physicochemical parameters for three-dimensional-structure-directed quantitative structure-activity relationships. 2. Modeling dispersive and hydrophobic interactions [J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1987, 27(1): 21–35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ci00053a005.
BROWN C J M, GOTSBACHER M P, HOLLAND J P, et al. Endo-hydroxamic acid monomers for the assembly of a suite of non-native dimeric macrocyclic siderophores using metal-templated synthesis [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2019, 58(20): 13591–13603. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b00878.
CORDEIRO R, KACHROO M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of anti-tubercular activity of Schiff bases of 2-Amino thiazoles [J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2020, 30(24): 127655. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127655.
FU Jun-hao, HAN Hai-sheng, WEI Zhao, et al. Selective separation of scheelite from calcite using tartaric acid and Pb-BHA complexes [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 622: 126657. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126657.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Projects(2020GDASYL-20200302009, 2020GDASYL-20200302004, 2019GDASYL-0501007) supported by Guandong Academy of Sciences, China; Project(2020YFC1909202) supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of China
Contributors
ZHAO Gang and LI Fang-xu provided the concept and edited the draft of manuscript. ZHOU Xiao-tong conducted the literature review. FU Guang-qin and SHANG Xing-ke edited the draft of manuscript.
Conflict of interest
ZHAO Gang, ZHOU Xiao-tong, LI Fang-xu, FU Guang-qin and SHANG Xing-ke declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Zhou, Xt., Li, Fx. et al. Flotation performance of anisic hydroxamic acid as new collector for tungsten and tin minerals. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 3645–3655 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5182-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5182-7