Abstract
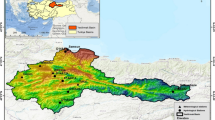
The management of water resources and the modeling of river flow have a prominent position within environmental research. They form a critical bridge between human societies and the delicate ecosystems they inhabit. Scholars have focused on benefiting more efficient methods based on the use of artificial intelligence for river flow forecasting, notably because modeling hydrological systems is quite challenging. This study primarily centered on exploring the predictive capacities of hybrid models in establishing a link between daily flow data and prospective data. In the study, the mentioned algorithms, firefly algorithm (FFA), artificial bee colony (ABC), genetic algorithm (GA), were hybridized with the artificial neural network (ANN) model and data analyzes were examined with the stations in the Konya Closed Basin. A comparative analysis of FFA–ANN, GA–ANN, ABC–ANN, and long short-term memory (LSTM) models was conducted for daily flow forecasting for daily flow forecasting according to a range of graphical and statistical metrics. The outcomes indicate that the FFA–ANN hybrid model generally performed better than other models and the deep learning algorithm.













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data will be available upon reasonable request.
References
Abdul Kareem B, Zubaidi SL, Ridha HM et al (2022) Applicability of ANN model and CPSOCGSA algorithm for multi-time step ahead river streamflow forecasting. Hydrology 9:171. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9100171
Abdullah NA, Abd Rahim N, Gan CK, Nor Adzman N (2019) Forecasting solar power using hybrid firefly and particle swarm optimization (HFPSO) for optimizing the parameters in a wavelet transform-adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (WT-ANFIS). Appl Sci 9(16):3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163214
Adnan RM, Mirboluki A, Mehraein M et al (2023) Improved prediction of monthly streamflow in a mountainous region by metaheuristic-enhanced deep learning and machine learning models using hydroclimatic data. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04624-9
Aghelpour P, Graf R, Tomaszewski E (2023) Coupling ANFIS with ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm for 1-, 2-, and 3-days ahead forecasting of daily streamflow, a case study in Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(19):56440–56463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26239-3
Ahmad D, Afzal M (2021) Flood hazards, human displacement and food insecurity in rural riverine areas of Punjab, Pakistan: policy implications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:10125–10139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11430-7
Akdağ M, Celebi M (2022) The weight optimization of oil-type transformer with firefly algorithm. Dicle Univ J Eng 13(2):169–180. https://doi.org/10.24012/dumf.1075008
Armaghani DJ, Asteris PG (2021) A comparative study of ANN and ANFIS models for the prediction of cement-based mortar materials compressive strength. Neural Comput Appl 33:4501–4532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05244-4
Aydilek İB (2017) Değiştirilmiş ateşböceği optimizasyon algoritması ile kural tabanlı çoklu sınıflama yapılması: multi-class classification with modified firefly optimization algorithm. J Fac Eng Archit Gazi Univ 32:1097–1107. https://doi.org/10.17341/gazimmfd.369406
Balachennaiah P, Suryakalavathi M, Nagendra P (2018) Firefly algorithm based solution to minimize the real power loss in a power system. Ain Shams Eng J 9:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2015.10.005
Banadkooki FB, Haghighi AT (2023) Groundwater level modeling using multiobjective optimization with hybrid artificial intelligence methods. Environ Model Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-023-09938-6
Beiranvand B, Ashofteh P-S (2023) A systematic review of optimization of dams reservoir operation using the meta-heuristic algorithms. Water Resour Manag 37:3457–3526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03510-3
Bezdan T, Cvetnic D, Gajic L, et al. (2021) Feature selection by firefly algorithm with improved initialization strategy. In: 7th Conference on the engineering of computer based systems. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, pp 1–8
Bozdağ A (2015) Combining AHP with GIS for assessment of irrigation water quality in Çumra irrigation district (Konya), Central Anatolia, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 73:8217–8236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3972-4
Darbandi S, Pourhosseini FA (2018) River flow simulation using a multilayer perceptron-firefly algorithm model. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0713-y
Descovi CS, Zuffo AC, Mohammadizadeh S et al (2023) Utilizing long short-term memory (LSTM) networks for river flow prediction in the Brazilian Pantanal Basin. HOLOS. https://doi.org/10.15628/holos.2023.16315
Di Nunno F, Zhu S, Ptak M et al (2023) A stacked machine learning model for multi-step ahead prediction of lake surface water temperature. Sci Total Environ 890:164323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164323
