Abstract
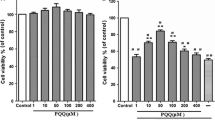
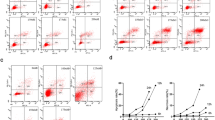
Rutin is well known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties against oxidative stress. However, its protective function in nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) remains unclear. This study was aimed to explore the effects of rutin on oxidative stress in NPCs. Primary NPCs were obtained from 1-mo-old SD rats. The NPCs were treated with tert-butyl hydrogen peroxide (TBHP) to obtain the oxidative stress, and different concentrations of rutin were used to observe its influence on the oxidative stress in NPCs. Fluorescent probe DCFH-DA was used to detect reactive oxide species (ROS). The antioxidant proteins and genes of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD), catalase, aggrecan and collagen II in NPCs were measured by western blot and real-time PCR. With the stimulation of TBHP, the content of ROS in NPCs increased significantly and showed solubility correlation. Rutin effectively reduced the accumulation of ROS in a dose-dependent manner. The antioxidant proteins of HSP70, Mn-SOD, and catalase and the matrix proteins of aggrecan and collagen II decreased remarkably with the stimulation of TBHP, while the matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) significantly increased after TBHP intervention. Rutin boosted the expressions of the HSP70, Mn-SOD, and catalase, elevated the contents of aggrecan and collagen II, and inhibited the expression of MMP-13 in NPCs. The findings of this study suggested that rutin is able to reverse oxidative stress and maintain cellular function of NPCs, and it was indicated that rutin could be a possible therapeutic option for intervertebral disc degeneration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afanas'Ev IB, Dorozhko AI, Brodskii AV, Kostyuk VA, Potapovitch AI (1989) Chelating and free radical scavenging mechanisms of inhibitory action of rutin and quercetin in lipid peroxidation. Biochem Pharmacol 38(11):1763–1769
Alvarez-Garcia O, Matsuzaki T, Olmer M, Masuda K, Lotz MK (2017) Age-related reduction in the expression of FOXO transcription factors and correlations with intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res 35(12):2682–2691
Chen D, Xia D, Pan Z, Xu D, Zhou Y, Wu Y, Cai N, Tang Q, Wang C, Yan M, Zhang JJ, Zhou K, Wang Q, Feng Y, Wang X, Xu H, Zhang X, Tian N (2016) Metformin protects against apoptosis and senescence in nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates disc degeneration in vivo. Cell Death Dis 7(10):e2441
Dimozi A, Mavrogonatou E, Sklirou A, Kletsas D (2015) Oxidative stress inhibits the proliferation, induces premature senescence and promotes a catabolic phenotype in human nucleus pulposus intervertebral disc cells. Eur Cell Mater 30(89-102):103
Feng C, Yang M, Lan M, Liu C, Zhang Y, Huang B et al (2017) ROS: crucial intermediators in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:5601593
Ganeshpurkar A, Saluja AK (2017) The pharmacological potential of rutin. Saudi Pharm J 25(2):149–164
Gul A, Kunwar B, Mazhar M, Faizi S, Ahmed D, Shah MR, Simjee SU (2018) Rutin and rutin-conjugated gold nanoparticles ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis in rats through inhibition of NF-kappaB and iNOS activation. Int Immunopharmacol 59:310–317
Hou G, Lu H, Chen M, Yao H, Zhao H (2014) Oxidative stress participates in age-related changes in rat lumbar intervertebral discs. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 59(3):665–669
Kauppila T, Kauppila J, Larsson NG (2017) Mammalian mitochondria and aging: an update. Cell Metab 25(1):57–71
Khomenko IP, Bakhtina LY, Zelenina OM, Kruglov SV, Manukhina EB, Bayda LA, Malyshev IY (2007) Role of heat shock proteins HSP70 and HSP32 in the protective effect of adaptation of cultured HT22 hippocampal cells to oxidative stress. Bull Exp Biol Med 144(2):174–177
Kong G, Huang Z, Ji W, Wang X, Liu J, Wu X, Huang Z, Li R, Zhu Q (2017) The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate attenuates oxidative stress in spinal cord injury by suppression of class I histone deacetylases. J Neurotrauma 34(18):2645–2655
Kurashova NA, Madaeva IM, Kolesnikova LI (2019) Expression of heat shock proteins HSP70 under oxidative stress. Adv Gerontol 32(4):502–508
Le Maitre CL, Pockert A, Buttle DJ, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA (2007) Matrix synthesis and degradation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Soc Trans 35(Pt 4):652–655
Magalingam KB, Radhakrishnan A, Haleagrahara N (2013) Rutin, a bioflavonoid antioxidant protects rat pheochromocytoma (PC-12) cells against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Med 32(1):235–240
Martinez DTI, De la Fuente M (2015) The role of Hsp70 in oxi-inflamm-aging and its use as a potential biomarker of lifespan. Biogerontology 16(6):709–721
Na JY, Song K, Kim S, Kwon J (2016) Rutin protects rat articular chondrocytes against oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide through SIRT1 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473(4):1301–1308
Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE, Schleicher E, Rohrbach H, Paesold G, Boos N (2007) Immunomorphological analysis of RAGE receptor expression and NF-kappaB activation in tissue samples from normal and degenerated intervertebral discs of various ages. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1096:239–248
