Abstract
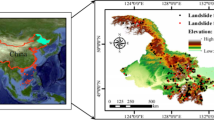
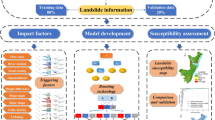
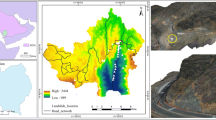
This work was to generate landslide susceptibility maps for the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) area, China by using different machine learning models. Three advanced machine learning methods, namely, gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT), random forest (RF) and information value (InV) models, were used, and the performances were assessed and compared. In total, 202 landslides were mapped by using a series of field surveys, aerial photographs, and reviews of historical and bibliographical data. Nine causative factors were then considered in landslide susceptibility map generation by using the GBDT, RF and InV models. All of the maps of the causative factors were resampled to a resolution of 28.5 m. Of the 486289 pixels in the area, 28526 pixels were landslide pixels, and 457763 pixels were non-landslide pixels. Finally, landslide susceptibility maps were generated by using the three machine learning models, and their performances were assessed through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, the sensitivity, specificity, overall accuracy (OA), and kappa coefficient (KAPPA). The results showed that the GBDT, RF and InV models in overall produced reasonable accurate landslide susceptibility maps. Among these three methods, the GBDT method outperforms the other two machine learning methods, which can provide strong technical support for producing landslide susceptibility maps in TGR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed B, Dewan A (2017) Application of bivariate and multivariate statistical techniques in landslide susceptibility modeling in Chittagong City Corporation, Bangladesh. Remote Sensing 9(4): 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040304
Althuwaynee F, Pradhan B, Lee S (2012) Application of an evidential belief function model in landslide susceptibility mapping. Computers & Geosciences 44(44): 120–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.03.003
Bai SB, Wang J, Lu GN, et al. (2010) GIS-based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping of the Zhongxian segment in the Three Gorges Area, China. Geomorphology 115: 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.09.025
Bi RN, Schleier M, Rohn J, et al. (2014) Landslide susceptibility analysis based on ArcGIS and Artificial Neural Network for a large catchment in Three Gorges region, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 72(6): 1925–1938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3100-5
Brabb E (1991) The world landslide problem. Episodes 14:52–61
Breiman L, Friedman H, Olshen A (1984) Classification and regression trees. Chapman & Hall, New York.
Bui D, Tuan T, Klempe H (2016) Spatial prediction models for shallow landslide hazards: a comparative assessment of the efficacy of support vector machines, artificial neural networks, kernel logistic regression, and logistic model tree. Landslides 13(2): 361–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0557-6
Chen T, Niu R, Du B (2015) Landslide spatial susceptibility mapping by using GIS and Remote Sensing techniques: a case study in Zigui County, the Three Georges reservoir, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 73(9): 5571–5583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3811-7
Chen T, Niu R, Jia X (2016) A comparison of information value and logistic regression models in landslide susceptibility mapping by using GIS. Environmental Earth Sciences 75(10): 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5317-y
Chen W, Peng J, Hong H (2018) Landslide susceptibility modelling using GIS-based machine learning techniques for Chongren County, Jiangxi Province, China. Science of The Total Environment 626: 1121–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.124
Chen W, Pourghasemi H, Kornejady A (2017a) Landslide spatial modeling: introducing new ensembles of ANN, MaxEnt, and SVM machine learning techniques. Geoderma, 305: 314–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.06.020
Chen W, Pourghasemi H, Naghibi S (2017b) A comparative study of landslide susceptibility maps produced using support vector machine with different kernel functions and entropy data mining models in China. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 77(2):647–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1010-y
Chung C, Fabbri A (2003) Validation of spatial prediction models for landslide hazard mapping. Natural Hazards 30(3): 451–472. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000007172.62651.2b
Devkota K, Regmi A, Pourghasemi H (2013) Landslide susceptibility mapping using certainty factor, index of entropy and logistic regression models in GIS and their comparison at Mugling–Narayanghat road section in Nepal Himalaya. Natural Hazards 5(1): 135–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0347-6
Dou J, Yamagishi H, Pourghasemi HR, et al. (2015) An integrated artificial neural network model for the landslide susceptibility assessment of Osado Island, Japan. Natural Hazards 78(3): 1749–1776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1799-2
