Abstract
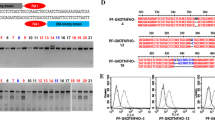
Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) is an immunoinhibitory receptor required to suppress inappropriate immune responses such as autoimmunity. Immune checkpoint antibodies that augment the PD-1 pathway lead to immune-related adverse events (irAEs), organ non-specific side effects due to autoimmune activation in humans. In this study, we generated a PD-1 mutant pig using electroporation-mediated introduction of the CRISPR/Cas9 system into porcine zygotes to evaluate the PD-1 gene deficiency phenotype. We optimized the efficient guide RNAs (gRNAs) targeting PD-1 in zygotes and transferred electroporated embryos with the optimized gRNAs and Cas9 into recipient gilts. One recipient gilt became pregnant and gave birth to two piglets. Sequencing analysis revealed that both piglets were biallelic mutants. At 18 mo of age, one pig showed non-purulent arthritis of the left elbow/knee joint and oligozoospermia, presumably related to PD-1 modification. Although this study has a limitation because of the small number of cases, our phenotypic analysis of PD-1 modification in pigs will provide significant insight into human medicine and PD-1-deficient pigs can be beneficial models for studying human irAEs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ansari MJ, Salama AD, Chitnis T, Smith RN, Yagita H, Akiba H, Yamazaki T, Azuma M, Iwai H, Khoury SJ, Auchincloss H Jr, Sayegh MH (2003) The programmed death-1 (PD-1) pathway regulates autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. J Exp Med 198:63–69
Brinkman EK, Chen T, Amendola M, van Steensel B (2014) Easy quantitative assessment of genome editing by sequence trace decomposition. Nucleic Acids Res 42:e168
Buttenschon J, Svensmark B, Kyrval J (1995) Non-purulent arthritis in Danish slaughter pigs. I. A study of field cases. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A 42:633–641
Calabrese LH, Calabrese C, Cappelli LC (2018) Rheumatic immune-related adverse events from cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol 14:569–579
Cradick TJ, Qiu P, Lee CM, Fine EJ, Bao G (2014) COSMID: a web-based tool for identifying and validating CRISPR/Cas off-target sites. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 3:e214
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H, Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, Lennon VA, Celis E, Chen L (2002) Tumor-associated B7–H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med 8:793–800
Ganbaatar O, Konnai S, Okagawa T, Nojima Y, Maekawa N, Ichikawa Y, Kobayashi A, Shibahara T, Yanagawa Y, Higuchi H, Kato Y, Suzuki Y, Murata S, Ohashi K (2021) Programmed death-ligand 1 expression in swine chronic infections and enhancement of interleukin-2 production via programmed death-1/programmed death-ligand 1 blockade. Immun Inflamm Dis.
Ganbaatar O, Konnai S, Okagawa T, Nojima Y, Maekawa N, Minato E, Kobayashi A, Ando R, Sasaki N, Miyakoshi D, Ichii O, Kato Y, Suzuki Y, Murata S, Ohashi K (2020) PD-L1 expression in equine malignant melanoma and functional effects of PD-L1 blockade. PLoS ONE 15:e0234218
Goto S, Konnai S, Okagawa T, Nishimori A, Maekawa N, Gondaira S, Higuchi H, Koiwa M, Tajima M, Kohara J, Ogasawara S, Kato Y, Suzuki Y, Murata S, Ohashi K (2017) Increase of cells expressing PD-1 and PD-L1 and enhancement of IFN-gamma production via PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in bovine mycoplasmosis. Immun Inflamm Dis 5:355–363
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu WJ, Kefford R, Wolchok JD, Hersey P, Joseph RW, Weber JS, Dronca R, Gangadhar TC, Patnaik A, Zarour H, Joshua AM, Gergich K, Elassaiss-Schaap J, Algazi A, Mateus C, Boasberg P, Tumeh PC, Chmielowski B, Ebbinghaus SW, Li XN, Kang SP, Ribas A (2013) Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N Engl J Med 369:134–144
Henick BS, Herbst RS, Goldberg SB (2014) The PD-1 pathway as a therapeutic target to overcome immune escape mechanisms in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 18:1407–1420
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, Honjo T (1992) Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J 11:3887–3895
Kroner A, Mehling M, Hemmer B, Rieckmann P, Toyka KV, Maurer M, Wiendl H (2005) A PD-1 polymorphism is associated with disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 58:50–57
Kula A, Dawidowicz M, Kiczmer P, Prawdzic Senkowska A, Swietochowska E (2020) The role of genetic polymorphism within PD-L1 gene in cancer. Review Exp Mol Pathol 116:104494
