Abstract
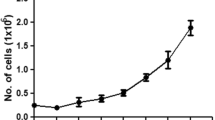
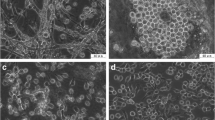
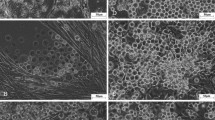
A novel cell line, NRCAN-Tb521, was developed from larvae of the longhorn beetle Tylonotus bimaculatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), a pest of North American ash trees. The cell line has been successfully passaged more than 50 times and displayed very strong attachment to the substrate and a modal chromosomal count distribution of 19. Sequencing of a 649 bp fragment of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I gene confirmed the identity of NRCAN-Tb521 as T. bimaculatus. The response of the cell line to 20-hydroxyecdysone and diacylhydrazine ecdysone agonist insecticides was also studied. At 10−6 M, 20-hydroxyecdysone, tebufenozide, methoxyfenozide and halofenozide triggered the production of numerous filamentous cytoplasmic extensions, and the cells tended to form aggregates, indicative of a cell differentiation response. This response was followed by a strong decrease in viability after 4 d. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) experiments and sequencing of PCR fragments showed that the 20E receptor gene EcR is expressed in the cells and that 20E, tebufenozide, methoxyfenozide and halofenozide also induce the expression of the nuclear hormone receptor gene HR3. This report establishes that NRCAN-Tb521 is a valuable in vitro model to study effects of ecdysone agonists in wood-boring cerambycids.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljabr AM, Rizwan-ul-Haq M, Hussain A, Al-Mubarak AI, AL-Ayied HY (2014) Establishing midgut cell culture from Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) and toxicity assessment against ten different insecticides. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 50:296–303
Arif B, Pavlik L (2013) Insect cell culture: virus replication and applications in biotechnology. J Invertebr Pathol 112:S138–S141
Berghe TV, Linkermann A, Jouan-Lanhouet S, Walczak H, Vandenabeele P (2014) Regulated necrosis: the expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:135–147
Chittaranjan S, McConechy M, Hou YC, Freeman JD, Devorkin L, Gorski SM (2009) Steroid hormone control of cell death and cell survival: molecular insights using RNAi. PLoS Genet 5(2):1–17
Cruz J, Martín D, Bellés X (2007) Redundant ecdysis regulatory functions of three nuclear receptor HR3 isoforms in the direct-developing insect Blattella germanica. Mech Dev 124:180–189
Dhadialla T, Retnakaran A, Smagghe G (2005) Insect growth-and development-disrupting insecticides. In: Gilbert LI, Iatrou K, Gill SS (eds) Comprehensive insect molecular science, volume 6: control. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 121–181
Dübendorfer A, Liebig B (1992) Cell differentiation in vitro and establishment of permanent, ecdysone-responsive cell lines from embryonic tissues of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata. J Insect Physiol 38(6):397–407
Fallon AM, Gerenday A (2010) Ecdysone and the cell cycle: investigations in a mosquito cell line. J Insect Physiol 56(10):1396–1401
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Marine Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299
Gandhi JKJ, Herms DA (2010) North American arthropods at risk due to widespread Fraxinus mortality caused by the alien emerald ash borer. Biol Invasions 12:1839–1846
Gonsalves SE, Neal SJ, Kehoe AS, Westwood JT (2011) Genome-wide examination of the transcriptional response to ecdysteroids 20-hydroxyecdysone and ponasterone A in Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Genomics 12:475
Goodman CL, Stanley D, Ringbauer JA Jr, Beeman RW, Silver K, Park Y (2012) A cell line derived from the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 48:426–433
Goodwin RH, Tompkins GJ, McCawley P (1978) Gypsy moth cell lines divergent in viral susceptibility. I. Culture and identification. In Vitro 14:485–494
Harvey G, Sohi S (1985) Isozyme characterization of 28 cell lines from five insect species. Can J Zool 63:2270–2276
Hashimoto Y, Zhang S, Zhang S, Chen Y, Blissard GW (2012) Correction: BTI-Tnao38, a new cell line derived from Trichoplusia ni, is permissive for AcMNPV infection and produces high levels of recombinant proteins. BMC Biotechnol 12:12. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-12-12
Herms DA, McCullough DG (2014) Emerald ash borer invasion of North America: history, biology, ecology, impacts, and management. Annu Rev Entomol 59:13–30