Dou J, Yunus AP, Bui DT, et al. (2019) Assessment of advanced random forest and decision tree algorithms for modeling rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility in the Izu-Oshima Volcanic Island, Japan. Science of the Total Environment 662: 332–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.221
Elith J, Leathwick J, Hastie T (2008) A working guide to boosted regression trees. Journal of Animal Ecology 77: 802–813. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01390.x
Felicísimo Á, Cuartero A, Remondo J (2013) Mapping landslide susceptibility with logistic regression, multiple adaptive regression splines, classification and regression trees, and maximum entropy methods: a comparative study. Landslides 10(2): 175–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0320-1
Friedman J (2002) Stochastic gradient boosting. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis 38: 367–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-9473(01)00065-2
Guzzetti F, Reichenbach P, Ardizzone F (2006) Estimating the quality of landslide susceptibility models. Geomorphology 81(1): 166–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.04.007
He K, Li X, Yan X (2008) The landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China and the effects of water storage and rain on their stability. Environmental Geology 55: 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0964-7
Hong H, Ilia I, Tsangaratos P (2017) A hybrid fuzzy weight of evidence method in landslide susceptibility analysis on the Wuyuan area, China. Geomorphology 290: 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.04.002
Hong H, Liu J, Bui D (2018) Landslide susceptibility mapping using J48 Decision Tree with AdaBoost, Bagging and Rotation Forest ensembles in the Guangchang area (China). Catena 163: 399–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.01.005
Hung L, Van N, Duc D (2016) Landslide susceptibility mapping by combining the analytical hierarchy process and weighted linear combination methods: a case study in the upper Lo River catchment (Vietnam). Landslides 13(5): 1285–1301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0657-3
Kausar N, Majid A (2016) Randomforest-based scheme using feature and decision levels information for multi-focus image fusion. Pattern Analysis and Applications 19(1): 221–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-015-0448-4
Lee J, Sameen M, Pradhan B (2018) Modeling landslide susceptibility in data-scarce environments using optimized data mining and statistical methods. Geomorphology 303: 284–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.12.007
Lee M, Park I, Lee S (2015) Forecasting and validation of landslide susceptibility using an integration of frequency ratio and neuro-fuzzy models: a case study of Seorak mountain area in Korea. Environmental Earth Sciences 74(1): 413–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4048-9
Liu C, Liu Y, Wen M (2009) Geo-Hazard Initiation and Assessment in the Three Gorges Reservoir. In Landslide Disaster Mitigation in Three Gorges Reservoir, China;Wang, F.W., Li, T.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 3–40
Martha T, Kerle N, Jetten V (2010) Characterising spectral, spatial and morphometric properties of landslides for semi-automatic detection using object-oriented methods. Geomorphology 116(1-2): 24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.10.004
Neuhauser B, Damm B, Terhorst B (2012) GIS-based assessment of landslide susceptibility on the base of the Weights-of- Evidence model. Landslides 9(4): 511–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-011-0305-5
Pawluszek K, Borkowski A (2017) Impact of DEM-derived factors and analytical hierarchy process on landslide susceptibility mapping in the region of Roznów Lake, Poland. Natural Hazards 86(2): 919–952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2725-y
Peng L, Niu R, Huang B (2014) Landslide susceptibility mapping based on rough set theory and support vector machines: a case of the Three Gorges area, China. Geomorphology 204: 287–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.08.013
Pham BT, Prakash I, Dou J, et al. (2019) A novel hybrid approach of landslide susceptibility modelling using rotation forest ensemble and different base classifiers. Geocarto International 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1559885
Pradhan B, Lee S (2010) Delineation of landslide hazard areas on Penang Island, Malaysia, by using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network models. Environmental Earth Sciences 60(5): 1037–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0245-8
Sarkar S, Kanungo D, Patra A (2006) GIS Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping - A Case Study in Indian Himalaya in Disaster Mitigation of Debris Flows, Slope Failures and Landslides, Universal Academic Press, Tokyo, 617–624
Schapire R (2003) The boosting approach to machine learning: an overview. Nonlinear Estimation and Classification 171: 149–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-21579-2_9
Smith M, Goodchild M, Longley P (2014) Geospatial analysis–the comprehensive guide to principles, techniques and software tools. Webversion (Oct 2007). Trans GIS. 12(5): 645–647.
