Abstract
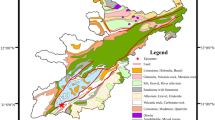
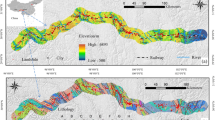
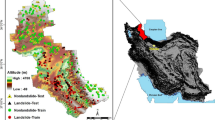
With its high mountains, deep valleys, and complex geological formations, the Jiuzhaigou County has the typical characteristics of a disaster-prone mountainous region in southwestern China. On August 8, 2017, a strong Ms 7.0 earthquake occurred in this region, causing some of the mountains in the area to become loose and cracked. Therefore, a survey and evaluation of landslides in this area can help to reveal hazards and take effective measures for subsequent disaster management. However, different evaluation models can yield different spatial distributions of landslide susceptibility, and thus, selecting the appropriate model and performing the optimal combination of parameters is the most effective way to improve susceptibility evaluation. In order to construct an evaluation indicator system suitable for Jiuzhaigou County, we extracted 12 factors affecting the occurrence of landslides, including slope, elevation and slope surface, and made samples. At the core of the transformer model is a self-attentive mechanism that enables any two of the features to be interlinked, after which feature extraction is performed via a forward propagation network (FFN). We exploited its coding structure to transform it into a deep learning model that is more suitable for landslide susceptibility evaluation. The results show that the transformer model has the highest accuracy (86.89%), followed by the random forest and support vector machine models (84.47% and 82.52%, respectively), and the logistic regression model achieves the lowest accuracy (79.61%). Accordingly, this deep learning model provides a new tool to achieve more accurate zonation of landslide susceptibility in Jiuzhaigou County.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Alhaija H, Mustikovela SK, Mescheder L, et al. (2018) Augmented Reality Meets Computer Vision: Efficient Data Generation for Urban Driving Scenes. Int J Comput Vis 126:961–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-018-1070-x
Ahmad F, Abbasi A, Li J, et al. (2020) A Deep Learning Architecture for Psychometric Natural Language Processing. ACM Trans Inf Syst 38:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1145/3365211
Bae HS, Lee HJ, Lee SG (2016) Voice recognition based on adaptive MFCC and deep learning. 2016 IEEE 11th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA). pp 1542–1546. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1708.01566
Bai S-B, Wang J, Lü GN, et al. (2010) GIS-based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping of the Zhongxian segment in the Three Gorges area, China. Geomorphology 115:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.09.025
Bortoloti FD, Castro Junior RM, Araújo LC, De Morais MGB (2015) Preliminary landslide susceptibility zonation using GIS-based fuzzy logic in Vitória, Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 74: 2125–2141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4200-6
Brückl EP (2001) Cause-effect models of large landslides. Nat Hazards 23:291–314. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011160810423
Catani F, Segoni S, Falorni G (2010) An empirical geomorphology-based approach to the spatial prediction of soil thickness at catchment scale. Water Resour Res 46 (5). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007450
Chen C-Y, Yu F-C (2011) Morphometric analysis of debris flows and their source areas using GIS. Geomorphology 129:387–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.03.002
Chen T, Zhu L, Niu R, et al. (2020) Mapping landslide susceptibility at the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, using gradient boosting decision tree, random forest and information value models. J Mt Sci 17:670–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5839-3
Chen W, Peng J, Hong H, et al. (2018) Landslide susceptibility modelling using GIS-based machine learning techniques for Chongren County, Jiangxi Province, China. Sci Total Environ 626:1121–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.124
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994018
Crosta G, Frattini P (2008) Rainfall — induced landslides and debris flows. Hydrol Process 22:473–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6885
Crosta GB (2001) Failure and flow development of a complex slide: the 1993 Sesa landslide. Eng Geol 59:173–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00073-9
Das I, Sahoo S, van Westen C, et al. (2010) Landslide susceptibility assessment using logistic regression and its comparison with a rock mass classification system, along a road section in the northern Himalayas (India). Geomorphology 114:627–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.09.023
De Guidi G, Scudero S, Dewez T, Goswami R (2013) Landslide susceptibility assessment in the Peloritani Mts.(Sicily, Italy) and clues for tectonic control of relief processes. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13: 949–963. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-949-2013
Devkota KC, Regmi AD, Pourghasemi HR, et al. (2013) Landslide susceptibility mapping using certainty factor, index of entropy and logistic regression models in GIS and their comparison at Mugling-Narayanghat road section in Nepal Himalaya. Nat Hazards 65:135–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0347-6
Dou J, Yunus AP, Merghadi A, et al. (2020) Different sampling strategies for predicting landslide susceptibilities are deemed less consequential with deep learning. Sci Total Environ 720:137320 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137320
Du J, Glade T, Woldai T, et al. (2020) Landslide susceptibility assessment based on an incomplete landslide inventory in the Jilong Valley, Tibet, Chinese Himalayas. Eng Geol 270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105572
Fan X, Scaringi G, Xu Q, et al. (2018) Coseismic landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake (Sichuan, China): factors controlling their spatial distribution and implications for the seismogenic blind fault identification. Landslides 15:967–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0960-x
Feby B, Achu AL, Jimnisha K, et al. (2020) Landslide susceptibility modelling using integrated evidential belief function based logistic regression method: A study from Southern Western Ghats, India. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 20:100411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2020.100411
Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y (2011) Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In: Proceedings of the fourteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, pp 315–323.
