Abstract
Background
During the radical operation, the suprapancreatic area is featured by anatomical complexity, and the lymph node dissection for this area is technically difficult and demanding.1,2,3,4 Previously, we have demonstrated the presence of disseminated cancer cells in the mesogastrium5,6 and presented a mesogastrium model for gastrectomy.7 As a consequence, laparoscopic D2 lymphadenectomy plus complete mesogastric excision (D2+CME) was proposed as a new concept in the surgical treatment of advanced gastric cancer.8 D2+CME procedure has been shown to be associated to lower number of free intraperitoneal cancer cells and with a better disease-free survival than conventional D2 gastrectomy.9 Under the concept of mesogastrium model, the proposed D2+CME procedure could help surgeons better define the anatomical boundaries of suprapancreatic mesogastrium, thus using it to achieve a complete and standard excision of the suprapancreatic area dissection. Here, we briefly present perioperative results of our case series with the laparoscopic curative subtotal gastrectomy and D2+CME with a R0 resection and present a video to detail the technical aspects of a laparoscopic D2+CME approach for suprapancreatic area dissection.
Methods
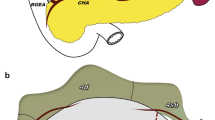
All patients in this study underwent laparoscopic subtotal gastrectomy (D2+CME) with a curative R0 resection. This study was approved by the Tongji Hospital Ethics Committee (Unique Reference Number: TJ-IRB20180811). The procedures in the video are described as follows. Based on our previous mesogastrium model (also named “Table model”, Supplemental Figure 1), the suprapancreatic mesogastrium is attached to the lesser curvature or the posterior gastric wall and extended to the suprapancreatic area, respectively.7 Surgeon stands on patient left side, and the assistant lifts the stomach upward and cephalic to expose the suprapancreatic mesogastrium including left gastric mesentery (LGM), right gastric mesentery (RGM) and posterior gastric mesentery (PGM). First of all, towards to the left side of the suprapancreatic area, the “tri-junction” point of LGM is exposed. Using an energy devise, surgeon opens serosa layer and identifies the retrogastric space. The LGM and PGM are mobilized bluntly, between which a fusion retrogastric space is revealed. Both the LGM and PGM are covered by smooth and shiny surfaces of fascial propria and regarded as the “meso-bed” mutually. Secondly, at the inner side of duodenum, surgeon bluntly separates the adjuvant tissues along gastro-duodenal artery (GDA) upward and exposes right gastric mesentery (RGM). Next, after mobilizing the left gastric mesentery, surgeon removes the adipose tissue adherent to the common hepatic artery (CHA) and exposes the root of the left gastric artery after dissecting the perivascular sheath with triple-clips. Then, surgeon dissects RGM along the CHA and portal vein (HPV) towards the right side of the suprapancreatic area; afterwards, the right gastric vessels and RGM are identified and ligated. Lastly, the superior border of splenic vessels is dissected. The anterior lobe of the PGM is raised up with ligated posterior gastric vessels. Remarkably, posterior gastric vessels may be absent in some cases. Reconstruction of the alimentary tract is Roux-en-Y method. Standard recovery protocols are followed in postoperative treatments.
Results
Between August 28th 2017 and December 27th 2018, 107 patients receiving laparoscopic curative subtotal gastrectomy (D2+CME) with a R0 resection were retrospective collected in this study. After exposing the suprapancreatic mesogastrium including RGM, PGM and LGM with D2+CME procedure, the LNs and fat tissues around 7, 9, 8a, 12a and 11p were removed en bloc in all patients. This study recruited 67 males and 40 females. The median age was 55 years, with body mass index (BMI) 23.0 kg/m2 (Supplemental Table 1). The median number of retrieved regional lymph nodes was 31 (range 25–41), including 22 (range 17–27.5) suprapancreatic lymph nodes. The median volume of blood loss was 14 ml (range 6-34). The median total operation time was 287 min (range 265.5–313.5) and laparoscopic surgery time was 132 min (range 116–142) (Supplemental Table 2). Postoperative morbidity occurred at a rate of 9.3 %, and the mortality rate was 0% (Supplemental Table 3). The median follow-up was 10 months (range 8–13). No patient was lost during follow-up (Supplemental Table 4).
Conclusion
A laparoscopic subtotal gastrectomy with D2+CME procedure provides for a complete and standardized en bloc excision of the suprapancreatic area dissection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D2+CME:
-
D2 lymphadenectomy plus complete mesogastric excision
References
Song KY, Kim SN, Park CH. Laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy with D2 lymph node dissection for gastric cancer: technical and oncologic aspects. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:655–659.
Noshiro H, Nagai E, Shimizu S, Uchiyama A, Tanaka M. Laparoscopically assisted distal gastrectomy with standard radical lymph node dissection for gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2005;19:1592–1596
Satoh S, Okabe H, et al. A novel laparoscopic approach for safe and simplified suprapancreatic lymph node dissection of gastric cancer. Surg Endosc.2009; 23(2):436–437
Kanaya S, Haruta S, et al. Laparoscopy distinctive technique for suprapancreatic lymph node dissection: medial approach for laparoscopic gastric cancer surgery. Surg Endosc 2011;25(12) :2928–9
Xie D, Osaiweran H, Liu L, et al. Mesogastrium: a fifth route of metastasis in gastric cancer? Med Hypotheses. 2013; 80(4):498–500.
Xie D, Liu L, Osaiweran H, et al. Detection and characterization of metastatic cancer cells in the mesogastrium of gastric cancer patients. PLoS One. 2015; 10(11):e0142970.
Xie D, Gao C, Lu A, et al. Proximal segmentation of the dorsal mesogastrium reveals new anatomical implications for laparoscopic surgery. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:16287.
Xie D, Yu C, Liu L, et al. Short-term outcomes of laparoscopic D2 lymphadenectomy with complete mesogastrium excision for advanced gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30(11):5138–9.
Xie D, Wang Y, Shen J, et al. Detection of carcinoembrionic antigen in peritoneal fluid of patients undergoing laparoscopic distal gastrectomy with complete mesogastric excision. British Journal of Surgery. 2018; DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.10881.
Acknowledgements
We thank Jackson Ferdinand Masau for recording the video and Dr. Chaoran Yu and Dr. Yi Li for the revision of the figures and manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China, grant number: 81773053, 81874185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.G., D.X. and A.X. performed the operations; B.C., J.S. collected the data; D.X. and B.C. wrote the paper; J.G. designed the research. All authors have reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, B., Xiao, A., Shen, J. et al. An Optimal Surgical Approach for Suprapancreatic Area Dissection in Laparoscopic D2 Gastrectomy with Complete Mesogastric Excision. J Gastrointest Surg 24, 916–917 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04467-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04467-8