Abstract
Purpose
To test inter- and intraobserver consistency of liver stiffness measurement on MR elastography (MRE) at 3.0 T.
Materials and methods
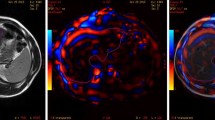
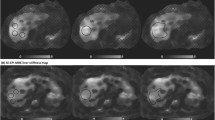
Two abdominal radiologists independently measured stiffness of the liver on MRE in three volunteers and seven patients with chronic liver diseases using three different region-of-interest (ROI) placement methods. Methods 1 and 2 involved placing circular and free-hand-drawn ROIs, respectively, visually referring to anatomical (three-dimensional T1-weighted) and wave images. Method 3 involved placing ROIs on the fused images of MRE and anatomical images developed on a work station, visually referring to wave images. The inter- and intraobserver consistency was assessed with regression and Bland–Altman analysis.
Results
Thirty-eight images were available for measurement in total. As for interobserver consistency, method 3 showed the best regression coefficient, correlation coefficient, and y intercept. The absolute values of the interobserver differences for method 3 were significantly smaller than those of method 1 or method 2 (p < 0.05, each). Intraobserver consistency of method 3 was excellent for both observers.
Conclusion
Stiffness measurement of the liver on MRE performed with the fusion method at 3.0 T provides the highest inter- and intraobserver consistency.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rouviere O, Yin M, Dresner MA, et al. MR elastography of the liver: preliminary results. Radiology. 2006;240:440–8.
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Salameh N, et al. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography versus aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology. 2007;245:458–66.
Klatt D, Asbach P, Rump J, et al. In vivo determination of hepatic stiffness using steady-state free precession magnetic resonance elastography. Invest Radiol. 2006;41:841–8.
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:32–40.
Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography of the liver: preliminary results and estimation of interrater reliability. Jpn J Radiol. 2010;28:623–7.
Asbach P, Klatt D, Schlosser B, et al. Viscoelasticity-based staging of hepatic fibrosis with multifrequency MR elastography. Radiology. 2010;257:80–6.
Shire NJ, Yi M, Chen J, et al. Test–retest repeatability of MR elastography for noninvasive liver fibrosis assessment in hepatitis C. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34:947–55.
Hines CDG, Bley TA, Lindstrom MJ, Reeder SB. Repeatability of magnetic resonance elastography for quantification of hepatic stiffness. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31:725–31.
Kim BH, Lee JM, Lee YJ, et al. MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: experience from a tertiary center in Asia. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34:1110–6.
Lee DH, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI. MR elastography of healthy liver parenchyma: normal value and reliability of the liver stiffness value measurement. JMRI, 2013 [pEpub ahead of print].
Sonn GA, Natarajan S, Margolis DJ, et al. Targeted biopsy in the detection of prostate cancer using an office based magnetic resonance ultrasound fusion device. J Urol. 2012;189:86–9.
Nishie A, Stolpen AH, Obuchi M, Kuehn DM, Dagit A, Andresen K. Evaluation of locally recurrent pelvic malignancy: performance of T2- and diffusion-weighted MRI with image fusion. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;28(3):705–13.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mitsufuji, T., Shinagawa, Y., Fujimitsu, R. et al. Measurement consistency of MR elastography at 3.0 T: comparison among three different region-of-interest placement methods. Jpn J Radiol 31, 336–341 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-013-0195-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-013-0195-7