Hink WF (1970) Established insect cell line from the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Nature 226:466–467
Hoshino K, Hirose M, Iwabuchi K (2009) A new insect cell line from the longicorn beetle Plagionotus christophi (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 45:19–22
Hu W, Cook BJ, Ampasala DR, Zheng S, Caputo G, Krell PJ, Retnakaran A, Arif BM, Feng Q (2004) Morphological and molecular effects of 20-hydroxyecdysone and its agonist tebufenozide on CF-203, a midgut-derived cell line from the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 55:68–78
Iwabuchi K (1999) An established cell line from the beetle, Xylotrechus pyrrhoderus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 35:612–615
Kayukawa T, Tateishi K, Shinoda T (2013) Establishment of a versatile cell line for juvenile hormone signaling analysis in Tribolium castaneum. Sci Rep 3:1570. doi:10.1038/srep01570
Khurad AM, Zhang M, Deshmukh CG, Bahekar RS, Tiple AD, Zhang C (2009) A new continuous cell line from larval ovaries of silkworm, Bombyx mori. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 45:414–419
Lam G, Hall BL, Bender M, Thummel C (1999) DHR3 is required for the prepupal–pupal transition and differentiation of adult structures during Drosophila metamorphosis. Dev Biol 212:204–216
Lawrence J (1982) Coleoptera. In: Parker SB (ed) Synopsis and classification of living organisms, vol 2. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 482–553
Lee LE, Bufalino MR, Christie AE, Frischer ME, Soin T, Tsui CK, Hanner RH, Smagghe G (2011) Misidentification of OLGA-PH-J/92, believed to be the only crustacean cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47:665–674
Lingafelter SW, Horner NV (1993) The cerambycidae of north-central Texas. Coleopt Bull 47:159–191
Lynn DE (2002) Methods for maintaining insect cell cultures. J Insect Sci 2:9
Lynn DE (2007) Available lepidopteran insect cell lines. Methods Mol Biol 388:117–137
Mayr LM, Bojanic D (2009) Novel trends in high-throughput screening. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:580–588
McIntosh AH, Grasela JJ, Matteri RL (1996) Identification of insect cell lines by DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF). Insect Mol Biol 5:187–195
Mitsuhashi J (2002) Invertebrate tissue culture methods. Springer, Tokyo
Mosallanejad H, Soin T, Smagghe G (2008) Selection for resistance to methoxyfenozide and 20-hydroxyecdysone in cells of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 67:36–49
Mosallanejad H, Badisco L, Swevers L, Soin T, Knapen D et al (2010) Ecdysone signaling and transcript signature in Drosophila cells resistant against methoxyfenozide. J Insect Physiol 56:1973–1985
Nakagawa Y (2005) Nonsteroidal ecdysone agonists. Vitam Horm 73:131–173
Palli SR, Sohi SS, Cook BJ, Lambert D, Ladd TR, Retnakaran A (1995) Analysis of ecdysteroid action in Malacosoma disstria cells: cloning selected regions of E75- and MHR3-like genes. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25:697–707
Pushparajan C, Claus JD, Marshall SDG, Visnovsky G (2013) Characterization of growth and Oryctes rhinoceros nudivirus production in attached cultures of the DSIR-HA-1179 coleopteran insect cell line. Cytotechnology 65:1003–1016
Ratnasingham S, Hebert PDN (2007) BOLD: the barcode of life data system: barcoding. Mol Ecol Notes 7:355–364
Retnakaran A, Krell P, Feng Q, Arif B (2003) Ecdysone agonists: mechanism and importance in controlling insect pests of agriculture and forestry. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 54:187–199
Rinaldini LM (1959) An improved method for the isolation and quantitative cultivation of embryonic cells. Exp Cell Res 16:477–505
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Smagghe G (2007) Insect cell lines as tools in insecticide mode of action research. In: Ishaaya I, Nauen R, Horowitz AR (eds) Insecticides design using advanced technologies. Springer, Berlin, pp 263–304
Smagghe G, Gomez LE, Dhadialla TS (2012) Bisacylhydrazine insecticides for selective pest control. Adv In Insect Phys 43:163–249
Smith SG, Virkki N (1978) Coleoptera. In: John B, Bauer H, Kayano H, Levan A, White M (eds) Animal cytogenetics, Vol. 3. Insecta 5. Gebrüder Borntraeger, Berlin
Sohi SS, Palli SR, Cook BJ, Retnakaran A (1995) Forest insect cell lines responsive to 20-hydroxyecdysone and two nonsteroidal ecdysone agonists, RH-5849 and RH-5992. J Insect Physiol 41:457–464