Hakim WL, Rezaie F, Nur AS, et al. (2022) Convolutional neural network (CNN) with metaheuristic optimization algorithms for landslide susceptibility mapping in Icheon, South Korea. J Environ Manage 305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114367
Hong H, Chen W, Xu C, et al. (2017) Rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility assessment at the Chongren area (China) using frequency ratio, certainty factor, and index of entropy. Geocarto Int. 32:139–154. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2015.1130086
Hong H, Panahi M, Shirzadi A, et al. (2018) Flood susceptibility assessment in Hengfeng area coupling adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system with genetic algorithm and differential evolution. Sci Total Environ 621:1124–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.114
Hussin HY, Zumpano V, Reichenbach P, et al. (2016) Different landslide sampling strategies in a grid-based bi-variate statistical susceptibility model. Geomorphology 253:508–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.10.030
Kavzoglu T, Kutlug Sahin E, Colkesen I (2015) An assessment of multivariate and bivariate approaches in landslide susceptibility mapping: a case study of Duzkoy district. Nat Hazards 76:471–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1506-8
Kavzoglu T, Sahin EK, Colkesen I (2014) Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis, support vector machines, and logistic regression. Landslides 11:425–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0391-7
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Krkač M, Bernat Gazibara S, Arbanas Ž, et al. (2020) A comparative study of random forests and multiple linear regression in the prediction of landslide velocity. Landslides 17:2515–2531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01476-6
Kumar D, Thakur M, Dubey CS, Shukla DP (2017) Landslide susceptibility mapping & prediction using Support Vector Machine for Mandakini River Basin, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Geomorphology 295:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.06.013
Lee C-F, Huang W-K, Chang Y-L, et al. (2018) Regional landslide susceptibility assessment using multi-stage remote sensing data along the coastal range highway in northeastern Taiwan. Geomorphology 300:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.10.019
Li B, Yin YP, Gao Y (2020) Critical issues in rock avalanches in the karst mountain areas of southwest China. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 47:5–13. https://doi.org/10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003060
Li W, Fang Z, Wang Y (2021) Stacking ensemble of deep learning methods for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36, 2207–2228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02032-x
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, et al. (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005
Nam K, Wang F (2020) An extreme rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility assessment using autoencoder combined with random forest in Shimane Prefecture, Japan. Geoenviron Disasters 7(6). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-020-0143-7
Netrapalli P (2019) Stochastic gradient descent and its variants in machine learning. J Indian Inst Sci 99:201–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41745-019-0098-4
Ngo PTT, Panahi M, Khosravi K, et al. (2021) Evaluation of deep learning algorithms for national scale landslide susceptibility mapping of Iran. Geosci Front 12:505–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.06.013
Nhu V-H, Hoang N-D, Nguyen H, et al. (2020) Effectiveness assessment of Keras based deep learning with different robust optimization algorithms for shallow landslide susceptibility mapping at tropical area. CATENA 188:104458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104458
Noda K, Yamaguchi Y, Nakadai K, et al. (2015) Audio-visual speech recognition using deep learning. Appl Intell 42:722–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-014-0629-7
Paudel U, Oguchi T, Hayakawa Y (2016) Multi-Resolution Landslide Susceptibility Analysis Using a DEM and Random Forest. Int J Geoences 07:726–743. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2016.75056
Peethambaran B, Anbalagan R, Kanungo DP, et al. (2020) A comparative evaluation of supervised machine learning algorithms for township level landslide susceptibility zonation in parts of Indian Himalayas. CATENA 195:104751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104751
Pham BT, Pradhan B, Tien Bui D, et al. (2016) A comparative study of different machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility assessment: A case study of Uttarakhand area (India). Environ Model Softw 84:240–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.07.005
Pradhan B (2011) Use of GIS-based fuzzy logic relations and its cross application to produce landslide susceptibility maps in three test areas in Malaysia. Environ Earth ences 63:329–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0705-1
Qi S, Xu Q, Lan H, et al. (2010) Spatial distribution analysis of landslides triggered by 2008.5. 12 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. Eng Geol 116:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.07.011
Rae JW, Potapenko A, Jayakumar SM, Lillicrap TP (2019) Compressive transformers for long-range sequence modelling. arXiv Prepr arXiv191105507. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1911.05507
Ramesh V, Anbazhagan S (2015) Landslide susceptibility mapping along Kolli hills Ghat road section (India) using frequency ratio, relative effect and fuzzy logic models. Environ Earth Sci 73:8009–8021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3954-6
Rossi M, Guzzetti F, Reichenbach P, et al. (2010) Optimal landslide susceptibility zonation based on multiple forecasts. Geomorphology 114:129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.06.020
