Abstract
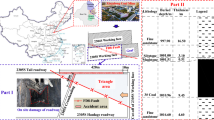
The angle α between the fault strike and the axial direction of the roadway produces different damage characteristics. In this paper, the research methodology includes theoretical analyses, numerical simulations and field experiments in the context of the Daqiang coal mine located in Shenyang, China. The stability control countermeasure of “pre-splitting cutting roof + NPR anchor cable” (PSCR-NPR) is simultaneously proposed. According to the different deformation characteristics of the roadway, the faults are innovatively classified into three types, with α of type I being 0°–30°, α of type II being 30°–60°, and α of type III being 60°–90°. The full-cycle stress evolution paths during mining roadway traverses across different types of faults are investigated by numerical simulation. Different pinch angles α lead to high stress concentration areas at different locations in the surrounding rock. The non-uniform stress field formed in the shallow surrounding rock is an important reason for the instability of the roadway. The pre-cracked cut top shifted the high stress region to the deep rock mass and formed a low stress region in the shallow rock mass. The high prestressing NPR anchor cable transforms the non-uniform stress field of the shallow surrounding rock into a uniform stress field. PSCR-NPR is applied in the fault-through roadway of Daqiang mine. The low stress area of the surrounding rock was enlarged by 3–7 times, and the cumulative convergence was reduced by 45%–50%. It provides a reference for the stability control of the deep fault-through mining roadway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data/Materials: Data supporting this research article are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
He MC (2021) Research progress of deep shaft construction mechanics. J Chin Coal Soc 46(3): 21. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.YT21.0124
He MC, Wang Q (2022) Excavation compensation method and key technology for surrounding rock control. Eng Geol 106784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106784
Dou L, He J, Cao A, et al. (2015) Rock burst prevention methods based on theory of dynamic and static combined load induced in coal mine. J. Chin Coal Soc 40(7): 1469–1476. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.1815
Li ZL, Dou LM, Cai W, et al. (2016) Mechanical analysis of static stress within fault-pillars based on a voussoir beam structure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49: 1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0754-6
Cai W, Dou L, Si G, et al. (2021) Fault-induced coal burst mechanism under mining-induced static and dynamic stresses. Engineering 7(5): 687–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.03.017
Cai W, Bai X, Si G, et al. (2020) A monitoring investigation into rock burst mechanism based on the coupled theory of static and dynamic stresses. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02237-6
Cai W, Dou L, Wang G, et al. (2019) Mechanism of fault reactivation and its induced coal burst caused by coal mining activities. J Min Saf Eng 36(6): 1193–1202. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2019.06.016
Pan YS, Wang K (2014) Pendulum-type waves theory on the mechanism of anomalously low friction between rock masses. Seismol Geo 36(3): 833–844. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.022
Dai L, Pan Y, Li Z, et al. (2021) Quantitative mechanism of roadway rockburst in deep extra-thick coal seams: Theory and case histories. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 111: 103861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2021.103861
Shan RL, Li Z, Wang C, et al. (2021) Research on the mechanism of asymmetric deformation and stability control of near-fault roadway under the influence of mining. Eng Fail Anal 127: 105492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105492
Bai J, Dou L, Makowski P, et al. (2021) Mechanical properties and damage behavior of rock-coal-rock combined samples under coupled static and dynamic loads. Geofluids 2021: 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3181697
Li ZL, He X, Dou L, et al. (2019) Investigating the mechanism and prevention of coal mine dynamic disasters by using dynamic cyclic loading tests. Safety Sci 115: 215–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.02.011
Li X, Li Q, Wang Y, et al. (2023) Experimental study on instability mechanism and critical intensity of rainfall of high-steep rock slopes under unsaturated conditions. Int J Min Sci Techno. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2023.07.009
Yin Q, Wu J, Zhu C, et al. (2021) The role of multiple heating and water cooling cycles on physical and mechanical responses of granite rocks. Geomech Geophys Geo 7, 69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00267-0
Yin Q, Liu R, Jing H, et al. (2019) Experimental study of nonlinear flow behaviors through fractured rock samples after high-temperature exposure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52: 2963–2983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-1741-0
Ren F, Zhu C, Yuan Z, et al. (2023) Recognition of shear and tension signals based on acoustic emission parameters and waveform using machine learning methods. Int J Rock Mech Min. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2023.105578
Zhao S (2016) Experiments on the characteristics of thrust fault activation influenced by mining operation. J Min Saf Eng 33(2): 354. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2016.02.026
Wang Q, Wang Y, He M, et al. (2022) Experimental study on the mechanism of pressure releasing control in deep coal mine roadways located in faulted zone. Geomech Geophys Geo 8(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00337-3
Zhou K, Dou L, Li X, et al. (2022) Coal burst and mining-induced stress evolution in a deep isolated main entry area - A case study. Eng Fail Anal 137: 106289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106289
Bai J, Dou L, Li J, et al. (2022) Mechanism of coal burst triggered by mining-induced fault slip under high-stress conditions: a case study. Front Earth Sci 10: 884974. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.884974
Zhang Z, Li S, Yu X, et al. (2020) Deformation mechanism and stability control of surrounding rock in deep roadway through the fault. J Hunan Univ Sci Technol 35(1):10–16. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13582/j.cnki.1672-9102.2020.01.002
Yang G, Li L, Liu H, et al. (2023) Experimental study on evolution law of dynamic characteristic parameters during the tunnel surrounding rock block collapse process. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 140: 105336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2023.105336
Dou L, Zhou K, Song S, et al. (2021) Occurrence mechanism, monitoring and prevention technology of rock burst in coal mines. J Eng Geo 29(4):917–932. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0337