Li H, Xu J, Bai Y, Zhang S, Cheng M, Jin J (2021) Nephrotoxicity in patients with solid tumors treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Invest New Drugs 39:860–870
Lippross S, Moeller B, Haas H, Tohidnezhad M, Steubesand N, Wruck CJ, Kurz B, Seekamp A, Pufe T, Varoga D (2011) Intraarticular injection of platelet-rich plasma reduces inflammation in a pig model of rheumatoid arthritis of the knee joint. Arthritis Rheum 63:3344–3353
Naidoo J, Page DB, Li BT, Connell LC, Schindler K, Lacouture ME, Postow MA, Wolchok JD (2015) Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Ann Oncol 26:2375–2391
Naito Y, Hino K, Bono H, Ui-Tei K (2015) CRISPRdirect: software for designing CRISPR/Cas guide RNA with reduced off-target sites. Bioinformatics 31:1120–1123
Naujokat H, Sengebusch A, Loger K, Moller B, Acil Y, Wiltfang J (2021) Therapy of antigen-induced arthritis of the temporomandibular joint via platelet-rich plasma injections in domestic pigs. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 49:726–731
Naujokat H, Sengebusch A, Moller B, Wieker H, Acil Y, Wiltfang J (2019) Antigen-induced arthritis of the temporomandibular joint via repeated injections of bovine serum albumin in domestic pigs. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 47:932–939
Nguyen TV, Tanihara F, Do LTK, Sato Y, Taniguchi M, Takagi M, Van Nguyen T, Otoi T (2017) Chlorogenic acid supplementation during in vitro maturation improves maturation, fertilization and developmental competence of porcine oocytes. Reprod Domest Anim 52:969–975
Niemann H, Kues WA (2003) Application of transgenesis in livestock for agriculture and biomedicine. Anim Reprod Sci 79:291–317
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N, Honjo T (1999) Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 11:141–151
Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Nakatani K, Hara M, Matsumori A, Sasayama S, Mizoguchi A, Hiai H, Minato N, Honjo T (2001) Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice. Science 291:319–322
Okazaki T, Honjo T (2007) PD-1 and PD-1 ligands: from discovery to clinical application. Int Immunol 19:813–824
Okazaki T, Iwai Y, Honjo T (2002) New regulatory co-receptors: inducible co-stimulator and PD-1. Curr Opin Immunol 14:779–782
Okazaki T, Maeda A, Nishimura H, Kurosaki T, Honjo T (2001) PD-1 immunoreceptor inhibits B cell receptor-mediated signaling by recruiting src homology 2-domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2 to phosphotyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:13866–13871
Onishi A, Iwamoto M, Akita T, Mikawa S, Takeda K, Awata T, Hanada H, Perry AC (2000) Pig cloning by microinjection of fetal fibroblast nuclei. Science 289:1188–1190
Peng JM, Tian ZJ, Liu HG, An TQ, Zhou YJ, Wang Y, Li DY, Chen JZ, Yang YQ, Tong GZ (2010) Cloning and identification of porcine programmed death 1. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 136:157–162
Salmaninejad A, Khoramshahi V, Azani A, Soltaninejad E, Aslani S, Zamani MR, Zal M, Nesaei A, Hosseini SM (2018) PD-1 and cancer: molecular mechanisms and polymorphisms. Immunogenetics 70:73–86
Sardar S, Andersson A (2016) Old and new therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis: in vivo models and drug development. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 38:2–13
Shin JH, Park HB, Choi K (2016) Enhanced anti-tumor reactivity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing PD-1 decoy. Immune Netw 16:134–139
Stamatouli AM, Quandt Z, Perdigoto AL, Clark PL, Kluger H, Weiss SA, Gettinger S, Sznol M, Young A, Rushakoff R, Lee J, Bluestone JA, Anderson M, Herold KC (2018) Collateral damage: insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes 67:1471–1480
Tanihara F, Hirata M, Namula Z, Do LTK, Yoshimura N, Lin Q, Takebayashi K, Sakuma T, Yamamoto T, Otoi T (2023) Pigs with an INS point mutation derived from zygotes electroporated with CRISPR/Cas9 and ssODN. Front Cell Dev Biol 11:884340
Tanihara F, Hirata M, Nguyen NT, Le QA, Hirano T, Takemoto T, Nakai M, Fuchimoto DI, Otoi T (2018) Generation of a TP53-modified porcine cancer model by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene modification in porcine zygotes via electroporation. PLoS ONE 13:e0206360
Tanihara F, Hirata M, Nguyen NT, Sawamoto O, Kikuchi T, Doi M, Otoi T (2020a) Efficient generation of GGTA1-deficient pigs by electroporation of the CRISPR/Cas9 system into in vitro-fertilized zygotes. BMC Biotechnol 20:40
