Abstract
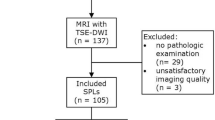
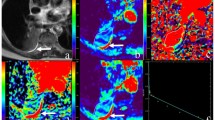
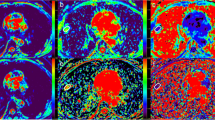
In order to prospectively assess various parameters of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs), 58 patients (40 men and 18 women, and mean age of 48.1±10.4 years old) with SPNs undergoing conventional MR, DWI using b=500 s/mm2 on a 1.5T MR scanner, were studied. Various DWI parameters [apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), lesion-tospinal cord signal intensity ratio (LSR), signal intensity (SI) score] were calculated and compared between malignant and benign SPNs groups. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was employed to compare the diagnostic capabilities of all the parameters for discrimination between benign and malignant SPNs. The results showed that there were 42 malignant and 16 benign SPNs. The ADC was significantly lower in malignant SPNs (1.40±0.44)×10−3 mm2/s than in benign SPNs (1.81±0.58)×10−3 mm2/s. The LSR and SI scores were significantly increased in malignant SPNs (0.90±0.37 and 2.8±1.2) as compared with those in benign SPNs (0.68±0.39 and 2.2±1.2). The area under the ROC curves (AUC) of all parameters was not significantly different between malignant SPNs and benign SPNs. It was suggested that as three reported parameters for DWI, ADC, LSR and SI scores are all feasible for discrimination of malignant and benign SPNs. The three parameters have equal diagnostic performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin, 2017,67(1):7–30
Kim HS, Lee KS, Ohno Y, et al. PET/CT versus MRI for diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of lung cancer. JMRI, 2015,42(2):247–260
Viallon M, Cuvinciuc V, Delattre B, et al. State-ofthe-art MRI techniques in neuroradiology: principles, pitfalls, and clinical applications. Neuroradiology, 2015,57(5):441–467
Connolly M, Srinivasan A. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Head and Neck Cancer: Technique, Limitations, and Applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am, 2018,26(1):121–133
Partridge SC, Nissan N, Rahbar H, et al. Diffusionweighted breast MRI: Clinical applications and emerging techniques. JMRI, 2017,45(2):337–355
Shenoy-Bhangle A, Baliyan V, Kordbacheh H, et al. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of liver: Principles, clinical applications and recent updates. World J Hepatol, 2017,9(26):1081–1091
Woo S, Suh CH, Kim SY, et al. Diagnostic Performance of DWI for Differentiating High-From Low-Grade Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Roentgenol, 2017,209(6):W374–W381
Addley H, Moyle P, Freeman S. Diffusion-weighted imaging in gynaecological malignancy. Clin Radiol, 2017,72(11):981–990
Satoh S, Kitazume Y, Ohdama S, et al. Can malignant and benign pulmonary nodules be differentiated with diffusion-weighted MRI? Am J Roentgenol, 2008,191(2):464–470
Matoba M, Tonami H, Kondou T, et al. Lung carcinoma: diffusion-weighted MRimaging—preliminary evaluation with apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology, 2007,243(2):570–577
Koyama H, Ohno Y, Seki S, et al. Value of diffusionweighted MRimaging using various parameters for assessment and characterization of solitary pulmonary nodules. Eur J Radiol, 2015,84(3):509–515
Wu LM, Xu JR, Hua J, et al. Can diffusion-weighted imaging be used as a reliable sequence in the detection of malignant pulmonary nodules and masses? Magn Reson Imaging, 2013,31(2):235–246
Uto T, Takehara Y, Nakamura Y, et al. Higher sensitivity and specificity for diffusion-weighted imaging of malignant lung lesions without apparent diffusion coefficient quantification. Radiology, 2009,252(1):247–254
Çakmak V, Ufuk F, Karabulut N. Diffusion-weighted MRI of pulmonary lesions: Comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and lesion-to-spinal cord signal intensity ratio in lesion characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2017,45(3):845–854
Yin Y, Sedlaczek O, Muller B, et al. Tumor Cell Load and Heterogeneity Estimation From Diffusion-Weighted MRI Calibrated With Histological Data: an Example From Lung Cancer. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018,37(1):35–46
Cui L, Yin JB, Hu CH, et al. Inter-and intraobserver agreement of ADC measurements of lung cancer in free breathing, breath-hold and respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin Imaging, 2016,40(5):892–896
Weller A, Papoutsaki MV, Waterton JC, et al. Diffusion-weighted (DW) MRI in lung cancers: ADC test-retest repeatability. Eur Radiol, 2017,27(11):4552–4562
Satoh S, Kitazume Y, Ohdama S, et al. Can malignant and benign pulmonary nodules be differentiated with diffusion-weighted MRI? Am J Roentgenol, 2008,191(2):464
Çakır Ç, Gençhellaç H, Temizöz O, et al. Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Characterization of Solitary Pulmonary Lesions. Balkan Med J, 2015,32(4):403
Holder CA, Muthupillai R, Mukundan S, Jr., et al. Diffusion-weighted MRimaging of the normal human spinal cord in vivo. Am J Neuroradiol, 2000,21(10):1799–1806
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, Hx., Pan, Yy., Wang, Yj. et al. Comparison of Various Parameters of DWI in Distinguishing Solitary Pulmonary Nodules. CURR MED SCI 38, 920–924 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1963-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1963-5