Abstract
Background
Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) induces more rapid liver growth than portal vein ligation (PVL). Transection of parenchyma in ALPPS may prevent the formation of collaterals between lobes. The aim of this study was to determine if abrogating the formation of collaterals through parenchymal transection impacted growth rate.
Methods
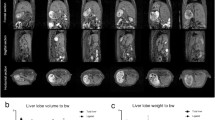
Twelve Yorkshire Landrace pigs were randomized to undergo ALPPS, PVL, or “partial ALPPS” by varying degrees of parenchymal transection. Hepatic volume was measured after 7 days. Portal blood flow and pressure were measured. Portal vein collaterals were examined from epoxy casts.
Results
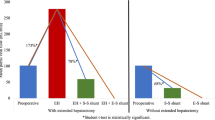
PVL, ALPPS, and partial ALPPS led to volume increases of the RLL by 15.5% (range 3–22), 64% (range 45–76), and 32% (range 18–77), respectively, with significant differences between PVL and ALPPS/partial ALPPS (p < 0.05). In PVL and partial ALPPS, substantial new portal vein collaterals were found. The number of collaterals correlated inversely with the growth rate (p = 0.039). Portal vein pressure was elevated in all models after ligation suggesting hyperflow to the portal vein-supplied lobe (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
These data suggest that liver hypertrophy following PVL is inversely proportional to the development of collaterals. Hypertrophy after ALPPS is likely more rapid due to reduction of collaterals through transection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vauthey JN, Mizuno T. Portal Vein Embolization: Tailoring, Optimizing, and Quantifying an Invaluable Procedure in Hepatic Surgery. Annals of surgical oncology. 2017
van Lienden KP, van den Esschert JW, de Graaf W, Bipat S, Lameris JS, van Gulik TM et al. Portal Vein Embolization Before Liver Resection: A Systematic Review. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology. 2012
Kishi Y, Madoff DC, Abdalla EK, Palavecino M, Ribero D, Chun YS et al. Is embolization of segment 4 portal veins before extended right hepatectomy justified? Surgery. 2008;144(5):744–51
Schnitzbauer AA, Lang SA, Goessmann H, Nadalin S, Baumgart J, Farkas SA et al. Right portal vein ligation combined with in situ splitting induces rapid left lateral liver lobe hypertrophy enabling 2-staged extended right hepatic resection in small-for-size settings. Annals of surgery. 2012;255(3):405–14
Schadde E, Ardiles V, Slankamenac K, Tschuor C, Sergeant G, Amacker N et al. ALPPS offers a better chance of complete resection in patients with primarily unresectable liver tumors compared with conventional-staged hepatectomies: results of a multicenter analysis. World journal of surgery. 2014;38(6):1510–9
van Lienden KP, Hoekstra LT, Bennink RJ, van Gulik TM. Intrahepatic left to right portoportal venous collateral vascular formation in patients undergoing right portal vein ligation. Cardiovascular and interventional radiology. 2013;36(6):1572–9
Wilms C, Mueller L, Lenk C, Wittkugel O, Helmke K, Krupski-Berdien G et al. Comparative study of portal vein embolization versus portal vein ligation for induction of hypertrophy of the future liver remnant using a mini-pig model. Annals of surgery. 2008;247(5):825–34
Kilkenny C, Altman DG. Improving bioscience research reporting: ARRIVE-ing at a solution. Lab Anim. 2010;44(4):377–8
Croome KP, Mao SA, Glorioso JM, Krishna M, Nyberg SL, Nagorney DM. Characterization of a porcine model for associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for a staged hepatectomy. HPB : the official journal of the International Hepato Pancreato Biliary Association. 2015;17(12):1130–6
Denys AL, Abehsera M, Sauvanet A, Sibert A, Belghiti J, Menu Y. Failure of right portal vein ligation to induce left lobe hypertrophy due to intrahepatic portoportal collaterals: successful treatment with portal vein embolization. AJR American journal of roentgenology. 1999;173(3):633–5
Furrer K, Tian Y, Pfammatter T, Jochum W, El-Badry AM, Graf R et al. Selective portal vein embolization and ligation trigger different regenerative responses in the rat liver. Hepatology. 2008;47(5):1615–23
Broering DC, Hillert C, Krupski G, Fischer L, Mueller L, Achilles EG et al. Portal vein embolization vs. portal vein ligation for induction of hypertrophy of the future liver remnant. Journal of gastrointestinal surgery : official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 2002;6(6):905–13; discussion 13
