Abstract
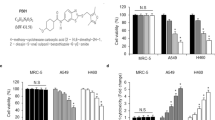
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. Radiation is widely used for the treatment of lung cancer. However, radioresistance and toxicity limit its effectiveness. Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) is a positive monomer extracted from ginseng and has been shown to the anti-cancer ability on many tumors. The aim of the present study was to ascertain whether Rg3 is able to enhance the radiosensitivity of lung cancer cells and investigate the underlying mechanisms. The effect of Rg3 on cell proliferation was examined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and radiosensitivity was measured by colony formation assay. Flow cytometry, transwell, and wound healing assay were used to determine apoptosis, cell cycle, and metastasis. Western blot was used to detect the main protein levels of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. We found that Rg3 inhibited cell proliferation, promoted apoptosis, and suppressed migration and invasion in radio-induced lung cancer cells. In addition, Rg3 increased the proportion of G2/M phase cells and inhibited the formation of cell colonies. Moreover, Rg3 decreased the expression levels of PI3K, p-AKT, and PDK1 in radio-induced cells. These findings indicate that Rg3 may be able to enhance the radiosensitivity in lung cancer cells by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. These results demonstrate the therapeutic potential of Rg3 as a radiosensitizer for lung cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acehan D, Jiang X, Morgan DG, Heuser JE, Wang X, Akey CW (2002) Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol Cell 9:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00442-2
Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS (1999) Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol 58:1685–1693. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00212-9
Bamodu OA, Chang HL, Ong JR, Lee WH, Yeh CT, Tsai JT (2020) Elevated PDK1 expression drives PI3K/AKT/MTOR signaling promotes radiation-resistant and dedifferentiated phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells 9:746. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030746
Barnes RP, Fouquerel E, Opresko PL (2019) The impact of oxidative DNA damage and stress on telomere homeostasis. Mech Ageing Dev 177:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.013
Brown S, Banfill K, Aznar MC, Whitehurst P, Faivre Finn C (2019) The evolving role of radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Radiol 92:20190524. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20190524
Cain K, Bratton SB, Cohen GM (2002) The Apaf-1 apoptosome: a large caspase-activating complex. Biochimie 84:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01376-7
Chan C, Lang S, Rowbottom C, Guckenberger M, Faivre-Finn C, Committee IART (2014) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for lung cancer: current status and future developments. J Thorac Oncol 9:1598–1608. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000346
Changizi V, Gharekhani V, Motavaseli E (2021) Co-treatment with ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 and curcumin increases radiosensitivity of MDA-MB-231 cancer cell line. Iran J Med Sci 46:291–297. https://doi.org/10.30476/ijms.2020.83977.1334
Chen AY, Phan C, Chang YC, Shih SJ (2004) Targeted radiosensitization with DNA topoisomerase I drugs. Discov Med 4:208–212
Chen CJ, Sgritta M, Mays J, Zhou H, Lucero R, Park J, Wang IC, Park JH, Kaipparettu BA, Stoica L, Jafar-Nejad P, Rigo F, Chin J, Noebels JL, Costa-Mattioli M (2019) Therapeutic inhibition of mTORC2 rescues the behavioral and neurophysiological abnormalities associated with Pten-deficiency. Nat Med 25:1684–1690. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0608-y
Choi YJ, Kang LJ, Lee SG (2014) Stimulation of DDX3 expression by ginsenoside Rg3 through the Akt/p53 pathway activates the innate immune response via TBK1/IKKepsilon/IRF3 signalling. Curr Med Chem 21:1050–1060. https://doi.org/10.2174/09298673113206660306
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326(Pt 1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3260001
Cole AJ, Hanna GG, Jain S, O’Sullivan JM (2014) Motion management for radical radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Oncol (r Coll Radiol) 26:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2013.11.001
D’Arcy MS (2019) Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int 43:582–592. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11137
