Summary
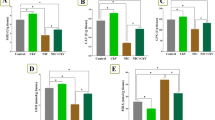
Melatonin has been reported to inhibit hepatic fibrosis and the mechanism may be correlated to its anti-oxidant effect. Nevertheless, the mechanism is not completely identified. This study was conducted to investigate the effects of melatonin on TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in liver fibrosis in rats. The liver fibrosis model was made by the subcutaneous injection of CCl4. The liver pathology changes were detected using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and Van Gieson (VG) staining. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activities were measured with an autoanalyzer. Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities and levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydroxyproline (Hyp) in liver were evaluated by spectrophotometry. Expression levels of TGF-β1, Smad2/3, phosphorylated Smad2/3 (p-Smad2/3) and Smad7 in liver were detected by immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. Results showed that melatonin suppressed CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, along with an improvement in histological changes, significant decreases in pathologic grading sores and obvious decreases in Hyp levels in liver. Melatonin improved liver function indicated by decreased serum ALT and AST activities. In addition, melatonin exerted its anti-oxidant effects, as supported by decreased MDA levels and increased GPx activities in liver. Furthermore, melatonin inhibited TGF-β1/Smad pathway, as evidenced by decreased TGF-β1, Smad2/3 and p-Smad2/3 expression and increased Smad7 expression in liver. In conclusion, melatonin may suppress CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad pathway. It is possible for melatonin to be a potential reagent to treat and cure liver fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP. Reversibility of liver fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair, 2010, 5(Suppl 1):S26
Zhou WC, Zhang QB, Qiao L. Pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(23):7312–7324
Baghy K, Iozzo RV, Kovalszky I. Decorin-TGFbeta axis in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Histoch m Cytochem, 2012,60(4):262–268
Lee JH, Jang EJ, Seo HL, et al. Sauchinone attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation through TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact, 2014,224:58–67
Kajdaniuk D, Marek B, Borgiel-Marek H, et al. Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFbeta1) in physiology and pathology. Endokrynol Pol, 2013,64(5):384–396
Yao QY, Xu BL, Wang JY, et al. Inhibition by curcumin of multiple sites of the transforming growth factor-beta1 signalling pathway ameliorates the progression of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2012,12:156
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R. Modern pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and TGF-β β as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med, 2006,10(1):76–99
Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ. Melatonin as a natural ally against oxidative stress: a physicochemical examination. J Pineal Res, 2011,51(1):1–16
Allegra M, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, et al. The chemistry of melatonin’s interaction with reactive species. J Pineal Res, 2003,34(1):1–10
Tahan V, Atug O, Akin H, et al. Melatonin ameliorates methionine-and choline-deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. J Pineal Res, 2008,46(4):401–407
Hong RT, Xu JM, Mei Q. Melatonin ameliorates experimental hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. World J Gastroenterol, 2009,15(12):1452–1458
Hong RT, Xu JM, Shen JL, et al. Effects of melatonin on hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats and its mechanisms. Chin Pharm Bull (Chinese), 2012,28(8):1141–1145
Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology, 1996,24(2):289–293
Jiang Y, Wang C, Li YY, et al. Mistletoe alkaloid fractions alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation via TGF-beta/Smad interference. J Ethnopharmacol, 2014,158 Pt A:230–238
Rosa DP, Bona S, Simonetto D, et al. Melatonin protects the liver and erythrocytes against oxidative stress in cirrhotic rats. Arq Gastroenterol, 2010,47(1):72–78
Sagor AT, Chowdhury MR, Tabassum N, et al. Supplementation of fresh ucche (Momordica charantia L. var. muricata Willd) prevented oxidative stress, fibrosis and hepatic damage in CCl4 treated rats. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2015,15:115
Parola M, Robino G. Oxidative stress-related molecules and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol, 2001,35(2):297–306
Tahan G, Tarcin O, Tahan V, et al. The effects of N-acetylcysteine on bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Dig Dis Sci, 2007,52(12): 3348–3354
Morsy MA, Abdalla AM, Mahmoud AM, et al. Protective effects of curcumin, alpha-lipoic acid, and N-acetylcysteine against carbon tetrachlorideinduced liver fibrosis in rats. J Physiol Biochem, 2012,68(1):29–35
Claustrat B, Brun J, Chazot G. The basic physiology and pathophysiology of melatonin. Sleep Med Rev, 2005,9(1):11–24
Hatzis G, Ziakas P, Kavantzas N, et al. Melatonin attenuates high fat diet-induced fatty liver disease in rats. World J Hepatol, 2013,5(4):160–169
Tomás-Zapico C, Coto-Montes A. Melatonin as antioxidant under pathological processes. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov, 2007,1(1):63–82
Choi HS, Kang JW, Lee SM. Melatonin attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis via inhibition of necroptosis. Transl Res, 2015,166(3):292–303
Hu S, Yin S, Jiang X, et al. Melatonin protects against alcoholic liver injury by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol, 2009,616(1-3):287–292
Hong, RT, Chen SL, Ruan HL, et al. Effects of melatonin on acute liver injury induced by ethanol in rats. Chin Pharm Bull (Chinese), 2011,27(11):1596–1599
Koh PO. Melatonin prevents hepatic injury-induced decrease in Akt downstream targets phosphorylations. J Pineal Res, 2011,51(2):214–219
Jung KH, Hong SW, Zheng HM, et al. Melatonin downregulates nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 and nuclear factor-kappaB during prevention of oxidative liver injury in a dimethylnitrosamine model. J Pineal Res, 2009,47(2):173–183
Tahan G, Akin H, Aydogan F, et al. Melatonin ameliorates liver fibrosis induced by bile-duct ligation in rats. Can J Surg, 2010,53(5):313–318
Leask A, Abraham DJ. TGF-beta signaling and the fibrotic response. FASEB J, 2004,18(7):816–827
Fan X, Zhang Q, Li S, et al. Attenuation of CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice by vaccinating against TGF-beta1. PLoS One, 2013,8(12):e82190
Huang W, Li L, Tian X, et al. Astragalus and Paeoniae Radix Rubra extract (APE) inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by modulating transforming growth factor-beta/Smad pathway. Mol Med Rep, 2015,11(4):2569–2577
Xu MY, Hu JJ, Shen J, et al. Stat3 signaling activation crosslinking of TGF-beta1 in hepatic stellate cell exacerbates liver injury and fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014,1842(11):2237–2245
Sferra R, Vetuschi A, Catitti V, et al. Boswellia serrata and Salvia miltiorrhiza extracts reduce DMN-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice by TGFbeta1 downregulation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2012,16(11):1484–1498
Chen BL, Peng J, Li QF, et al. Exogenous bone morphogenetic protein-7 reduces hepatic fibrosis in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice via transforming growth factor-beta/Smad signaling. World J Gastroenterol, 2013,19(9):1405–1415
Dooley S, Dijke PT. TGF-beta in progression of liver disease. Cell Tissue Res, 2012,347(1):245–256
Li J, Li X, Xu W, et al. Antifibrotic effects of luteolin on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by targeting AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and TGFbeta/Smad signalling pathways. Liver Int, 2015,35(4):1222–1233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the Natural Science Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province (No. KJ2013A155) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81370529).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yr., Hong, Rt., Xie, Yy. et al. Melatonin Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride in Rats via Inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad Signaling Pathway. CURR MED SCI 38, 236–244 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1871-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1871-8