Soin T, Iga M, Swevers L, Rougé P, Janssen CR, Smagghe G (2009) Towards Coleoptera-specific high-throughput screening systems for compounds with ecdysone activity: development of EcR reporter assays using weevil (Anthonomus grandis)-derived cell lines and in silico analysis of ligand binding to A. grandis EcR ligand-binding pocket. Insect Biochem Molec Biol 39:523–534
Solomon JD (1995) Guide to insect borers in North American broadleaf trees and shrubs. USDA Forest Service Agriculture Handbook AH-706:735 pp
Spomer SM (2014) The longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) of Nebraska, USA: new state records, a checklist of known Species, and distribution maps. Coleopt Bull 68:297–315
Staheli JP, Boyce R, Kovarik D, Rose TM (2011) CODEHOP PCR and CODEHOP PCR primer design. Methods Mol Biol 687:57–73
Swevers L, Farrell PJ, Kravariti L, Xenou-Kokoletsi M, Sdralia N, Lioupis A, Morou E, Balatsos NA, Douris V, Georgoussi Z, Mazomenos B, Iatrou K (2003) Transformed insect cells as high throughput screening tools for the discovery of new bioactive compounds. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci 68:333–341
Swevers L, Soin T, Mosallanejad H, Iatrou K, Smagghe G (2008) Ecdysteroid signaling in ecdysteroid-resistant cell lines from the polyphagous noctuid pest Spodoptera exigua. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38(9):825–833
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Toya T, Fukasawa H, Masui A, Endo Y (2002) Potent and selective partial ecdysone agonist activity of chromafenozide in Sf9 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292(4):1087–1091
Tunnock S, Tagestad A (1973) Incidence of wood borer activity in green ash windbreak plantings in North Dakota. USDA Forest Service Division of State & Private Forestry R1, Missoula, Montana, Report no. 73–5, 13 p
Vaughn JL, Goodwin RH, Tompkins GJ, McCawley P (1977) The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro 13:213–217
Wheelock CE, Nakagawa Y, Harada T, Oikawa N, Akamatsu M, Smagghe G, Stefanou D, Iatrou K, Swevers L (2006) High-throughput screening of ecdysone agonists using a reporter gene assay followed by 3-D QSAR analysis of the molting hormonal activity. Bioorg Med Chem 14:1143–1159
Zhang Z (2011) Animal biodiversity: an introduction to higher-level classification and taxonomic richness. Zootaxa 3148:7–12
Zhang H, Zhang Y, Qin Q, Wang Y, Li X, Miao L, Yin Z, Zhang A, Qu L, Ding C (2006) A new cell line from larval fat bodies of the bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 42:290–293
Zheng G, Li M, Li C (2014) Establishment and characterization of three new cell lines from the embryonic tissue of Holotrichia oblita Faldermann (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 50:483–488
Zotti MJ, De Geyter E, Swevers L, Braz ASK, Scott LPB, Rougé P, Coll J, Grutzmacher AD, Lenardão EJ, Smagghe G (2013) A cell-based reporter assay for screening for EcR agonist/antagonist activity of natural ecdysteroids in Lepidoptera (Bm5) and Diptera (S2) cell cultures, followed by modeling of ecdysteroid-EcR interactions and normal mode analysis. Pestic Biochem Physiol 107:309–320
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Genomics Research and Development Initiative grant from NRCan to DD and a NSERC Strategic Grant, STP322185-05 to PJK. We would like to thank Dr. Guoxing Quan (Natural Resources Canada) for sharing results of preliminary experiments done with the NRCAN-Tb521 cell line.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: T. Okamoto
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table S1
CellTiter-Glo luminescent cell viability assay data (luminescence units) of 20E and three ecdysone agonists on NRCAN-Tb521 cells. (XLS 37 kb)
Supplementary Table S2
EC50 values of 20E, tebufenozide, methoxyfenozide and halofenozide on NRCAN-Tb521 cells. (XLS 34 kb)
Supplementary Figure S1
Sequence and pairwise alignment of the HR3 PCR products amplified from NRCAN-Tb521 cells. A DNA sequence of the HR3 “short” fragment, B DNA sequence of the HR3 “long” fragment, C Clustal Omega pairwise alignment of the translated “long” and “short” HR3 fragments. (DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, F., Caputo, G., Hooey, S. et al. Establishment of a cell line from the ash and privet borer beetle Tylonotus bimaculatus Haldeman and assessment of its sensitivity to diacylhydrazine insecticides. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 51, 905–914 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9917-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9917-8