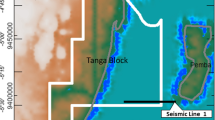
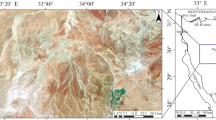
Abstract
West Papua province in eastern Indonesia is positioned in a dynamic tectonic zone along with the collision of the Australian, Pacific, and Eurasian plates. The interaction resulted in the formation of strike-slip faults such as Koor, Sorong, Ransiki, and Yapen, that are prone to earthquakes in the region. The rocks of West Papua in the northern part are a contribution to the Pacific Ocean plate consisting of ophiolite and volcanic arcs of the archipelago, even while the rocks of the Australian plate in the southern part are dominated by quaternary and siliciclastic sedimentary. It has a wide variety of resources, including oil and gas. This study combines the interpretation of regional gravity and magnetic data derived from satellite observations to identify the subsurface structure of West Papua. This is performed since most studies were conducted on the surface and did not significantly focus on the subsurface. The composition of subsurface is determined through three-dimensional (3-D) unconstrained inversion modeling using the iterative reweighting inversion of regional gravity and magnetic anomalies as a function of density contrast and magnetic susceptibility of rocks. In depth variations, gravity inversion produces density contrast ranging from − 0.348 to 0.451 gr/cm3, whereas magnetic inversion provides rock susceptibility varying between − 0.363 and 0.223 SI. Gravity and magnetic inversions characterize the subduction of the Pacific Ocean plate in the north, extensive intrusion of igneous rocks, and low density-susceptibility contrast in the Bintuni basin as a source of oil and natural gas. The boundary between the sediment layer and the basement is believed to be 15–20 km deep, with rocks from the uplifted mantle in the north and a Silur-Devon aged Kemum formation in the south.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Abderbi J, Khattach D, Kenafi J (2017) Multiscale analysis of the geophysical lineaments of the High Plateaus (Eastern Morocco): structural implications. J Mat Environ Sci 8(2):467–475
Afshar A, Norouzi G-H, Moradzadeh A, Riahi M-A (2018) Application of magnetic and gravity methods to the exploration of sodium sulfate deposits, case study: Garmab mine, Semnan, Iran. J Appl Geophys 159:586–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.10.003
Akin U, Şeri̇foğlu Bİ, Duru M, (2011) The use of tilt angle in gravity and magnetic methods. Bull Miner Res Explor 143(143):1–12
Baldwin SL, Fitzgerald PG, Webb LE (2012) Tectonics of the New Guinea region. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 40(1):495–520. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152540
Balmino G, Vales N, Bonvalot S, Briais A (2012) Spherical harmonic modelling to ultra-high degree of Bouguer and isostatic anomalies. J Geodesy 86(7):499–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0533-4
Charlton TR (2010) The Pliocene-recent anticlockwise rotation of the Bird’s head, the opening of the Aru Trough—Cendrawasih Bay Sphenochasm, and the Closure of the Banda Double Arc. http://archives.datapages.com/data/ipa_pdf/081/081001/pdfs/IPA10-G-008.htm
Daniarsyad G, Suardi I (2017) Stress triggering among MW ≥ 6.0 significant earthquakes in Manokwari Trough. AIP Conf Proc 1857(1):020014. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4987056
Dentith MC, Mudge ST (2014) Geophysics for the mineral exploration geoscientist. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
El-Isa ZH, Eaton DW (2014) Spatiotemporal variations in the b-value of earthquake magnitude–frequency distributions: classification and causes. Tectonophysics 615–616:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2013.12.001
Ellis RG, MacLeod IN (2013) Constrained voxel inversion using the Cartesian cut cell method. ASEG Ext Abstr 2013(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1071/ASEG2013ab222
Eshaghzadeh A, Dehghanpour A, Kalantari RA (2018) Application of the tilt angle of the balanced total horizontal derivative filter for the interpretation of potential field data. Bollettino Di Geofisica Teorica Ed Applicata 59(2):161–178. https://doi.org/10.4430/bgta0233
Gold DP, Burgess PM, BouDagher-Fadel MK (2017a) Carbonate drowning successions of the Bird’s Head, Indonesia. Facies 63(4):25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-017-0506-z
