Abstract
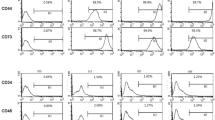
The aim of the present study was to investigate the renogenic characteristics of amniotic fluid stem cells (AFSCs) and to evaluate their in vitro differentiation potential into renal proximal tubular-like cells and juxtaglomerular-like cells. We culture expanded AFSCs derived from rat amniotic fluid. The AFSCs grew as adherent spindle-shaped cells and expressed mesenchymal markers CD73, CD90, and CD105 as well as renal progenitor markers WT1, PAX2, SIX2, SALL1, and CITED1. AFSCs exhibited an in vitro differentiation potential into renal proximal tubular epithelial-like cells, as shown by the upregulation of expression of proximal tubular cell–specific genes like AQP1, CD13, PEPT1, GLUT5, OAT1, and OCT1. AFSCs could also be differentiated into juxtaglomerular-like cells as demonstrated by the expression of renin and α-SMA. The AFSCs also expressed pluripotency markers OCT4, NANOG, and SOX2 and could be induced into embryoid bodies with differentiation into all the three germ layers, highlighting the pluripotent nature of these cells. Our results show that amniotic fluid contains a population of primitive stem cells that express renal-progenitor markers and also possess the propensity to differentiate into two renal lineage cell types and, thus, may have a therapeutic potential in renal regenerative medicine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonucci I, Di Pietro R, Alfonsi M, Centurione MA, Centurione L, Sancilio S, Pelagatti F, D’Amico MA, Di Baldassarre A, Piattelli A, Tete S, Palka G, Borlongan CV, Stuppia L (2014) Human second trimester amniotic fluid cells are able to create embryoid body-like structures in vitro and to show typical expression profiles of embryonic and primordial germ cells. Cell Transplant. 23:1501–1515
Basta JM, Robbins L, Kiefer SM, Dorsett D, Rauchman M (2014) Sall1 balances self-renewal and differentiation of renal progenitor cells. Development 141:1047–1058
Brunskill EW, Sequeira-Lopez MLS, Pentz ES, Lin E, Yu J, Aronow BJ, Potter SS, Gomez RA (2011) Genes that confer the identity of the renin cell. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22:2213–2225
Cananzi M, De Coppi P (2012) CD117(+) amniotic fluid stem cells: state of the art and future perspectives. Organogenesis 8:77–88
Da Monteiro Carvalho Mori Cunha MG, Zia S, Arcolino FO, Carlon MS, Beckmann DV, Pippi NL, Graça DL, Levtchenko E, Deprest J, Toelen J (2015) Amniotic fluid derived stem cells with a renal progenitor phenotype inhibit interstitial fibrosis in renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One 10:1–21
Da Sacco S, Sedrakyan S, Boldrin F, Giuliani S, Parnigotto P, Habibian R, Warburton D, De Filippo RE, Perin L (2010) Human amniotic fluid as a potential new source of organ specific precursor cells for future regenerative medicine applications. J. Urol. 183:1193–1200
Ditadi A, de Coppi P, Picone O, Gautreau L, Smati R, Six E, Bonhomme D, Ezine S, Frydman R, Cavazzana-Calvo M (2009) Human and murine amniotic fluid c-Kit+ Lin- cells display hematopoietic activity. Blood 113:3953–3960
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A, Prockop D, Horwitz E (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Frey IM, Rubio-Aliaga I, Siewert A, Sailer D, Drobyshev A, Beckers J, de Angelis MH, Aubert J, Bar Hen A, Fiehn O, Eichinger HM, Daniel H (2007) Profiling at mRNA, protein, and metabolite levels reveals alterations in renal amino acid handling and glutathione metabolism in kidney tissue of Pept2-/-mice. Physiol. Genomics 28:301–310
Fukuzawa T, Fukazawa M, Ueda O, Shimada H, Kito A, Kakefuda M, Kawase Y, Wada NA, Goto C, Fukushima N, Jishage K-I, Honda K, King GL, Kawabe Y (2013) SGLT5 reabsorbs fructose in the kidney but its deficiency paradoxically exacerbates hepatic steatosis induced by fructose. PLoS One 8:e56681
Gupta AK, Jadhav SH, Tripathy NK, Nityanand S (2015a) Fetal Kidney cells can ameliorate ischemic acute renal failure in rats through their anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative effects. PLoS One 10:e0131057
Gupta AK, Jadhav SH, Tripathy NK, Nityanand S (2015b) Fetal kidney stem cells ameliorate cisplatin induced acute renal failure and promote renal angiogenesis. World J. Stem Cells 7:776–788