Eshmuminov D, Raptis DA, Linecker M, Wirsching A, Lesurtel M, Clavien PA. Meta-analysis of associating liver partition with portal vein ligation and portal vein occlusion for two-stage hepatectomy. The British journal of surgery. 2016;103(13):1768–82
Schlegel A, Lesurtel M, Melloul E, Limani P, Tschuor C, Graf R et al. ALPPS: from human to mice highlighting accelerated and novel mechanisms of liver regeneration. Annals of surgery. 2014;260(5):839–46; discussion 46-7
Yao L, Li C, Ge X, Wang H, Xu K, Zhang A et al. Establishment of a rat model of portal vein ligation combined with in situ splitting. PloS one. 2014;9(8):e105511
Almau Trenard HM, Moulin LE, Padin JM, Stringa P, Gondolesi GE, Barros Schelotto P. Development of an experimental model of portal vein ligation associated with parenchymal transection (ALPPS) in rats. Cirugia espanola. 2014;92(10):676–81
Wei W, Zhang T, Zafarnia S, Schenk A, Xie C, Kan C et al. Establishment of a rat model: Associating liver partition with portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy. Surgery. 2016;159(5):1299–307
Budai A, Fulop A, Hahn O, Onody P, Kovacs T, Nemeth T et al. Animal Models for Associating Liver Partition and Portal Vein Ligation for Staged Hepatectomy (ALPPS): Achievements and Future Perspectives. Eur Surg Res. 2017;58(3–4):140–57
Dhar DK, Mohammad GH, Vyas S, Broering DC, Malago M. A novel rat model of liver regeneration: possible role of cytokine induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 in augmented liver regeneration. Ann Surg Innov Res. 2015;9:11
Mise Y, Aloia TA, Conrad C, Huang SY, Wallace MJ, Vauthey JN. Volume regeneration of segments 2 and 3 after right portal vein embolization in patients undergoing two-stage hepatectomy. Journal of gastrointestinal surgery : official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 2015;19(1):133–41
Robles R, Parrilla P, Lopez-Conesa A, Brusadin R, de la Pena J, Fuster M et al. Tourniquet modification of the associating liver partition and portal ligation for staged hepatectomy procedure. The British journal of surgery. 2014;101(9):1129–34; discussion 34
Gall TM, Sodergren MH, Frampton AE, Fan R, Spalding DR, Habib NA et al. Radio-frequency-assisted Liver Partition With Portal Vein Ligation (RALPP) for Liver Regeneration. Annals of surgery. 2015;261(2):e45–6
Denys AL, Abehsera M, Leloutre B, Sauvanet A, Vilgrain V, O'Toole D et al. Intrahepatic hemodynamic changes following portal vein embolization: a prospective Doppler study. European radiology. 2000;10(11):1703–7
Schadde E, Tsatsaris C, Swiderska-Syn M, Breitenstein S, Urner M, Schimmer R et al. Hypoxia of the growing liver accelerates regeneration. Surgery. 2016
Allard MA, Adam R, Bucur PO, Termos S, Cunha AS, Bismuth H et al. Posthepatectomy portal vein pressure predicts liver failure and mortality after major liver resection on noncirrhotic liver. Annals of surgery. 2013;258(5):822–9; discussion 9-30
Belghiti J, Dokmak S, Schadde E. ALPPS: Innovation for innovation’s sake. Surgery. 2016;159(5):1287–8
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the extensive contributions of Karen Ohara to the organization and Diana Goldstein and Britanny Erdenberger to the performance of the animal experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All persons who meet authorship criteria are listed as authors, and all authors certify that they have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content, including participation in the concept, design, analysis, writing, or revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Approval for the experiments was obtained from the Internal Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Rush University Medical Center. All experiments were performed in compliance with the “Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals” by the National Research Council, 2011 edition (https://www.nap.edu/download/12910) and the ARRIVE guidelines.
Financial Support
The authors have not received extramural support for this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deal, R., Frederiks, C., Williams, L. et al. Rapid Liver Hypertrophy After Portal Vein Occlusion Correlates with the Degree of Collateralization Between Lobes—a Study in Pigs. J Gastrointest Surg 22, 203–213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-017-3512-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-017-3512-0