Gold DP, White LT, Gunawan I, BouDagher-Fadel MK (2017b) Relative sea-level change in western New Guinea recorded by regional biostratigraphic data. Mar Petroleum Geol 86:1133–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.016
Gómez-García ÁM, Meeßen C, Scheck-Wenderoth M, Monsalve G, Bott J, Bernhardt A, Bernal G (2019) 3-D Modeling of vertical gravity gradients and the delimitation of tectonic boundaries: the Caribbean oceanic domain as a case study. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 20(11):5371–5393. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GC008340
Gushurst G, Mahatsente R (2020) Lithospheric structure of the Central Andes Forearc from gravity data modeling: implication for plate coupling. Lithosphere 2020(1):8843640. https://doi.org/10.2113/2020/8843640
Handyarso A, Padmawidjaja T (2017) Struktur Geologi Bawah Permukaan Cekungan Bintuni Berdasarkan Data Gaya Berat. Jurnal Geologi Dan Sumberdaya Mineral 18(2):53–65. https://doi.org/10.33332/jgsm.geologi.v18i2.125
Hinze WJ, von Frese RRB, Saad AH (2013) Gravity and magnetic exploration: principles, practices, and applications. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511843129
Ibraheem IM, Haggag M, Tezkan B (2019) Edge detectors as structural imaging tools using aeromagnetic data: a case study of Sohag Area, Egypt. Geosciences 9(5):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9050211
Ince ES, Barthelmes F, Reißland S, Elger K, Förste C, Flechtner F, Schuh H (2019) ICGEM—15 years of successful collection and distribution of globalgravitational models, associated services and future plans. Earth Syst Sci Data 11(2):647–674. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-2019-17
Ingram DM, Causon DM, Mingham CG (2003) Developments in Cartesian cut cell methods. Math Comput Simul 61(3):561–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4754(02)00107-6
Kalaneh S, Agh-Atabai M (2016) Spatial variation of earthquake hazard parameters in the Zagros fold and thrust belt, SW Iran. Nat Hazards 82(2):933–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2227-y
Laske G, Masters G, Ma Z, Pasyanos M (2013) Update on CRUST1.0—A 1-degree global model of Earth’s crust. In: Abstract EGU2013-2658 Presented at 2013 Geophys. Res. Abstracts, vol 15, no 15, p 2658
Lewerissa R, Sismanto S, Setiawan A, Pramumijoyo S (2020) The igneous rock intrusion beneath Ambon and Seram islands, eastern Indonesia, based on the integration of gravity and magnetic inversion: its implications for geothermal energy resources. Turkish J Earth Sci 29(4):596–616. https://doi.org/10.3906/yer-1908-17
Lewerissa R, Rumakey R, Syakur YA, Lapono L (2021) Completeness magnitude (Mc) and b-value characteristics as important parameters for future seismic hazard assessment in the West Papua province Indonesia. Arab J Geosci 14(23):2588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08885-4
Li Y, Oldenburg DW (1996) 3-D inversion of magnetic data. Geophysics 61(2):394–408. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1443968
Li Y, Oldenburg DW (1998) 3-D inversion of gravity data. Geophysics 63(1):109–119. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1444302
Makrup L, Hariyanto A, Winarno S (2018) Seismic Hazard Map for Papua Island. Int Rev Civ Eng (IRECE) 9:57. https://doi.org/10.15866/irece.v9i2.14090
Maus S, Barckhausen U, Berkenbosch H, Bournas N, Brozena J, Childers V, Dostaler F, Fairhead JD, Finn C, von Frese RRB, Gaina C, Golynsky S, Kucks R, Lühr H, Milligan P, Mogren S, Müller RD, Olesen O, Pilkington M, Saltus R, Schreckenberger B, Caratori Tontini F (2009) EMAG2: a 2-arc min resolution Earth Magnetic Anomaly Grid compiled from satellite, airborne, and marine magnetic measurements. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 10(8). https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GC002471
Meyer B, Chulliat A, Saltus R (2017) Derivation and Error analysis of the earth magnetic anomaly grid at 2 arc min resolution version 3 (EMAG2v3). Geochem Geophys Geosyst 18(12):4522–4537. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GC007280
Milsom J (1991) Gravity measurements and terrane tectonics in the New Guinea region. J Southeast Asian Earth Sci 6(3–4):319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/0743-9547(91)90077-B