Dai Y, Wang W, Sun Q, Tuohayi J (2019) Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes the antitumor activity of gefitinib in lung cancer cell lines. Exp Ther Med 17:953–959. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.7001
Fattahi S, Amjadi-Moheb F, Tabaripour R, Ashrafi GH, Akhavan-Niaki H (2020) PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in gastric cancer: epigenetics and beyond. Life Sci 262:118513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118513
Ferrandon S, DeVecchio J, Duraes L, Chouhan H, Karagkounis G, Davenport J, Orloff M, Liska D, Kalady MF (2020) CoA synthase (COASY) mediates radiation resistance via PI3K signaling in rectal cancer. Cancer Res 80:334–346. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1161
Ge X, Zhen F, Yang B, Yang X, Cai J, Zhang C, Zhang S, Cao Y, Ma J, Cheng H, Sun X (2014) Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances radiosensitization of hypoxic oesophageal cancer cell lines through vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha. J Int Med Res 42:628–640. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060513505491
Goldstein M, Kastan MB (2015) The DNA damage response: implications for tumor responses to radiation and chemotherapy. Annu Rev Med 66:129–143. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-081313-121208
Hay MP, Hicks KO, Wang J (2014) Hypoxia-directed drug strategies to target the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 772:111–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5915-6_6
Hofstetter B, Vuong V, Broggini-Tenzer A, Bodis S, Ciernik IF, Fabbro D, Wartmann M, Folkers G, Pruschy M (2005) Patupilone acts as radiosensitizing agent in multidrug-resistant cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 11:1588–1596. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1800
Huang T, Luo X, Wu B, Peng P, Dai Y, Hu G, Qiu H, Yuan X (2020) Pyrotinib enhances the radiosensitivity of HER2-overexpressing gastric and breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 44:2634–2644. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7820
Huang WC, Huang TH, Yeh KW, Chen YL, Shen SC, Liou CJ (2021) Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorates allergic airway inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. J Ginseng Res 45:654–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2021.03.002
Hwang SK, Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Park YY, Song KH, Chang YC (2022) Rg3-enriched red ginseng extract promotes lung cancer cell apoptosis and mitophagy by ROS production. J Ginseng Res 46:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2021.05.005
Jin Y, Chen Y, Tang H, Hu X, Hubert SM, Li Q, Su D, Xu H, Fan Y, Yu X, Chen Q, Liu J, Hong W, Xu Y, Deng H, Zhu D, Li P, Gong Y, Xia X, Gay CM, Zhang J, Chen M (2022) Activation of PI3K/AKT pathway is a potential mechanism of treatment resistance in small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 28:526–539. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1943
Li G, Xie B, Li X, Chen Y, Wang Q, Xu Y, Xu-Welliver M, Zou L (2012) Down-regulation of survivin and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha by beta-elemene enhances the radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma xenograft. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 27:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2011.1003
Liang J, Li H, Han J, Jiang J, Wang J, Li Y, Feng Z, Zhao R, Sun Z, Lv B, Tian H (2020) Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Dis 11:614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02858-3
Linam J, Yang LX (2015) Recent developments in radiosensitization. Anticancer Res 35:2479–2485
Liu T, Zuo L, Guo D, Chai X, Xu J, Cui Z, Wang Z, Hou C (2019) Ginsenoside Rg3 regulates DNA damage in non-small cell lung cancer cells by activating VRK1/P53BP1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 120:109483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109483
Lu JM, Yao Q, Chen C (2009) Ginseng compounds: an update on their molecular mechanisms and medical applications. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 7:293–302. https://doi.org/10.2174/157016109788340767
Ma ZJ, Lu L, Yang JJ, Wang XX, Su G, Wang ZL, Chen GH, Sun HM, Wang MY, Yang Y (2018) Lariciresinol induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells via mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 821:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.12.027
McNeely T, Leone M, Yanai H, Beerman I (2020) DNA damage in aging, the stem cell perspective. Hum Genet 139:309–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02047-z