Tanihara F, Hirata M, Nguyen NT, Sawamoto O, Kikuchi T, Otoi T (2021) One-step generation of multiple gene-edited pigs by electroporation of the CRISPR/Cas9 system into zygotes to reduce xenoantigen biosynthesis. Int J Mol Sci 22
Tanihara F, Hirata M, Thi Nguyen N, Le Anh Q, Hirano T, Otoi T (2020b) Generation of viable PDX1 gene-edited founder pigs as providers of nonmosaics. Mol Reprod Dev 87:471–481
Tanihara F, Takemoto T, Kitagawa E, Rao S, Do LTK, Onishi A, Yamashita Y, Kosugi C, Suzuki H, Sembon S (2016) Somatic cell reprogramming-free generation of genetically modified pigs. Sci Adv 2:e1600803
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Atkins MB, Leming PD, Spigel DR, Antonia SJ, Horn L, Drake CG, Pardoll DM, Chen L, Sharfman WH, Anders RA, Taube JM, McMiller TL, Xu H, Korman AJ, Jure-Kunkel M, Agrawal S, McDonald D, Kollia GD, Gupta A, Wigginton JM, Sznol M (2012) Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med 366:2443–2454
Topalian SL, Sznol M, McDermott DF, Kluger HM, Carvajal RD, Sharfman WH, Brahmer JR, Lawrence DP, Atkins MB, Powderly JD, Leming PD, Lipson EJ, Puzanov I, Smith DC, Taube JM, Wigginton JM, Kollia GD, Gupta A, Pardoll DM, Sosman JA, Hodi FS (2014) Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J Clin Oncol 32:1020–1030
Tucker CG, Dwyer AJ, Fife BT, Martinov T (2021) The role of programmed death-1 in type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 21:20
Wan X, Zinselmeyer BH, Zakharov PN, Vomund AN, Taniguchi R, Santambrogio L, Anderson MS, Lichti CF, Unanue ER (2018) Pancreatic islets communicate with lymphoid tissues via exocytosis of insulin peptides. Nature 560:107–111
Wang J, Yoshida T, Nakaki F, Hiai H, Okazaki T, Honjo T (2005) Establishment of NOD-Pdcd1-/- mice as an efficient animal model of type I diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:11823–11828
Weber JS, Kahler KC, Hauschild A (2012) Management of immune-related adverse events and kinetics of response with ipilimumab. J Clin Oncol 30:2691–2697
Yoneda S, Imagawa A, Hosokawa Y, Baden MY, Kimura T, Uno S, Fukui K, Goto K, Uemura M, Eguchi H, Iwahashi H, Kozawa J, Shimomura I (2019) T-lymphocyte infiltration to islets in the pancreas of a patient who developed type 1 diabetes after administration of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes Care 42:e116–e118
Yue F, Zhu YP, Zhang YF, Sun GP, Yang Y, Guo DG, Wang AG, Li BW, Yin M, Cheng AC, Wang MS, Wang XN (2014) Up-regulated expression of PD-1 and its ligands during acute Classical Swine Fever virus infection in swine. Res Vet Sci 97:251–256
Zamani MR, Asbagh FA, Massoud AH, Salmaninejad A, Massoud A, Rezaei N (2015) Association between a PD-1 gene polymorphism and antisperm antibody-related infertility in Iranian men. J Assist Reprod Genet 32:103–106
Zamani MR, Aslani S, Salmaninejad A, Javan MR, Rezaei N (2016) PD-1/PD-L and autoimmunity: A growing relationship. Cell Immunol 310:27–41
Acknowledgements
We thank the Nippon Food Packer, K. K. Shikoku (Tokushima, Japan), for supplying the pig ovaries. This study was supported in part by a grant from the Japan IDDM network and KAKENHI grant numbers JP18K12062 and JP19K16014 from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS). We acknowledge Tokushima University for providing financial support through the Research Clusters program of Tokushima University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.O. conceived the study and T-V.N. wrote the manuscript. T-V.N. performed most of the experiments. F.T. and T.O. designed the study, coordinated experiments, and reviewed the manuscript. M.H. performed the phenotype analysis. L.T.K.D., Q.L., M.N., and Z.N. participated in the laboratory work and contributed to the statistical analyses. M.W., F.T., and T.O. revised the manuscript. All of the authors read and accepted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical statement
The animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Tokushima University (approval number: T28-21). All animal care and experimental procedures, including the determination of experimental endpoints, were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for Animal Experiments of Tokushima University. All animals were housed and maintained in accordance with Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines.
Disclaimer
The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, TV., Do, L.T.K., Lin, Q. et al. Programmed cell death-1-modified pig developed using electroporation-mediated gene editing for in vitro fertilized zygotes. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-024-00869-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-024-00869-4