Nerlich AG, Schleicher ED, Boos N (1997) 1997 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies. Immunohistologic markers for age-related changes of human lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22(24):2781–2795
Peng B, Hou S, Shi Q, Jia L (2001) The relationship between cartilage end-plate calcification and disc degeneration: an experimental study. Chin Med J 114(3):308–312
Pulickal T, Boos J, Konieczny M, Sawicki LM, Muller-Lutz A, Bittersohl B et al (2019) MRI identifies biochemical alterations of intervertebral discs in patients with low back pain and radiculopathy. Eur Radiol 29(12):6443–6446
Sabirzhanov B, Stoica BA, Hanscom M, Piao CS, Faden AI (2012) Over-expression of HSP70 attenuates caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways and inhibits neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 123(4):542–554
Sandy JD (2001) Proteoglycan core proteins and catabolic fragments present in tissues and fluids. Methods Mol Biol 171:335–345
Sivan SS, Tsitron E, Wachtel E, Roughley P, Sakkee N, van der Ham F, Degroot J, Maroudas A (2006) Age-related accumulation of pentosidine in aggrecan and collagen from normal and degenerate human intervertebral discs. Biochem J 399(1):29–35
Song K, Kim S, Na JY, Park JH, Kim JK, Kim JH, Kwon J (2014) Rutin attenuates ethanol-induced neurotoxicity in hippocampal neuronal cells by increasing aldehyde dehydrogenase 2. Food Chem Toxicol 72:228–233
Su KY, Yu CY, Chen YW, Huang YT, Chen CT, Wu HF, Chen YLS (2014) Rutin, a flavonoid and principal component of Saussurea involucrata, attenuates physical fatigue in a forced swimming mouse model. Int J Med Sci 11(5):528–537
Suzuki S, Fujita N, Hosogane N, Watanabe K, Ishii K, Toyama Y, Takubo K, Horiuchi K, Miyamoto T, Nakamura M, Matsumoto M (2015) Excessive reactive oxygen species are therapeutic targets for intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther 17:316
Tonomura H, Takahashi KA, Mazda O, Arai Y, Shin-Ya M, Inoue A, Honjo K, Hojo T, Imanishi J, Kubo T (2008) Effects of heat stimulation via microwave applicator on cartilage matrix gene and HSP70 expression in the rabbit knee joint. J Orthop Res 26(1):34–41
Valko M, Jomova K, Rhodes CJ, Kuca K, Musilek K (2016) Redox- and non-redox-metal-induced formation of free radicals and their role in human disease. Arch Toxicol 90(1):1–37
Vo NV, Hartman RA, Patil PR, Risbud MV, Kletsas D, Iatridis JC, Hoyland JA, le Maitre CL, Sowa GA, Kang JD (2016) Molecular mechanisms of biological aging in intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res 34(8):1289–1306
Vo N, Niedernhofer LJ, Nasto LA, Jacobs L, Robbins PD, Kang J, Evans CH (2013) An overview of underlying causes and animal models for the study of age-related degenerative disorders of the spine and synovial joints. J Orthop Res 31(6):831–837
Yang D, Wang D, Shimer A, Shen FH, Li X, Yang X (2014) Glutathione protects human nucleus pulposus cells from cell apoptosis and inhibition of matrix synthesis. Connect Tissue Res 55(2):132–139
Yang L, Rong Z, Zeng M, Cao Y, Gong X, Lin L, Chen Y, Cao W, Zhu L, Dong W (2015) Pyrroloquinoline quinone protects nucleus pulposus cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Eur Spine J 24(8):1702–1710
Zeng Y, Song J, Zhang M, Wang H, Zhang Y, Suo H (2020) Comparison of in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of six flavonoids with similar structures. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(8)
Zhai X, Ding Y, Wang Q, Zhang H, Li F (2016) Rutin acid ameliorates neural apoptosis induced by traumatic brain injury via mitochondrial pathways in mice. Neuroimmunomodulation 23(3):179–187
Zhang S, Liu W, Wang P, Hu B, Lv X, Chen S, Wang B, Shao Z (2021) Activation of HSP70 impedes tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced apoptosis and senescence of human nucleus pulposus stem cells via inhibiting the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Mol Cell Biochem
Funding
This article was supported by the Scientific Research Projects of Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong (No. 20211243 and No. 20201231), the Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2020A1515110631), the Health Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (No. 20211A011078), the Medical Science and Technology Research Fund Project of Guangdong (No. 2020111220372206), and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Guangzhou (No. 201704020032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL and JZ were the major contributors in writing the manuscript and performing the experiments. QL and YH designed the study and were in charge of reviewing the manuscript. ZY, CX, and LL performed the experiments and analyzed the data. HH, YC, and YH interpreted the data and edited the important intellectual content of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Guangzhou Medical University.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Liu, Q., Yang, Z. et al. Rutin maintains redox balance to relieve oxidative stress induced by TBHP in nucleus pulposus cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 57, 448–456 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00581-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00581-7