Nakhjavani M, Smith E, Townsend AR, Price TJ, Hardingham JE (2020) Anti-angiogenic properties of ginsenoside Rg3. Molecules 25:4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214905
Nie J, Zhao C, Deng LI, Chen J, Yu B, Wu X, Pang P, Chen X (2016) Efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in treating cancer. Biomed Rep 4:3–14. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2015.537
Oehler C, von Bueren AO, Furmanova P, Broggini-Tenzer A, Orlowski K, Rutkowski S, Frei K, Grotzer MA, Pruschy M (2011) The microtubule stabilizer patupilone (epothilone B) is a potent radiosensitizer in medulloblastoma cells. Neuro Oncol 13:1000–1010. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor069
Pawlik TM, Keyomarsi K (2004) Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:928–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.005
Pharand C, Ackman ML, Jackevicius CA, Paradiso-Hardy FL, Pearson GJ, Canadian Cardiovascular Pharmacists N (2003) Use of OTC and herbal products in patients with cardiovascular disease. Ann Pharmacother 37:899–904. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1C163
Qin Q, Zuo Y, Yang X, Lu J, Zhan L, Xu L, Zhang C, Zhu H, Liu J, Liu Z, Tao G, Dai S, Zhang X, Ma J, Cai J, Sun X (2014) Smac mimetic compound LCL161 sensitizes esophageal carcinoma cells to radiotherapy by inhibiting the expression of inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Tumour Biol 35:2565–2574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1338-2
Ren B, Feng J, Yang N, Guo Y, Chen C, Qin Q (2021) Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates angiotensin II-induced myocardial hypertrophy through repressing NLRP3 inflammasome and oxidative stress via modulating SIRT1/NF-kappaB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 98:107841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107841
Santivasi WL, Xia F (2014) Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair. Antioxid Redox Signal 21:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5668
Schabath MB, Cote ML (2019) Cancer progress and priorities: lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 28:1563–1579. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0221
Shafiq J, Hanna TP, Vinod SK, Delaney GP, Barton MB (2016) A population-based model of local control and survival benefit of radiotherapy for lung cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 28:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2016.05.006
Shahcheraghi SH, Tchokonte-Nana V, Lotfi M, Lotfi M, Ghorbani A, Sadeghnia HR (2020) Wnt/beta-catenin and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in glioblastoma: two main targets for drug design: a review. Curr Pharm Des 26:1729–1741. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666200131100630
Shan K, Deng Y, Du Z, Yue P, Yang S (2022) Examination of combined treatment of ginsenoside Rg3 and 5-fluorouracil in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Comput Math Methods Med 2022:2813142. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2813142
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Standish LJ, Greene KB, Bain S, Reeves C, Sanders F, Wines RC, Turet P, Kim JG, Calabrese C (2001) Alternative medicine use in HIV-positive men and women: demographics, utilization patterns and health status. AIDS Care 13:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/095401201300059759
Sun C, Yu Y, Wang L, Wu B, Xia L, Feng F, Ling Z, Wang S (2016) Additive antiangiogenesis effect of ginsenoside Rg3 with low-dose metronomic temozolomide on rat glioma cells both in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0274-y
Sun M, Ye Y, Xiao L, Duan X, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2017) Anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 (Review). Int J Mol Med 39:507–518. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.2857
Sun X, Cheng L, Zhu W, Hu C, Jin R, Sun B, Shi Y, Zhang Y, Cui W (2014) Use of ginsenoside Rg3-loaded electrospun PLGA fibrous membranes as wound cover induces healing and inhibits hypertrophic scar formation of the skin. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 115:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.11.030
Tan AC (2020) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac Cancer 11:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13328
Tian C, Liu Y, Xue L, Zhang D, Zhang X, Su J, Chen J, Li X, Wang L, Jiao S (2022) Sorafenib inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and mobility and induces radiosensitivity by targeting the tumor cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Open Life Sci 17:616–625. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2022-0066