Rozos D, Pyrgiotis L, Skias S, Tsagaratos P (2008) An implementation of rock engineering system for ranking the instability potential of natural slopes in Greek territory. An application in Karditsa County. Landslides 5:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-008-0117-4
Sachdeva S, Bhatia T, Verma AK (2020) A novel voting ensemble model for spatial prediction of landslides using GIS. Int J Remote Sens 41:929–952. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2019.1654141
Sakkas G, Misailidis I, Sakellariou N, et al. (2016) Modeling landslide susceptibility in Greece: a weighted linear combination approach using analytic hierarchical process, validated with spatial and statistical analysis. Nat Hazards 84:1873–1904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2523-6
Scardapane S, Van Vaerenbergh S, Totaro S, Uncini A (2019) Kafnets: Kernel-based non-parametric activation functions for neural networks. Neural Networks 110:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.11.002
Schuster RL, Fleming RW (1986) Economic losses and fatalities due to landslides. Bull Assoc Eng Geol 23:11–28. https://doi.org/10.2113/gseegeosci.xxiii.1.11
Su C, Wang L, Wang X, et al. (2015) Mapping of rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility in Wencheng, China, using support vector machine. Nat Hazards 76:1759–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1562-0
Taalab K, Cheng T, Zhang Y (2018) Mapping landslide susceptibility and types using Random Forest. Big Earth Data 2:159–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/20964471.2018.1472392
Thanh LN, Smedt F De (2012) Application of an analytical hierarchical process approach for landslide susceptibility mapping in A Luoi district, Thua Thien Hue Province, Vietnam. Environ Earth Sci 66:1739–1752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1397-x
Tien Bui D, Tuan TA, Klempe H, et al. (2016) Spatial prediction models for shallow landslide hazards: a comparative assessment of the efficacy of support vector machines, artificial neural networks, kernel logistic regression, and logistic model tree. Landslides 13:361–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0557-6
Trigila A, Iadanza C, Esposito C, Scarascia-Mugnozza G (2015) Comparison of Logistic Regression and Random Forests techniques for shallow landslide susceptibility assessment in Giampilieri (NE Sicily, Italy). Geomorphology 249:119–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.06.001
Van Den Eeckhaut M, Vanwalleghem T, Poesen J, et al. (2006) Prediction of landslide susceptibility using rare events logistic regression: A case-study in the Flemish Ardennes (Belgium). Geomorphology 76:392–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.12.003
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 5998–6008. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762
Wang LJ, Guo M, Sawada K, et al. (2016) A comparative study of landslide susceptibility maps using logistic regression, frequency ratio, decision tree, weights of evidence and artificial neural network. Geosci J 20:117–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-015-0026-1
Wang Q, Li W, Chen W, Bai H (2015) GIS-based assessment of landslide susceptibility using certainty factor and index of entropy models for the Qianyang County of Baoji city, China. J Earth Syst Sci 124:1399–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0624-3
Wang Y, Fang Z, Hong H (2019) Comparison of convolutional neural networks for landslide susceptibility mapping in Yanshan County, China. Sci Total Environ 666:975–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.263
Westen CJ Van, Castellanos E, Kuriakose SL (2008) Spatial data for landslide susceptibility, hazard, and vulnerability assessment: An overview. Eng Geol 102:112–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.010
Xu D, Zhang S, Zhang H, Mandic DP (2021) Convergence of the rmsprop deep learning method with penalty for nonconvex optimization. Neural Networks 139:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2021.02.011
Youssef AM, Al-Kathery M, Pradhan B (2015) Landslide susceptibility mapping at Al-Hasher area, Jizan (Saudi Arabia) using GIS-based frequency ratio and index of entropy models. Geosci J 19:113–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-014-0032-8
Youssef AM, Pourghasemi HR, Pourtaghi ZS, Al-Katheeri MM (2016) Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest, boosted regression tree, classification and regression tree, and general linear models and comparison of their performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Landslides 13:839–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0614-1
Youssef AM, Pradhan B, Dikshit A, et al. (2022) Landslide susceptibility mapping using CNN-1D and 2D deep learning algorithms: comparison of their performance at Asir Region, KSA. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02657-4
Yue X, Wu S, Yin Y, et al. (2018) Risk Identification of Seismic Landslides by Joint Newmark and RockFall Analyst Models: A Case Study of Roads Affected by the Jiuzhaigou Earthquake. Int J Disaster Risk Sci 9:392–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13753-018-0182-9
Zêzere JL, Pereira S, Melo R, et al. (2017) Mapping landslide susceptibility using data-driven methods. Sci Total Environ 589:250–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.188
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 41771444) and Science and Technology Plan Project of Sichuan Province (Grants No. 2021YJ0369). We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Yang, Rh., Wang, X. et al. Evaluation of deep learning algorithms for landslide susceptibility mapping in an alpine-gorge area: a case study in Jiuzhaigou County. J. Mt. Sci. 20, 484–500 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7326-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7326-5