Milsom J, Masson D, Nichols G, Sikumbang N, Dwiyanto B, Parson L, Kallagher H (1992) The Manokwari Trough and the western end of the New Guinea Trench. Tectonics 11(1):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1029/91TC01257
Oldenburg DW, Li Y (1994) Subspace linear inverse method. Inverse Prob 10(4):915–935. https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/10/4/011
Oldenburg D, Li Y (2005) 5. Inversion for applied geophysics: a tutorial. Near Surf Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.9781560801719.ch5
Putra A, Husein S (2019) Regional overview of orogenic belts in Indonesia: emphasis on the occurrences of thrust wedge systems. Berita Sedimentologi 44:19–41
Reynolds JM (1997) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics. John Wiley, London
Saibi H, Hag DB, Alamri MSM, Ali HA (2021) Subsurface structure investigation of the United Arab Emirates using gravity data. Open Geosci 13(1):262–271. https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2020-0233
Serhalawan YR, Sianipar DSJ (2017) Pemodelan Mekanisme Sumber Gempa Bumi Ransiki 2012 Berkekuatan MW 6, 7. JST (jurnal Sains Dan Teknologi) 6(1):10
Shandini Y, Kouske PA, Nguiya S, Marcelin MP (2018) Structural setting of the Koum sedimentary basin (north Cameroon) derived from EGM2008 gravity field interpretation. Contrib Geophys Geodesy 48(4):281–298. https://doi.org/10.2478/congeo-2018-0013
Soulaimani S, Chakiri S, Manar A, Soulaimani A, Miftah A, Bouiflane M (2020) Potential-field geophysical data inversion for 3D modelling and reserve estimation (Example of the Hajjar mine, Guemassa massif, Morocco): magnetic and gravity data case. Comptes Rendus Géoscience 352(2):139–155. https://doi.org/10.5802/crgeos.10
Tian T, Zhang J, Jiang W, Tian Y (2020) Quantitative study of crustal structure spatial variation based on gravity anomalies in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau: Implication for earthquake susceptibility assessment. Earth Space Sci 7(3):e2019EA000943. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EA000943
Watkinson IM, Hall R (2017) Fault systems of the eastern Indonesian triple junction: evaluation of quaternary activity and implications for seismic hazards. Geol Soc Lond Special Publ 441(1):71–120. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP441.8
Webb M, White L (2016) Age and nature of Triassic magmatism in the Netoni Intrusive Complex, West Papua, Indonesia. J Asian Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.09.019
Zeng H, Xu D, Tan H (2007) A model study for estimating optimum upward-continuation height for gravity separation with application to a Bouguer gravity anomaly over a mineral deposit, Jilin province, northeast China. Geophysics 72(4):I45–I50. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2719497
Zingerle P, Pail R, Gruber T, Oikonomidou X (2020) The combined global gravity field model XGM2019e. J Geodesy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01398-0
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Gadjah Mada University for providing the opportunity to participate in the 2021 post-doctoral program with grant number: 6144/UN1.P.III/DIT-LIT/PT/2021. The authors also thank the International Bureau of Gravity Survey (BGI) for the WGM 2012 gravity data and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for the EMAG2-V3 data, which are freely accessible for research. Thanks are due also to Seequent for the opportunity to model the inversion of gravity and magnetic data in West Papua using the Oasis Montaj 9.10 software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.L has developed the research concepts and designs, as well as written the manuscript. S.S. writes and assesses research findings in the form of a published manuscript. L.L helps in the similarity checking process and also for changes and improvements to the English language of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they do not have any competing interests.
Additional information
Edited by Prof. Ivana Vasiljević (ASSOCIATE EDITOR) / Prof. Michał Malinowski (CO-EDITOR-IN-CHIEF).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lewerissa, R., Sismanto & Lapono, L.A.S. Identification of sediment–basement structure in West Papua province, Indonesia, using gravity and magnetic data inversion as an Earth’s crust stress indicator. Acta Geophys. 71, 209–226 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00913-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00913-5