Summary
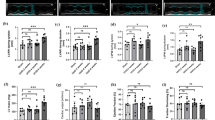
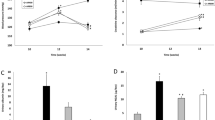
C1q/TNF-related protein 1 (CTRP1), a conserved protein of the C1q family, plays a key role in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. However, the role of CTRP1 in renal injury is unclear. The purpose of this study is to explore the role of CTRP1 in unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis and to elucidate the underlying mechanism. Using gene delivery system, CTRP1 was overexpressed in the kidney, then the mice were operated to induce UUO model after adenovirus transfection. It was found that the expression of CTRP1 in the renal tissue was decreased in mice after UUO. CTRP1 overexpression decreased the kidney function and kidney weight index. Moreover, CTRP1 reduced oxidative stress and renal collagen deposition in vivo. As expected, we found that CTRP1 activated AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) and decreased NOX4 expression, while silencing AMPKα1 abolished the protective effects of CTRP1 overexpression in mice after UUO. In conclusion, CTRP1 may protect against UUO-induced renal injury via AMPK/NOX4 signaling. Our results indicate that CTRP1 exhibits potential effects to treat renal fibrosis caused by UUO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. TGF-beta: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2016,12(6):325–338
Hu K, Wu C, Mars WM, et al. Tissue-type plasminogen activator promotes murine myofibroblast activation through LDL receptor-related protein 1-mediated integrin signaling. J Clin Invest, 2007,117(12):3821–3832
Wang P, Luo ML, Song E, et al. Long noncoding RNA lnc-TSI inhibits renal fibrogenesis by negatively regulating the TGF-beta/Smad3 pathway. Sci Transl Med, 2018,10 (462).pii: eaat2039
He W, Wang Y, Zhang MZ, et al. Sirt1 activation protects the mouse renal medulla from oxidative injury. J Clin Invest, 2010,120(4):1056–1068
Yang C, Nilsson L, Cheema MU, et al. Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticles targeting cyclooxygenase type 2 attenuate unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced kidney injury in mice. Theranostics, 2015,5(2):110–123
Pat B, Yang T, Kong C, et al. Activation of ERK in renal fibrosis after unilateral ureteral obstruction: modulation by antioxidants. Kidney Int, 2005,67(3):931–943
Jung KJ, Min KJ, Park JW, et al. Carnosic acid attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced kidney fibrosis via inhibition of Akt-mediated Nox4 expression. Free Radic Biol Med, 2016,97:50–57
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA. AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2012,13(4):251–262
Rabinovitch RC, Samborska B, Faubert B, et al. AMPK Maintains Cellular Metabolic Homeostasis through Regulation of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell Rep, 2017,21(1):1–9
DuPont JJ, Ramick MG, Farquhar WB, et al. NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species contribute to impaired cutaneous microvascular function in chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2014,306(12):F1499–1506
Babelova A, Avaniadi D, Jung O, et al. Role of Nox4 in murine models of kidney disease. Free Radic Biol Med, 2012,53(4):842–853
Tang JN, Shen DL, Liu CL, et al. Plasma levels of C1q/TNF-related protein 1 and interleukin 6 in patients with acute coronary syndrome or stable angina pectoris. Am J Med Sci, 2015,349(2):130–136
Schaffler A, Buechler C. CTRP family: linking immunity to metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2012,23(4):194–204
Shabani P, Emamgholipour S, Doosti M. CTRP1 in Liver Disease. Adv Clin Chem, 2017,79:1–23
Akiyama H, Otani M, Sato S, et al. A novel adipokine C1q/TNF-related protein 1 (CTRP1) regulates chondrocyte proliferation and maturation through the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2013,369(1–2):63–71
Kitanaka N, Nakano R, Sakai M, et al. ERK1/ATF-2 signaling axis contributes to interleukin-1beta-induced MMP-3 expression in dermal fibroblasts. PLoS One, 2019,14:e0222869
Liu M, Liu T, Shang P, et al. Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis via Klotho/TGF-beta/Smad signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med, 2018,22(10):4997–5007
Zhao DM, Zhu SQ, Wang FR, et al. Role of Mutant TBP in Regulation of Myogenesis on Muscle Satellite Cells. Curr Med Sci, 2019,39(5):734–740
Liu FY, Fan D, Yang Z, et al. TLR9 is essential for HMGB1-mediated post-myocardial infarction tissue repair through affecting apoptosis, cardiac healing, and angiogenesis. Cell Death Dis, 2019,10:480
Sato M, Muragaki Y, Saika S, et al. Targeted disruption of TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling protects against renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Clin Invest, 2003,112(10):1486–1494
Zheng Q, Yuan Y, Yi W, et al. C1q/TNF-related proteins, a family of novel adipokines, induce vascular relaxation through the adiponectin receptor-1/AMPK/eNOS/nitric oxide signaling pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2011,31(11):2616–2623
Barbieri D, Goicoechea M, Sanchez-Nino MD, et al. Obesity and chronic kidney disease progression-the role of a new adipocytokine: C1q/tumour necrosis factor-related protein-1. Clin Kidney J, 2019,12(3):420–426
Yagmur E, Buergerhausen D, Koek GH, et al. Elevated CTRP1 Plasma Concentration Is Associated with Sepsis and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Critically Ill Patients. J Clin Med, 2019,8(5):661
Qiu Q, Cao J, Wang Y, et al. Time Course of the Effects of Buxin Yishen Decoction in Promoting Heart Function and Inhibiting the Progression of Renal Fibrosis in Myocardial Infarction Caused Type 2 Cardiorenal Syndrome Rats. Front Pharmacol, 2019,10:1267
Kim JI, Noh MR, Kim KY, et al. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A deficiency exacerbates progression of kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. Free Radic Biol Med, 2015,12(89):201–208
Colon S, Luan H, Liu Y, et al. Peroxidasin and eosinophil peroxidase, but not myeloperoxidase, contribute to renal fibrosis in the murine unilateral ureteral obstruction model. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2019,316(2):F360–F371
Ostergaard M, Christensen M, Nilsson L, et al. ROS dependence of cyclooxygenase-2 induction in rats subjected to unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2014,306(2):F259–F270
Shevach EM. Garp as a therapeutic target for modulation of T regulatory cell function. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2017,21(2):191–200
Negri AL. Prevention of progressive fibrosis in chronic renal diseases: antifibrotic agents. J Nephrol, 2004,17:496–503
Wang S, Zhang C, Zhang M, et al. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha2 by nicotine instigates formation of abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice in vivo. Nat Med, 2012,18(6):902–910
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization or corporation or individual that can inappropriately influence this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Cheng, F., Songyang, Yy. et al. CTRP1 Attenuates UUO-induced Renal Fibrosis via AMPK/NOX4 Pathway in Mice. CURR MED SCI 40, 48–54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-020-2145-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-020-2145-9