Elgeldawi E, Sayed A, Galal AR, Zaki AM (2021) Hyperparameter tuning for machine learning algorithms used for Arabic sentiment analysis. Informatics 8:79. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics8040079
Esmaeili H, Hakami V, Minaei Bidgoli B, Shokouhifar M (2022) Application-specific clustering in wireless sensor networks using combined fuzzy firefly algorithm and random forest. Expert Syst Appl 210:118365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118365
Esraa E, Mohamed N, Fatma S, Ahmed B (2023) WEAP analysis for enhancing water resource sustainability in Egypt: a dynamic modeling approach for long-term planning and management. HBRC J 19:253–274. https://doi.org/10.1080/16874048.2023.2260602
Ewees AA, Abualigah L, Yousri D et al (2022) Improved slime mould algorithm based on firefly algorithm for feature selection: a case study on QSAR model. Eng Comput 38:2407–2421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01342-6
Farfán JF, Cea L (2021) Coupling artificial neural networks with the artificial bee colony algorithm for global calibration of hydrological models. Neural Comput & Applic 33:8479–8494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05601-3
Feigl M, Lebiedzinski K, Herrnegger M, Schulz K (2021) Machine-learning methods for stream water temperature prediction. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 25:2951–2977. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-25-2951-2021
Frame JM, Kratzert F, Klotz D et al (2022) Deep learning rainfall–runoff predictions of extreme events. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 26:3377–3392. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-26-3377-2022
Gao W, Liu S, Huang L (2012) A global artificial bee colony algorithm for global optimization. J Comput Appl Math 236:2741–2753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2012.01.013
Ghambari S, Rahati A (2018) An improved artificial bee colony algorithm and its application to reliability optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 62:736–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.10.040
Ghimire S, Deo RC, Downs NJ, Raj N (2019) Global solar radiation prediction by ANN integrated with European Centre for medium range weather forecast fields in solar rich cities of Queensland Australia. J Clean Prod 216:288–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.158
Haznedar B, Kilinc HC (2022) A Hybrid ANFIS-GA approach for estimation of hydrological time series. Water Resour Manag 36:4819–4842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03280-4
İgde E (2023) A research on mathematical models used in multilayer artificial neural networks. Master’s Thesis, Hatay Mustafa Kemal University, Hatay, Turkey
Karaboga D (2010) Artificial bee colony algorithm. Scholarpedia 5:6915. https://doi.org/10.4249/scholarpedia.6915
Karaboga D, Akay B (2009) A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl Math Comput 214:108–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2009.03.090
Karaman A, Karaboga D, Pacal I et al (2023) Hyper-parameter optimization of deep learning architectures using artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm for high performance real-time automatic colorectal cancer (CRC) polyp detection. Appl Intell 53:15603–15620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04299-1
Katipoğlu OM (2023) Evaluation of the performance of data-driven approaches for filling monthly precipitation gaps in a semi-arid climate conditions. Acta Geophys 71:2265–2285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00963-9
Khatibi R, Ghorbani MA, Pourhosseini FA (2017) Stream flow predictions using nature-inspired firefly algorithms and a multiple model strategy—directions of innovation towards next generation practices. Adv Eng Inform 34:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2017.10.002
Kılıç S (2023) Explaining artificial neural networks with decision tree ensembles. Master’s Thesis, Graduate School of Science and Engineering of Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey
Kisi O, Shiri J, Karimi S, Shamshirband S, Motamedi S, Petković D, Hashim R (2015) A survey of water level fluctuation predicting in Urmia Lake using support vector machine with firefly algorithm. Appl Math Comput 270:731–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2015.08.085
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Li J, Yuan X (2023) Daily streamflow forecasts based on cascade long short-term memory (LSTM) model over the Yangtze River Basin. Water 15:1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061019
Li Y, Zhao Y, Shang Y, Liu J (2021) An improved firefly algorithm with dynamic self-adaptive adjustment. PLoS ONE 16:e0255951. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0255951
Linzi Z (2023) Short-term power load forecasting based on FA-LSTM with similar day selection. In: 2023 IEEE 3rd international conference on electronic technology, communication and information (ICETCI), pp 1110–1115