Tungsukruthai S, Sritularak B, Chanvorachote P (2017) Cycloartobiloxanthone inhibits migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res 37:6311–6319. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.12082
Vinod SK, Hau E (2020) Radiotherapy treatment for lung cancer: current status and future directions. Respirology 25(Suppl 2):61–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.13870
Wang CZ, Aung HH, Ni M, Wu JA, Tong R, Wicks S, He TC, Yuan CS (2007) Red American ginseng: ginsenoside constituents and antiproliferative activities of heat-processed Panax quinquefolius roots. Planta Med 73:669–674. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-981524
Wang H, Mu X, He H, Zhang XD (2018) Cancer radiosensitizers. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39:24–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.11.003
Wang JH, Nao JF, Zhang M, He P (2014) 20(s)-ginsenoside Rg3 promotes apoptosis in human ovarian cancer HO-8910 cells through PI3K/Akt and XIAP pathways. Tumour Biol 35:11985–11994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2497-5
Wei Q, Ren Y, Zheng X, Yang S, Lu T, Ji H, Hua H, Shan K (2022) Ginsenoside Rg3 and sorafenib combination therapy relieves the hepatocellular carcinomaprogression through regulating the HK2-mediated glycolysis and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Bioengineered 13:13919–13928. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2074616
Wu P, Gao Y, Lu Y, Zhang H, Cai C (2013) High specific detection and near-infrared photothermal therapy of lung cancer cells with high SERS active aptamer-silver-gold shell-core nanostructures. Analyst 138:6501–6510. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an01375h
Wu R, Ru Q, Chen L, Ma B, Li C (2014) Stereospecificity of ginsenoside Rg3 in the promotion of cellular immunity in hepatoma H22-bearing mice. J Food Sci 79:H1430-1435. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12518
Xiong L, Tan B, Lei X, Zhang B, Li W, Liu D, Xia T (2021) SIRT6 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to enhance radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer and inhibit tumor progression. IUBMB Life 73:1092–1102. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2511
Yang J, McEachern D, Li W, Davis MA, Li H, Morgan MA, Bai L, Sebolt JT, Sun H, Lawrence TS, Wang S, Sun Y (2011) Radiosensitization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by a SMAC-mimetic compound, SM-164, requires activation of caspases. Mol Cancer Ther 10:658–669. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0643
Yang Q, Jiang W, Hou P (2019) Emerging role of PI3K/AKT in tumor-related epigenetic regulation. Semin Cancer Biol 59:112–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.04.001
Yang X, Zou J, Cai H, Huang X, Yang X, Guo D, Cao Y (2017) Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits colorectal tumor growth via down-regulation of C/EBPbeta/NF-kappaB signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 96:1240–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.092
Yu L, Wei J, Liu P (2021) Attacking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol S1044–579X:00188–00187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.06.019
Yue PY, Mak NK, Cheng YK, Leung KW, Ng TB, Fan DT, Yeung HW, Wong RN (2007) Pharmacogenomics and the Yin/Yang actions of ginseng: anti-tumor, angiomodulating and steroid-like activities of ginsenosides. Chin Med 2:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8546-2-6
Zhao D, Sun X, Tong J, Ma J, Bu X, Xu R, Fan R (2012) A novel multifunctional nanocomposite C225-conjugated Fe3O4/Ag enhances the sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to radiotherapy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 44:678–684. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gms051
Funding
This work was supported by Wuhan Young and Middle-aged Medical Backbone Personnel Training Project and Scientific Research Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission (Grant Number: WJ2021M221).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jialin Li conducted the experiments, performed data analysis, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Bo Yang contributed to the study conception and design and commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yang, B. Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the radiosensitivity of lung cancer A549 and H1299 cells via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 59, 19–30 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00749-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00749-3