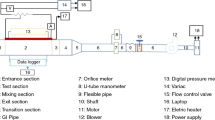
Abstract
This paper describes various aspects of the design methodology and heat transfer calculations for an elevated linear absorber. The absorber is a part of the linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator system, in which hot fluid is generated. The design of the absorber is an inverted trapezoidal air cavity with a glass cover enclosing a multi tube absorber. In a trapezoidal cavity absorber, a set of linear multi tube absorber with plate (named as “plane surface”) and without plate (named as “tube surface”) underneath are considered. An analytical simulation is done for different gaps between the tubes and for different depths of the cavity. A better design of the absorber is found out to maximize the heat transfer rate supplied to the absorber tube fluid. Also, the experimentally obtained overall heat loss coefficients are compared with the analytical values for the considered arrangements of absorber set up and results are discussed in details.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ac :
-
Area of the transparent cover placed at the bottom [m2]
- Ap :
-
Absorber plate area [m2]
- Ar :
-
Absorber tubes surface area [m2]
- c:
-
Specific heat of water [kJ/kgK]
- De :
-
Distance between the absorber surface and transparent cover [mm]
- do :
-
Outer diameter of tubular absorber [m]
- di :
-
Inner diameter of tubular absorber [m]
- f:
-
Height of tubular absorber from the reflector frame [m]
- g:
-
gap between the absorber tubes [mm]
- h:
-
Heat loss coefficient from the absorber surface [W/m2-K]
- hco :
-
Convection heat loss coefficient from the bottom glass surface [W/m2-K]
- hcp :
-
Convection heat loss coefficient from the absorber surface [W/m2-K]
- hro :
-
Radiation heat loss coefficient from the bottom glass surface [W/m2-K]
- hrp :
-
Radiation heat loss coefficient from the absorber surface [W/m2-K]
- m:
-
mass flow rate of the fluid [kg/s]
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number
- Re:
-
Reynolds Number
- Ta :
-
Ambient temperature [°C]
- Tc :
-
Cover temperature [°C]
- Ti :
-
Fluid inlet temperature [°C)]
- To :
-
Fluid outlet temperature [°C]
- Tp :
-
Absorber plate temperature [°C]
- Ts :
-
Absorber surface temperature [°C]
- Ul :
-
Overall heat loss coefficient [W/m2 °K]
- W:
-
Width of the absorber plane [m]
- z:
-
constant used to find Nusselt number
- ɛc :
-
Emissivity of the cover
- ɛp :
-
Emissivity of the plate
- σ:
-
Stefan Boltzman constant
References
Harry, K., and Charles. J.R. 1983. Solar photovoltaics energy systems. Handbook of Energy Technology and Economics, New York: John Wiley.
Duffie, J.A., and Beckman. W.A. 1983. Solar Engineering of thermal process. New York: John Wiley.
Duran, J.C., and Nicolas. R.O. 1987. Comparative optical analysis of cylindrical parabolic solar concentrator. Applied Optics 26(3): 578–585.
CHEN Zhenqian, GU Mingwei, PENG Donghua, PENG Changai and WU Zhishen. 2010 A numerical study on heat transfer of high efficient solar flat plate collectors with energy storage, International Journal of Green Energy, 7(3): 326–336.
Mathur, S.S., Negi, B.S. and Kandpal. T.C. 1990. Geometrical designs and performance analysis of a linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator with flat horizontal absorber. International Journal of Energy Resources 14(1): 107–124.
Negi, B. S., Kandpal, T.C. and Mathur. S. S. 1990. Designs and performance characteristics of a linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator with a flat vertical absorber. Solar Wind Technology 7(4): 379–392.
Goswami, R. P., Negi, B.S. Sehgal, H.C. and Sootha. G. D. 1990. Optical design and concentration characteristics of a linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator with a triangular absorber. Solar Energy Materials 21(2,3): 237–251.
Negi, B. S., and Sehgal. H. K. 1991. Performance characteristics of spray pyrolysed selective cobalt oxide coated tubular absorber operated with a linear solar concentrator. International Journal of Energy Resources 15(9): 715–722.
Singh, P. L., Sarviya, R.M. and Bhagoria. J.L. 2010. Thermal performance of linear Fresnel reflecting solar concentrator with trapezoidal cavity absorbers. Applied Energy 87: 541–550.
Mills, D., and Morrison. G.L. 2000. Compact linear Fresnel reflector solar thermal power plants, Solar Energy 68(3): 263–283.
Dey, C.J. 2004. Heat transfer aspects of an elevated linear absorber. Solar Energy 76: 243–249.
Jance, M. J., Morrison, G.L. and Behnia. M. 2000. Natural convection and radiation within an enclosed inverted absorber cavity: preliminary experimental results, International renewable energy transforming business: proceedings of solar. Brisbane: ANZSES.
Reynolds, D. J., Jance, M. J. Behnai M. and Morrison. A. 2004. An experimental and computational study of the heat loss characteristics of a trapezoidal cavity absorber. Solar Energy 76: 229–234.
Manikumar, R., and Valan Arasu. A. 2012. Design and theoretical performance analysis of linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator with a tubular absorber. International journal of renewable energy and technology 3(3): 221–236.
Kalogirou, S. 2004. Solar thermal collectors and applications. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 30: 231–295.
Sukhatme, S.P., and Nayak. J.K. 2009. Solar energy principles of thermal collection and storage. New York: Tata McGraw-Hill Publication.
Singh, P. L., Sarviya, R.M. and Bhagoria. J.L. 2010. Heat loss study of trapezoidal cavity absorbers for linear solar concentration collector, Energy Conversion and Management 51: 329–337.
Kothandaraman, C.P., and Subramanyan, S. 2008. Heat and Mass Transfer Data Book. Delhi: New Age International Publishers.
Pye John, D. 2008. System modelling of the compact linear Fresnel reflector, PhD thesis. University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia.
Negi, B.S., Mathur S.S. and Kandpal. T.C. 1989. Optical and Thermal Performance Evaluation of a Linear Fresnel Reflector Solar Concentrator, Solar and Wind Technology 6(5): 589–593.
Facao Jorge, and Armando Oliveria. C. 2011. Numerical simulation of a trapezoidal cavity receiver for a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator. Renewable Energy 36: 90–96.
Manikumar, R., Valan Arasu A. and Jayaraj. S. 2013. Numerical simulation of a trapezoidal cavity absorber in the linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator system. International Journal of Green Energy http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ljge20, Article in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manikumar, R., Palanichamy, R. & Valan Arasu, A. Heat transfer analysis of an elevated linear absorber with trapezoidal cavity in the linear Fresnel reflector solar concentrator system. J. Therm. Sci. 24, 90–98 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-015-0760-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-015-0760-8