Liu S, Zhou X, Li B et al (2023) Improving short-term streamflow forecasting by flow mode clustering. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37:1799–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02367-z
Merufinia E, Sharafati A, Abghari H, Hassanzadeh Y (2022) On the simulation of streamflow using hybrid tree-based machine learning models: a case study of Kurkursar basin. Iran Arab J Geosci 16:28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-11045-x
Mohammadi B (2023) Modeling various drought time scales via a merged artificial neural network with a firefly algorithm. Hydrology 10:58. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10030058
Mohammadi B, Vazifehkhah S, Duan Z (2024) A conceptual metaheuristic-based framework for improving runoff time series simulation in glacierized catchments. Eng Appl Artif Intell 127:107302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107302
Mughal RCZ, Nawaz U, Ahmed S et al (2023) A novel FFA–GWO-based optimization paradigm for solving a dynamic economic emission dispatch in power plants. IET Renew Power Gener 17:3163–3178. https://doi.org/10.1049/rpg2.12833
Ojile MO, Ogwara EO (2022) Vulnerability of communities to flood hazard and riverbank erosion along River Nun in Bayelsa State, Nigeria. Glob J Adv Eng Technol Sci 9:1–8
Ölmez E (2023) Bootstrapped dendritic neuron model artificial neural network. Master’s Thesis, Giresun University, Giresun, Turkey
Önder S (2006) Environmental pollution and solution recommendations of Konya City, Turkey. J Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2006.864.871
Ozturk AC, Haznedar H, Haznedar B et al (2023) Differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules with anfis by using genetic algorithm and proposing a novel CAD-based risk stratification system of thyroid nodules. Diagnostics 13:740. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13040740
Paryani S, Neshat A, Pourghasemi HR et al (2022) A novel hybrid of support vector regression and metaheuristic algorithms for groundwater spring potential mapping. Sci Total Environ 807:151055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151055
Rahimzad M, Moghaddam Nia A, Zolfonoon H et al (2021) Performance comparison of an LSTM-based deep learning model versus conventional machine learning algorithms for streamflow forecasting. Water Resour Manag 35:4167–4187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02937-w
Rowiński PM, Okruszko T, Radecki-Pawlik A (2022) Environmental hydraulics research for river health: recent advances and challenges. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 22:213–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2021.12.003
Samui P, Yesilyurt SN, Dalkilic HY et al (2023) Comparison of different optimized machine learning algorithms for daily river flow forecasting. Earth Sci Inform 16:533–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00896-3
Seidu J, Ewusi A, Kuma JSY et al (2023) Impact of data partitioning in groundwater level prediction using artificial neural network for multiple wells. Int J River Basin Manag 21:639–650. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2022.2079653
Shumilova O, Tockner K, Sukhodolov A et al (2023) Impact of the Russia–Ukraine armed conflict on water resources and water infrastructure. Nat Sustain 6:578–586. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-023-01068-x
Singh S, Chauhan P, Singh N (2020) Capacity optimization of grid connected solar/fuel cell energy system using hybrid ABC-PSO algorithm. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:10070–10088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.02.018
Sofi MS, Rautela KS, Muslim M et al (2023) Modeling the hydrological response of a snow-fed river in the Kashmir Himalayas through SWAT and artificial neural network. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05170-7
Song Z, Tang C, Song S et al (2023) A complex network-based firefly algorithm for numerical optimization and time series forecasting. Appl Soft Comput 137:110158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110158
Subramanian A, Mosur Nagarajan A, Vinod S et al (2023) Long-term impacts of climate change on coastal and transitional eco-systems in India: an overview of its current status, future projections, solutions, and policies. RSC Adv 13:12204–12228. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA07448F
Tao H, Al-Sulttani AO, Salih Ameen AM et al (2020) Training and testing data division influence on hybrid machine learning model process: application of river flow forecasting. Complexity 2020:e8844367. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8844367
Tongal H, Booij MJ (2023) Simulated annealing coupled with a Naïve Bayes model and base flow separation for streamflow simulation in a snow dominated basin. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37:89–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02276-1
Topak R, Bilal A (2010) Konya basin agriculture-environment relationships and sustainability. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international symposium on sustainable development, Sarajevo, Bosnia Herzegovina.