Jin W, Penington CJ, McCue SW, Simpson MJ (2017) A computational modelling framework to quantify the effects of passaging cell lines. PLoS One 12:e0181941
Kang M, Han Y-M (2014) Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into nephron progenitor cells in a serum and feeder free system. PLoS One 9:e94888
Krause M, Rak-Raszewska A, Pietila I, Quaggin SE, Vainio S (2015) Signaling during kidney development. Cells 4:112–132
Li Y, Jalili RB, Ghahary A (2016) Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites. Sci. Rep. 6:28979
Lu Y, Wang Z, Chen L, Wang J, Li S, Liu C, Sun D (2018) The in vitro differentiation of GDNF gene-engineered amniotic fluid-derived stem cells into renal tubular epithelial-like cells. Stem Cells Dev. 27(9):590–599
Marcus AJ, Woodbury D (2008) Fetal stem cells from extra-embryonic tissues: do not discard. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 12:730–742
Matsushita K, Morello F, Wu Y, Zhang L, Iwanaga S, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into renin-producing juxtaglomerular (JG)-like cells under the control of liver X receptor-alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 285:11974–11982
Mu D, Zhang X-L, Xie J, Yuan H-H, Wang K, Huang W, Li G-N, Lu J-R, Mao L-J, Wang L, Cheng L, Mai X-L, Yang J, Tian C-S, Kang L-N, Gu R, Zhu B, Xu B (2016) Intracoronary transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells with overexpressed integrin-linked kinase improves cardiac function in porcine myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 6:19155
Murphy AJ, Pierce J, de Caestecker C, Taylor C, Anderson JR, Perantoni AO, de Caestecker MP, Lovvorn HN III (2012) SIX2 and CITED1, markers of nephronic progenitor self-renewal, remain active in primitive elements of Wilms’ tumor. J. Pediatr. Surg. 47:1239–1249
Narayanan K, Schumacher KM, Tasnim F, Kandasamy K, Schumacher A, Ni M, Gao S, Gopalan B, Zink D, Ying JY (2013) Human embryonic stem cells differentiate into functional renal proximal tubular-like cells. Kidney Int. 83:593–603
Noronha IL, Cavaglieri RC, Janz FL, S a D, Lopes M a B, Zugaib M, Bydlowski SP (2011) The potential use of stem cells derived from human amniotic fluid in renal diseases. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1:77–82
Peired AJ, Sisti A, Romagnani P (2016) Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for kidney disease: a review of clinical evidence. Stem Cells Int. 2016:4798639
Persson PB (2003) Renin: origin, secretion and synthesis. J. Physiol. 552:667–671
Pfaller W, Gstraunthaler G (1998) Nephrotoxicity testing in vitro--what we know and what we need to know. Environ. Health Perspect. 106(Suppl):559–569
Siegel N, Rosner M, Hanneder M, Valli A, Hengstschläger M (2007) Stem cells in amniotic fluid as new tools to study human genetic diseases. Stem Cell Rev. 3:256–264
Underwood MA, Gilbert WM, Sherman MP (2005) Amniotic fluid: not just fetal urine anymore. J. Perinatol. 25:341–348
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to extend their sincere thanks to Miss Manali Jain and Miss Shobhita Katiyar for assisting them in performing the growth kinetics and flow cytometry experiments. We would also like to express our gratitude to Dr. Anup Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of Biostatistics, SGPGIMS, for extending his help for statistical analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by an Extramural Grant (BT/PR16863/MED/31/338/2016) of the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Govt. of India, sanctioned to SN and Wellcome Trust DBT India Alliance Fellowship Grant (IA/I/16/1/502374) sanctioned to CPC. EM is the recipient of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India, INSPIRE PhD fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minocha, E., Chaturvedi, C.P. & Nityanand, S. Renogenic characterization and in vitro differentiation of rat amniotic fluid stem cells into renal proximal tubular- and juxtaglomerular-like cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 55, 138–147 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-00315-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-018-00315-2