Abstract
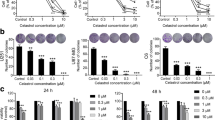
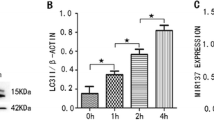
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is the most abundant n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid in the human brain and works as an anticancer agent to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cell lines. However, little is known about the connection between DHA and autophagy in GBM cells. We found that high-dose DHA caused cellular autophagy in cultured U251 and U118 GBM cell lines, but there was no effect with a low dose. Moreover, after treatment with a high dose of DHA at 12, 24, and 48 h, the protein expression of SQSTM1/p62 decreased in DHA-treated U251 cells at 12 and 24 h, but increased at 48 h, while in DHA-treated U118 cells, the protein expression increased at all time points. Interestingly, the level of SQSTM1/p62 mRNA was elevated in both DHA-treated U251 and U118 cells at all time points, indicating that DHA activated SQSTM1/p62 transcription in both cell lines. Furthermore, downregulation of SQSTM1/p62 by siRNA attenuated DHA-induced cellular autophagy in both cell lines. This report confirms that high-dose DHA induces cellular autophagy in GBM cells, and demonstrates that SQSTM1/p62 acts as a regulator and participates in DHA-induced autophagy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batash R, Asna N, Schaffer P, Francis N, Schaffer M (2017) Glioblastoma multiforme, diagnosis and treatment; recent literature review. Curr Med Chem 24:3002–3009
Batista CA, Larson RG, Kotov NA (2015) Nonadditivity of nanoparticle interactions. Science 350:1242477
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H, Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H, Johansen T (2005) p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 171:603–614
Daher A, de Groot J (2018) Rapid identification and validation of novel targeted approaches for glioblastoma: a combined ex vivo-in vivo pharmaco-omic model. Exp Neurol 299:281–288
Fine HA (2015) New strategies in glioblastoma: exploiting the new biology. Clin Cancer Res 21:1984–1988
Geng L, Zhou W, Liu B, Wang X, Chen B (2018) DHA induces apoptosis of human malignant breast cancer tissues by the TLR-4/PPAR-alpha pathways. Oncol Lett 15:2967–2977
Hashimoto M, Hossain S (2011) Neuroprotective and ameliorative actions of polyunsaturated fatty acids against neuronal diseases: beneficial effect of docosahexaenoic acid on cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. J Pharmacol Sci 116:150–162
Hashimoto M, Hossain S, Agdul H, Shido O (2005) Docosahexaenoic acid-induced amelioration on impairment of memory learning in amyloid beta-infused rats relates to the decreases of amyloid beta and cholesterol levels in detergent-insoluble membrane fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1738:91–98
Hashimoto M, Hossain S, Al Mamun A, Matsuzaki K, Arai H (2016) Docosahexaenoic acid: one molecule diverse functions. Crit Rev Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2016.1207153:1-19
Jing K, Song KS, Shin S, Kim N, Jeong S, Oh HR, Park JH, Seo KS, Heo JY, Han J, Park JI, Han C, Wu T, Kweon GR, Park SK, Yoon WH, Hwang BD, Lim K (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid induces autophagy through p53/AMPK/mTOR signaling and promotes apoptosis in human cancer cells harboring wild-type p53. Autophagy 7:1348–1358
Katsuragi Y, Ichimura Y, Komatsu M (2015) p62/SQSTM1 functions as a signaling hub and an autophagy adaptor. FEBS J 282:4672–4678
Kawakita E, Hashimoto M, Shido O (2006) Docosahexaenoic acid promotes neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience 139:991–997
Kim S, Jing K, Shin S, Jeong S, Han SH, Oh H, Yoo YS, Han J, Jeon YJ, Heo JY, Kweon GR, Park SK, Park JI, Wu T, Lim K (2018) omega3-polyunsaturated fatty acids induce cell death through apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma cells: in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep 39:239–246
Komatsu M, Kageyama S, Ichimura Y (2012) p62/SQSTM1/A170: physiology and pathology. Pharmacol Res 66:457–462
Lamark T, Svenning S, Johansen T (2017) Regulation of selective autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm. Essays Biochem 61:609–624
Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A (2017) Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 17:528–542
Li H, Yang Q, Han X, Tan X, Qin J, Jin G (2018a) Low-dose DHA-induced astrocyte proliferation can be attenuated by insufficient expression of BLBP in vitro. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 134:114–122
Li R, He Y, Zhang S, Qin J, Wang J (2018b) Cell membrane-based nanoparticles: a new biomimetic platform for tumor diagnosis and treatment. Acta Pharm Sin B 8:14–22
Liu PF, Chang HW, Cheng JS, Lee HP, Yen CY, Tsai WL, Cheng JT, Li YJ, Huang WC, Lee CH, Ger LP, Shu CW (2018) Map 1lc3b and Sqstm1 modulated autophagy for tumorigenesis and prognosis in certain subsites of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Med 7
Liu WJ, Ye L, Huang WF, Guo LJ, Xu ZG, Wu HL, Yang C, Liu HF (2016) p62 links the autophagy pathway and the ubiqutin-proteasome system upon ubiquitinated protein degradation. Cell Mol Biol Lett 21:29
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lu S, Xia D, Huang G, Jing H, Wang Y, Gu H (2010) Concentration effect of gold nanoparticles on proliferation of keratinocytes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 81:406–411
Merendino N, Costantini L, Manzi L, Molinari R, D’Eliseo D, Velotti F (2013) Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid DHA: a potential adjuvant in the treatment of cancer. Biomed Res Int 2013:310186
Mildenberger J, Johansson I, Sergin I, Kjobli E, Damas JK, Razani B, Flo TH, Bjorkoy G (2017) N-3 PUFAs induce inflammatory tolerance by formation of KEAP1-containing SQSTM1/p62-bodies and activation of NFE2L2. Autophagy 13:1664–1678
