Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to clarify the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings of large chromophobe renal cell carcinomas.
Materials and methods
Five patients diagnosed pathologically with chromophobe renal cell carcinoma are included. MRI findings were retrospectively evaluated for the tumor contour, uniformity and hypointensity of the rim of the tumor on T2-weighted images, “microscopic fat,” enhancement degree and pattern on dynamic study, and necrosis in the tumor, among other findings.
Results
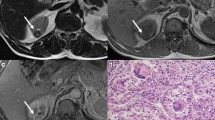
The tumor size ranged from 4.8 to 13.7 cm (mean 7.9 cm). The tumor contour was well defined in four patients. All but one tumor showed a hypointensity rim, and all tumors had a heterogeneous appearance on T2-weighted images. “Microscopic fat” was detected in one case. All tumors demonstrated low enhancement compared to that of the renal cortex. All tumors showed heterogeneous enhancement on postcontrast images. Necrosis was seen in four. Hemorrhage and renal vein thrombosis was seen in one.
Conclusion
Chromophobe renal cell carcinomas of large size tend to have a heterogeneous appearance on postcontrast and T2-weighted images, a well-defined tumor contour with a hypointensity rim on T2-wighted images, and lower enhancement than that of the renal cortex. Tumor necrosis is easily apparent, and “microscopic fat” may be observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thoenes W, Storkel S, Rumpelt HJ. Human chromophobe cell renal carcinoma. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 1985;48:207–217.
Amin MB, Paner GP, Alvarado-Cabrero I, Young AN, Stricker HJ, Lyles RH, et al. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: histomorphologic characteristics and evaluation of conventional pathologic prognostic parameters in 145 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1822–1834.
Thoenes W, Storkel S, Rumpelt HJ, Moll R, Baum HP, Werner S. Chromophobe cell renal carcinoma and its variants: a report on 32 cases. J Pathol 1988;155:277–287.
Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, Weaver AL, Blute ML. Comparisons of outcome and prognostic features among histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:612–624.
Capitanio U, Cloutier V, Zini L, Isbarn H, Jeldres C, Shariat SF, et al. A critical assessment of the prognostic value of clear cell, papillary and chromophobe histological subtypes in renal cell carcinoma: a population-based study. BJU Int 2009;103:1496–1500.
Gudbjartsson T, Hardarson S, Petursdottir V, Thoroddsen A, Magnusson J, Einarsson GV. Histological subtyping and nuclear grading of renal cell carcinoma and their implications for survival: a retrospective nation-wide study of 629 patients. Eur Urol 2005;48:593–600.
Schrader AJ, Olbert PJ, Hegele A, Varga Z, Hofmann R. Metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: current therapeutic options. BJU Int 2008;101:1343–1345.
Prasad SR, Humphrey PA, Catena JR, Narra VR, Srigley JR, Cortez AD, et al. Common and uncommon histologic sub types of renal cell carcinoma: imaging spectrum with pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2006;26:1795–1806; discussion 806–10.
Fujimoto H, Wakao F, Moriyama N, Tobisu K, Sakamoto M, Kakizoe T. Alveolar architecture of clear cell renal carcinomas (< or =5.0 cm) show high attenuation on dynamic CT scanning. Jpn J Clin Oncol 1999;29:198–203.
Jinzaki M, Tanimoto A, Mukai M, Ikeda E, Kobayasi S, Yuasa Y, et al. Double-phase helical CT of small renal parenchymal neoplasms: correlation with pathologic findings and tumor angiogenesis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2000;24:835–842.
Zhang J, Lefkowitz RA, Ishill NM, Wang L, Moskowitz CS, Russo P, et al. Solid renal cortical tumors: differentiation with CT. Radiology 2007;244:494–504.
Kim JK, Kim TK, Ahn HJ, Kim CS, Kim KR, Cho KS. Differentiation of subtypes of renal cell carcinoma on helical CT scans. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002;178:1499–1506.
Kondo T, Nakazawa H, Sakai F, Kuwata T, Onitsuka S, Hashimoto Y, et al. Spoke-wheel-like enhancement as an important imaging finding of chromophobe cell renal carcinoma: a retrospective analysis on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging studies. Int J Urol 2004;11:817–824.
Pedrosa I, Chou MT, Ngo L, H Baroni R, Genega EM, Galaburda L, et al. MR classification of renal masses with pathologic correlation. Eur Radiol 2008;18:365–375.
Sengupta S, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Frank I, Thompson RH, Webster WS, et al. Histologic coagulative tumor necrosis as a prognostic indicator of renal cell carcinoma aggressiveness. Cancer 2005;104:511–520.
Zini L, Leroy X, Lemaitre L, Devos P, Aubert S, Biserte J, et al. Tumour necrosis in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: clinical data to distinguish aggressive variants. Eur J Surg Oncol 2008;34:687–691.
Outwater EK, Bhatia M, Siegelman ES, Burke MA, Mitchell DG. Lipid in renal clear cell carcinoma: detection on opposedphase gradient-echo MR images. Radiology 1997;205:103–107.
Yoshimitsu K, Kakihara D, Irie H, Tajima T, Nishie A, Asayama Y, et al. Papillary renal carcinoma: diagnostic approach by chemical shift gradient-echo and echo-planar MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;23:339–344.
Onishi T, Ohishi Y, Goto H, Suzuki M, Miyazawa Y. Papillary renal cell carcinoma: clinicopathological characteristics and evaluation of prognosis in 42 patients. BJU Int 1999;83:937–943.
Rothman J, Egleston B, Wong YN, Iffrig K, Lebovitch S, Uzzo RG. Histopathological characteristics of localized renal cell carcinoma correlate with tumor size: a SEER analysis. J Urol 2009;181:29–33; discussion 33–24.
Roy C Sr, El Ghali S, Buy X, Lindner V, Lang H, Saussine C, et al. Significance of the pseudocapsule on MRI of renal neoplasms and its potential application for local staging: a retrospective study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184:113–120.
Sun MR, Ngo L, Genega EM, Atkins MB, Finn ME, Rofsky NM, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging for differentiation of tumor subtypes: correlation with pathologic findings. Radiology 2009;250:793–802.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaguri, K., Irie, H., Kamochi, N. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of large chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. Jpn J Radiol 28, 453–459 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0450-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0450-0