Kan J, Dou L, Li X, et al. (2022) Investigating the destressing mechanism of roof deep-hole blasting for mitigating rock bursts in underground coal mines. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 13: 2508–2534. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2022.2122594
Lu A, Dou L, Bai J, et al. (2021) Mechanism of hard-roof rock burst control by the deep-hole blasting: numerical study based on particle flow. Shock Vib 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9527956
Pan Y, Qi Q, Wang A, et al. (2020) Theory and technology of three levels support in bump-prone roadway. J Chin Coal Soc 45(5):1585–1594. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.DY20.0261
Xu X, He M, Gao Y (2021) Study on Mining Pressure Law and Pressure Relief Control under Influence of Key Layer. Mining Metall Explor 38: 1985–1996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-021-00465-0
Tang S, Huang R, Wang S, et al. (2017) Study of the fracture process in heterogeneous materials around boreholes filled with expansion cement. Int J Solids Struct 112: 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.03.002
Tang S, Zhang H, Tang C, et al. (2015) Numerical model for the cracking behavior of heterogeneous brittle solids subjected to thermal shock. Int J Solids Struct 80: 520–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.10.012
Tang S, Wang J, Chen P (2020) Theoretical and numerical studies of cryogenic fracturing induced by thermal shock for reservoir stimulation. Int J Rock Mech Min 125: 104160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104160
He M, Gao Y, Gai Q, et al. (2023) Mechanical principle and mining methods of automagical entry formation without coal pillars. Coal Sci Technol 51(1): 19–30. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2022-1850
Zhang X, Hu J, Xue H, et al. (2020) Innovative approach based on roof cutting by energy-gathering blasting for protecting roadways in coal mines. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 99: 103387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103387
Zhang X, He M, Yang J, et al. (2020) an innovative non-pillar coal-mining technology with automatically formed entry: a case study. Engineering 6(11): 1315–1329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.01.014
Zhang X, Pak R, Gao Y, et al. (2020) Field experiment on directional roof presplitting for pressure relief of retained roadways. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 134: 104436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104436
Gao Y, Wang J, Gao H, et al. (2019) Mine pressure distribution and surrounding rock control of gob-side entry formed by roof cutting and pressure release under the influence of faults. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 38: 2182–2193. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0617
He M, Ren S, Guo L, et al. (2022) Experimental study on influence of host rock strength on shear performance of Micro-NPR steel bolted rock joints. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 159–105236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2022.105236
Sun X, Li G, Zhao C, et al. (2019) Investigation of Deep Mine Shaft Stability in Alternating Hard and Soft Rock Strata Using Three-Dimensional Numerical Modeling. Processes 7: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010002
Sun X, Zhao C, Tao Z, et al. (2021) Failure mechanism and control technology of large deformation for Muzhailing Tunnel in stratified rock masses. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80: 4731–4750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02222-5
Sun X, Zhang B, Li G, et al. (2019) Application of Constant Resistance and Large Deformation Anchor Cable in Soft Rock Highway Tunnel. Adv Ci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4347302
Yang G, Yang X, Huang R, et al. (2023) Failure mechanism and bulking characteristic of goaf roof in no-pillar mining by roof cutting technology. Eng Fail Anal 150: 107320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107320
Ma X, He M, Hu B, et al. (2023) Study on key parameter design and adaptability technology of the 110 Mining method for the Yuwang NO.1 Coal Mine in the Diandong mining area. Minerals 13, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020176
Wang H, Wang J, Elmo D, et al. (2023) Ground response mechanism of entries and control methods induced by hard roof in longwall top coal caving panel. Eng Fail Anal 144: 106940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106940
Li Z, Wang C, Shan R, et al. (2021) Study on the influence of the fault dip angle on the stress evolution and slip risk of normal faults in mining. Bull Eng Geol Environ. 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02149-x
Wang P, Jiang L, Jiang J, et al. (2018) Strata behavior sand rock burst-inducing mechanism under the coupling effect of a hard, thick stratum and a normal fault. Int J Geomech 18 (2): 04017135. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001044
Wang H, Jiang Y, Zhao Y, et al. (2013) Numerical investigation of the dynamic mechanical state of a coal pillar during longwall mining panel extraction. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46(5): 1211–1221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0337-8
Cheng Y, Wang J, Xie G, et al (2010) Three-dimensional analysis of coal barrier pillars in tailgate area adjacent to the fully mechanized top caving mining face. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(8): 1372–1383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.08.008
Jiang Y, Wang H, Xue S, et al. (2012) Assessment and mitigation of coal bump risk during extraction of an island longwall panel. Int J Coal Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2012.02.003
Sun X, Wang J, Zhang Y, et al. (2023) Stability control measures for roof cutting and NPR supporting of mining roadways in fault areas of kilometre-deep coal mine. J Mt Sci 20, 3051–3065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8152-0
Zhang Y, Xu H, Song P, et al. (2020) Stress evolution law of surrounding rock with gob-side entry retaining by roof cutting and pressure release in composite roof. Adv Mater Sci Eng (5):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1961680
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52174096, 52304110), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2022YJSSB03), and the Scientific and Technological Projects of Henan Province (232102320238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SUN Xiaoming, HE Manchao, GUO Zhibiao: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition; WANG Jian: data curation, investigation, formal analysis, writing-original draft, writing-review; MIAO Chengyu, ZHANG Yong, ZHAO Wenchao, JIANG Ming, LI Zhihu: data curation, formal analysis, writing-review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Wang, J., Zhao, W. et al. Instability mechanism of mining roadway passing through fault at different angles in kilometre-deep mine and control measures of roof cutting and NPR cables. J. Mt. Sci. 21, 236–251 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8235-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8235-y