Tsangaratos P, Ilia I (2016) Landslide susceptibility mapping using a modified decision tree classifier in the Xanthi Perfection, Greece. Landslides 13(2): 305–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0565-6
Vasu N, Lee S (2016) A hybrid feature selection algorithm integrating an extreme learning machine for landslide susceptibility modeling of Mt. Woomyeon, South Korea. Geomorphology 263: 50–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.03.023
Wang Q, Wang Y, Niu R (2017) Integration of Information Theory, K-Means Cluster Analysis and the Logistic Regression Model for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in the Three Gorges Area, China. Remote Sensing 9(9): 938. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9090938
Wang Y, Fang Z, Hong H (2019) Comparison of convolutional neural networks for landslide susceptibility mapping in Yanshan County, China. Science of The Total Environment 666: 975–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.263
Wu S, Shi L, Wang R (2001) Zonation of the landslide hazards in the fore reservoir region of the Three Gorges Project on the Yangtze River. Engineering Geology 59: 51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00061-2
Wu X, Niu R, Ren F (2013) Landslide susceptibility mapping using rough sets and back-propagation neural networks in the Three Gorges, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 70(3): 1307–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2217-2
Xu K, Guo Q, Li Z (2015) Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on BPNN and GIS: a case of Guojiaba in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 29(7): 1111–1124. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2014.992436
Yalcin A (2008) GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping using analytical hierarchy process and bivariate statistics in Ardesen (Turkey): Comparisons of results and confirmations. Catena 72(1): 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2007.01.003
Yan T (1988) Recent advances of quantitative prognoses of landslide in China. In: Proceedings of the fifth international symposium on landslides, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2: 1263–1268.
Yin K, Yan T (1988) Statistical prediction models for slope instability of metamorphosed rocks. In: Proceedings of the fifth international symposium on landslides, Lausanne, Switzerland. 2: 1269–1272
Youssef A, Al-Kathery M, Pradhan B (2015) Landslide susceptibility mapping at Al-Hasher area, Jizan (Saudi Arabia) using GIS-based frequency ratio and index of entropy models. Geosciences Journal 19(1): 113–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-014-0032-8
Youssef A, Pourghasemi H, Pourtaghi Z (2016) Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest, boosted regression tree, classification and regression tree, and general linear models and comparison of their performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Landslides 13(5): 839–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0614-1
Yunus AP, Fan X, Tang X, et al. (2020) Decadal vegetation succession from MODIS reveals the spatio-temporal evolution of post-seismic landsliding after the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Remote Sensing of Environment 236: 111476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111476
Zêzere J, Pereira S, Melo R (2017) Mapping landslide susceptibility using data-driven methods. Science of The Total Environment 589: 250–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.188
Zhang G, Cai Y, Zheng Z (2016a) Integration of the Statistical Index Method and the Analytic Hierarchy Process technique for the assessment of landslide susceptibility in Huizhou, China. Catena 142: 233–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.03.028
Zhang KX, Wu XL, Niu RQ, et al. (2017) The assessment of landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest and decision tree methods in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 76(11): 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6731-5
Zhang M, Cao X, Peng L (2016b) Landslide susceptibility mapping based on global and local logistic regression models in Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 75(11): 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5764-5
Zhou C, Yin K, Cao Y (2018) Landslide susceptibility modeling applying machine learning methods: a case study from Longju in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Computers & Geosciences 112: 23–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.11.019
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61601418, 41602362, 61871259), in part by the Opening Foundation of Hunan Engineering and Research Center of Natural Resource Investigation and Monitoring (2020-5), in part by the Qilian Mountain National Park Research Center (Qinghai) (grant number: GKQ2019-01), and in part by the Geomatics Technology and Application Key Laboratory of Qinghai Province, Grant No. QHDX-2019-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Zhu, L., Niu, Rq. et al. Mapping landslide susceptibility at the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, using gradient boosting decision tree, random forest and information value models. J. Mt. Sci. 17, 670–685 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5839-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5839-3