Tounsi A, Abdelkader M, Temimi M (2023) Assessing the simulation of streamflow with the LSTM model across the continental United States using the MOPEX dataset. Neural Comput Appl 35:22469–22486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08922-1
Wahid F, Alsaedi AKZ, Ghazali R (2019) Using improved firefly algorithm based on genetic algorithm crossover operator for solving optimization problems. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 36(2):1547–1562
Wiek A, Larson KL (2012) Water, people, and sustainability—a systems framework for analyzing and assessing water governance regimes. Water Resour Manag 26:3153–3171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0065-6
Wu J, Wang Z (2022) A hybrid model for water quality prediction based on an artificial neural network, wavelet transform, and long short-term memory. Water 14:610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040610
Yang XS (2010) Firefly algorithm, levy flights and global optimization. In: Bramer M, Ellis R, Petridis M (eds) Research and development in intelligent systems XXVI. Springer, London, pp 209–218
Yang XS (2009) Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In: Proceedings of the stochastic algorithms: foundations and applications, lecture notes in computing sciences, 5th international symposium, SAGA 2009. Springer, Sapporo, pp 169–178
Yaseen ZM, Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H et al (2017) Novel approach for streamflow forecasting using a hybrid ANFIS-FFA model. J Hydrol 554:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.09.007
Yılmaz G, Çolak MA, Özgencil İK et al (2021) Decadal changes in size, salinity, waterbirds, and fish in lakes of the Konya Closed Basin, Turkey, associated with climate change and increasing water abstraction for agriculture. Inland Waters 11:538–555. https://doi.org/10.1080/20442041.2021.1924034
Zhu S, Di Nunno F, Ptak M et al (2023) A novel optimized model based on NARX networks for predicting thermal anomalies in Polish lakes during heatwaves, with special reference to the 2018 heatwave. Sci Total Environ 905:167121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167121
Zivkovic M, et al. (2021) Hybrid genetic algorithm and machine learning method for COVID-19 cases prediction. In: Proceedings of international conference on sustainable expert systems: ICSES 2020. Springer Singapore, Singapore
Acknowledgements
The author is immensely grateful to the General Directorate of State Hydraulic Works for their support and cooperation in sharing the required data. We would like to extend our sincere thanks to both the Editor and the anonymous reviewers for their invaluable contributions to the content and development of this paper.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HCK and OMK contributed to supervision, methodology, validation, and software. BH contributed to conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, and software. FO contributed to writing—reviewing and editing. The authors give their full consent for the publication of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
The authors undertake that this article has not been published in any other journal and that no plagiarism has occurred.
Consent to participate
The authors agree to participate in the journal.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publish in the journal.
Additional information
Edited by Dr. Hossein Hamidifar (ASSOCIATE EDITOR) / Prof. Jochen Aberle (CO-EDITOR-IN-CHIEF).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kilinc, H.C., Haznedar, B., Katipoğlu, O.M. et al. A comparative study of daily streamflow forecasting using firefly, artificial bee colony, and genetic algorithm-based artificial neural network. Acta Geophys. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-024-01362-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-024-01362-y