Summary
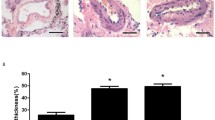
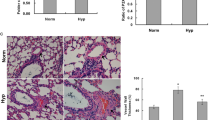
This study investigated the potential role of ERK1/2-cyclinE1 signaling pathway in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (rPASMCs) proliferation and pulmonary vascular remodeling induced by cigarette smoke exposure. A total of 24 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 4 groups: control group (C group), S-1M, S-3M and S-6M groups (animals in the groups were exposed to smoke for 1, 3, and 6 months, respectively). HE staining and anti-α-smooth muscle actin antibody staining were performed to observe the degree of pulmonary vascular remodeling. Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting were performed to evaluate ERK1/2 and cyclinE1 expression in pulmonary vessels. Primary cultured rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (rPASMCs) were exposed to cigarette smoke extract (CSE). ERK inhibitor (PD98059) and cyclinE1 siRNA were used to verify the role of ERK1/2 and cyclinE1 in CSE-induced rPASMCs proliferation. Cell proliferation was assessed by cell counting and 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation. Our results showed that abnormal pulmonary vascular remodeling was found in cigarette smoked rats. Compared to C group, activated ERK1/2 and cyclinE1 expression was significantly increased in smoke-exposure groups. This up-regulated expression was positively correlated with the severity of pulmonary vascular remodeling, and there was positive correlation between the expression of ERK1/2 and cyclinE1. PD98059 and cyclinE1 siRNA inhibited the proliferation of rPASMCs. The expression of cyclinE1 could be down-regulated by PD98059. Our data demonstrated that increased expression of ERK1/2 and cyclinE1 might be involved in the pathogenesis of abnormal rPASMCs proliferation and rat pulmonary vascular remodelling induced by cigarette smoke exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Churg A, Cosio M, Wright JL. Mechanisms of cigarette smoke-induced COPD: insights from animal models. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2008,294(4):L612–L631
Stenmark KR, Mecham RP. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pulmonary vascular remodeling. Annu Rev Physiol, 1997,59:89–144
Humbert M, Sitbon O, Simonneau G. Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med, 2004,351(14):1425–1436
Santos S, Peinado VI, Ramirez J, et al. Characterization of pulmonary vascular remodelling in smokers and patients with mild COPD. Eur Respir J, 2002,19(4):632–638
Chaouat A, Naeije R, Weitzenblum E. Pulmonary hypertension in COPD. Eur Respir J, 2008,32(5):1371–1385
Peinado VI, Pizarro S, Barbera JA. Pulmonary vascular involvement in COPD. Chest, 2008,134(4):808–814
Wright JL, Levy RD, Churg A. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: current theories of pathogenesis and their implications for treatment. Thorax, 2005,60(7):605–609
Mandegar M, Fung YC, Huang W, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pulmonary vascular remodeling: role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. Microvasc Res, 2004,68(2):75–103
Ferrer E, Peinado VI, Diez M, et al. Effects of cigarette smoke on endothelial function of pulmonary arteries in the guinea pig. Respir Res, 2009,10:76
Mebratu Y, Tesfaigzi Y. How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle, 2009,8(8):1168–1175
Ramos JW. The regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in mammalian cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2008,40(12):2707–2719
Bai J, Liu XS, Xu YJ, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in airway smooth muscle cell proliferation in chronic asthmatic rats. Shengli Xuebao, 2007,59(3):311–318
Xie M, Liu XS, Xu YJ, et al. Role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway in regulating the secretion of bronchial smooth muscle cells in a rat model of chronic asthma. Chin Med J (Engl), 2008, 121(1):73–77
Xie M, Liu XS, Xu YJ, et al. ERK1/2 signaling pathway modulates the airway smooth muscle cell phenotype in the rat model of chronic asthma. Respiration, 2007, 74(6):680–690
Liu B, Ryer EJ, Kundi R, et al. Protein kinase C-delta regulates migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. J Vasc Surg, 2007,45(1):160–168
Preston IR, Hill NS, Warburton RR, et al. Role of 12-lipoxygenase in hypoxia-induced rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2006,290(2):L367–L374
Ding Q, Gros R, Limbird LE, et al. Estradiol-mediated ERK phosphorylation and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells requires GPR 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2009,297(5):C1178–1187
Mercer BA, Kolesnikova N, Sonett J, et al. Extracellular regulated kinase/mitogen activated protein kinase is up-regulated in pulmonary emphysema and mediates matrix metalloproteinase-1 induction by cigarette smoke. J Biol Chem, 2004,279(17):17690–17696
Rahman I. Oxidative stress in pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2005,43(1):167–188
Moroy T, Geisen C. Cyclin E. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2004,36(8):1424–1439
Bessard A, Fremin C, Ezan F, et al. RNAi-mediated ERK2 knockdown inhibits growth of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene, 2008,27(40):5315–5325
Kisielewska J, Philipova R, Huang JY, et al. MAP kinase dependent cyclinE/cdk2 activity promotes DNA replication in early sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol, 2009, 334(2):383–394
Lents NH, Keenan SM, Bellone C, et al. Stimulation of the Raf/MEK/ERK cascade is necessary and sufficient for activation and Thr-160 phosphorylation of a nuclear-targeted CDK2. J Biol Chem, 2002,277(49), 47469–47475
Keenan SM, Bellone C, Baldassare JJ. Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 nucleocytoplasmic translocation is regulated by extracellular regulated kinase. J Biol Chem, 2001,276(25): 22404–22409
Lee SH, Park C, Jin CY, et al. Involvement of extracellular signal-related kinase signaling in esculetin induced G1 arrest of human leukemia U937 cells. Biomed Pharmacother, 2008,62(10):723–729
Zeng DX, Xu YJ, Liu XS, et al. Cigarette smoke extract induced rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells proliferation via PKCalpha-mediated cyclin D1 expression. J Cell Biochem, 2011,112(8):2082–2088
Carraway MS, Ghio AJ, Suliman HB, et al. Carbon monoxide promotes hypoxic pulmonary vascular remodeling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2002,282(4): L693–L702
Stedman RL. The chemical composition of tobacco and tobacco smoke. Chem Rev, 1968,68(2):153–207
Zhu Z, Xu Y, Zou H, et al. Effects of puerarin on pulmonary vascular remodeling and protein kinase C-alpha in chronic cigarette smoke exposure smoke-exposed rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2008,28(1): 27–32
Yamato H, Sun JP, Churg A, et al. Guinea pig pulmonary hypertension caused by cigarette smoke cannot be explained by capillary bed destruction. J Appl Physiol, 1997,82(5):1644–1653
Wright JL, Tai H, Churg A. Vasoactive mediators and pulmonary hypertension after cigarette smoke exposure in the guinea pig. J Appl Physiol, 2006,100(2):672–678
Hu Y, Dietrich H, Metzler B, et al. Hyperexpression and activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) in atherosclerotic lesions of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2000,20(1):18–26
Dasgupta P, Rastogi S, Pillai S, et al. Nicotine induces cell proliferation by beta-arrestin-mediated activation of Src and Rb-Raf-1 pathways. J Clin Invest, 2006, 116(8): 2208–2217
Eder AM, Sui X, Rosen DG, et al. Atypical PKCiota contributes to poor prognosis through loss of apical-basal polarity and cyclin E overexpression in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005,102(35):12519–12524
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81070044).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Mq., Liu, Xs., Wu, Hx. et al. ERK1/2 Promotes cigarette smoke-induced rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells proliferation and pulmonary vascular remodeling via up-regulating cycline1 expression. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 33, 315–322 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1117-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1117-8