Moustaka K, Maleskou E, Lambrianidou A, Papadopoulos S, Lekka ME, Trangas T, Kitsiouli E (2019) Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits proliferation of EoL-1 leukemia cells and induces cell cycle arrest and cell differentiation. Nutrients 11
Narayanan BA, Narayanan NK, Reddy BS (2001) Docosahexaenoic acid regulated genes and transcription factors inducing apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 19:1255–1262
Neuwelt E, Abbott NJ, Abrey L, Banks WA, Blakley B, Davis T, Engelhardt B, Grammas P, Nedergaard M, Nutt J, Pardridge W, Rosenberg GA, Smith Q, Drewes LR (2008) Strategies to advance translational research into brain barriers. Lancet Neurol 7:84–96
Neuwelt EA, Bauer B, Fahlke C, Fricker G, Iadecola C, Janigro D, Leybaert L, Molnar Z, O’Donnell ME, Povlishock JT, Saunders NR, Sharp F, Stanimirovic D, Watts RJ, Drewes LR (2011) Engaging neuroscience to advance translational research in brain barrier biology. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:169–182
Nezis IP, Stenmark H (2012) p62 at the interface of autophagy, oxidative stress signaling, and cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal 17:786–793
Noonan J, Zarrer J, Murphy BM (2016) Targeting autophagy in glioblastoma. Crit Rev Oncog 21:241–252
Oksman M, Iivonen H, Hogyes E, Amtul Z, Penke B, Leenders I, Broersen L, Lutjohann D, Hartmann T, Tanila H (2006) Impact of different saturated fatty acid, polyunsaturated fatty acid and cholesterol containing diets on beta-amyloid accumulation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol Dis 23:563–572
Oono K, Takahashi K, Sukehara S, Kurosawa H, Matsumura T, Taniguchi S, Ohta S (2017) Inhibition of PC3 human prostate cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration by eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Mol Clin Oncol 7:217–220
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Liao P, Rouse C, Chen Y, Dowling J, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan J (2014) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007-2011. Neuro-oncology 16(Suppl 4):iv1–i63
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A, Bruun JA, Outzen H, Overvatn A, Bjorkoy G, Johansen T (2007) p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem 282:24131–24145
Pettersen K, Monsen VT, Hakvag Pettersen CH, Overland HB, Pettersen G, Samdal H, Tesfahun AN, Lundemo AG, Bjorkoy G, Schonberg SA (2016) DHA-induced stress response in human colon cancer cells - focus on oxidative stress and autophagy. Free Radic Biol Med 90:158–172
Pizato N, Luzete BC, Kiffer L, Correa LH, de Oliveira Santos I, Assumpcao JAF, Ito MK, Magalhaes KG (2018) Omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid induces pyroptosis cell death in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Sci Rep 8:1952
Ruan M, Liu J, Ren X, Li C, Zhao AZ, Li L, Yang H, Dai Y, Wang Y (2019) Whole transcriptome sequencing analyses of DHA treated glioblastoma cells. J Neurol Sci 396:247–253
Shin S, Jing K, Jeong S, Kim N, Song KS, Heo JY, Park JH, Seo KS, Han J, Park JI, Kweon GR, Park SK, Wu T, Hwang BD, Lim K (2013) The omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid DHA induces simultaneous apoptosis and autophagy via mitochondrial ROS-mediated Akt-mTOR signaling in prostate cancer cells expressing mutant p53. Biomed Res Int 2013:568671
Shinde RL, Devarajan PV (2017) Docosahexaenoic acid-mediated, targeted and sustained brain delivery of curcumin microemulsion. Drug Deliv 24:152–161
Siddiqui RA, Harvey KA, Xu Z, Bammerlin EM, Walker C, Altenburg JD (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid: a natural powerful adjuvant that improves efficacy for anticancer treatment with no adverse effects. Biofactors 37:399–412
Su H, Wang X (2011) p62 stages an interplay between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy in the heart of defense against proteotoxic stress. Trends Cardiovasc Med 21:224–228
Wang F, Bhat K, Doucette M, Zhou S, Gu Y, Law B, Liu X, Wong ET, Kang JX, Hsieh TC, Qian SY, Wu E (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) sensitizes brain tumor cells to etoposide-induced apoptosis. Curr Mol Med 11:503–511
Wang J, Hong Y, Shao S, Zhang K, Hong W (2018) FFAR1-and FFAR4-dependent activation of Hippo pathway mediates DHA-induced apoptosis of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 506:590–596
Weller M, van den Bent M, Hopkins K, Tonn JC, Stupp R, Falini A, Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E, Frappaz D, Henriksson R, Balana C, Chinot O, Ram Z, Reifenberger G, Soffietti R, Wick W, European Association for Neuro-Oncology Task Force on Malignant G (2014) EANO guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of anaplastic gliomas and glioblastoma. Lancet Oncol 15:e395–e403
Zhang YB, Gong JL, Xing TY, Zheng SP, Ding W (2013) Autophagy protein p62/SQSTM1 is involved in HAMLET-induced cell death by modulating apotosis in U87MG cells. Cell Death Dis 4:e550
Zhou Y, Zhu C, Wu YF, Zhang L, Tang JB (2015) Effective modulation of transforming growth factor-beta1 expression through engineered microRNA-based plasmid-loaded nanospheres. Cytotherapy 17:320–329
Funding
This work was supported by grants of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81801301), the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and the “Qing Lan Project” of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, X., Zou, L., Qin, J. et al. SQSTM1/p62 is involved in docosahexaenoic acid–induced cellular autophagy in glioblastoma cell lines. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 55, 703–712 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00387-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00387-8