Summary
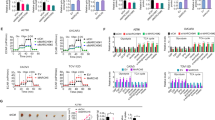
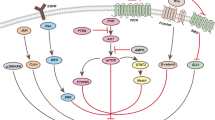
This study explored the molecular mechanisms underlying the time-dependent autophagy and apoptosis induced by nutrient depletion in human multiple myeloma cell line RPMI8226 cells. RT-PCR and qRT-PCR were used to evaluate the transcriptional levels of Deptor, JNK1, JNK2, JNK3, Raf-1, p53, p21 and NFκB1 at 0, 6, 12, 18, 24 and 48 h after nutrient depletion in RPMI8226 cells. We found that transcriptional levels of Deptor were increased time-dependently at 0, 6, 12 and 18 h, and then decreased. Its alternation was consistent with autophagy. Transcriptional levels of Raf-1, JNK1, JNK2, p53 and p21 were increased time-dependently at 0, 6, 12, 18, 24 and 48 h accompanying with the increase of apoptosis. Transcriptional levels of NFκB1 at 6, 12, 18, 24 and 48 h were decreased as compared with 0 h. It was suggested that all the studied signaling molecules were involved in cellular response to nutrient depletion in RPMI8226 cells. Deptor contributed to autophagy in this process. Raf-1/JNK /p53/p21 pathway may be involved in apoptosis, and NFκB1 may play a possible role in inhibiting apoptosis. It remained to be studied whether Deptor was involved in both autophagy and apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peterson TR, Laplante M, Thoreen CC, et al. DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival. Cell, 2009,137(5):873–886
Schaeffer HJ, Weber MJ. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: specific messages from ubiquitous messengers. Mol Cell Biol, 1999,19(4):2435–2444
Davis RJ. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell, 2000,103(2):239–252
Nishina H, Vaz C, Billia P, et al. Defective liver formation and liver cell apoptosis in mice lacking the stress signaling kinase SEK1/MKK4. Development, 1999, 126(3):505–516
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, et al. Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol, 2006,26(24):9220–9231
Wei Y, Pattingre S, Sinha S, et al. JNK1-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2 regulates starvation-induced autophagy. Autophagy, 2008,30(5):678–688
Howe LR, Leevers SJ, Gomez N, et al. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell, 1992,71(2):335–341
Chang L, Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades. Nature, 2001,410(6824):37–40
Schireiber M, Kolbus A, Piu F, et al. Control of cell cycle progression by c-Jun is p53 dependent. Genes Dev, 1999,13(5):607–619
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ, et al. Surfing the p53 network. Nature, 2000,408(6810):307–310
Deiry WS, Harper JW, Connor PM, et al. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res, 1994,54(5):1169–1174
Miyashita T, Reed JC. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell, 1995,80(2):293–299
Kucharczak J, Simmons MJ, Fan Y, et al. To be, or not to be: NF-κB is the answer — role of Rel/NF-κB in the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene, 2003,22(56):8961–8982
Gilmore TD. The Rel1/NF-κB/IκB signal transduction pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Res, 2003,115:241–265
Karin M, Lin A. NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol, 2002,3(3):221–227
Hoffmann A, Leung TH, Baltimore D et al. Genetic analysis of NF-κB/Rel transcription factors defines functional specificities. EMBO, 2003,22(20):5530–5539
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, et al. Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin Invest, 2008,118(9):3065–3074
Davis RJ. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell, 2000,103(2):239–252
Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP. JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene, 2008,27(22):6245–6251
Tournier C, Hess P, Yang DD, et al. Requirement of JNK for stress-induced activation of the cytochrome c-mediated death pathway. Science, 2000,288(5467):870–874
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, et al. Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science, 2004, 303(5660):1010–1014
Bost F, McKay R, Bost M, et al. The Jun kianse 2 isoform is preferentially required for epidermal growth factor-induced transformation of human A549 lung carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol, 1999,19(3):1938–1949
Potapova O, Anisimov SV, Gorospe M, et al. Targets of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 2-mediated tumor growth regulation revealed by serial analysis of gene expression. Cancer Res, 2002,62(11):3257–3263
Potapova O, Gorospe M, Dougherty RH, et al. Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 expression suppresses growth and induces apoptosis of human tumor cells in a p53-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol, 2000,20(5):1713–1722
Wu H, Wang MC, Bohmann D. JNK protects Drosophila from oxidative stress by trancriptionally activating autophagy. Mech Dev, 2009,126(8–9):624–637
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K. Regulation of the aging process by autophagy. Trends Mol Med, 2009,15(5):217–224
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Wu D, et al. NF-κB facilitates oridonin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in HT1080 cells through a p53-mediated pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2009,489(1–2):25–33
Papa S, Zazzeroni F, Pham CG, et al. Linking JNK signaling to NF-κB: a key to survival. J Cell Sci, 2004,117(Pt22):5197–5208
Nakano H, Nakajima A, Sakon-Komazawa S, et al. Reactive oxygen species mediate crosstalk between NF-κB and JNK. Cell Death Different, 2006,13(5):730–737
Liu J, Lin A. Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: A double-edged sword. Cell Res, 2005,15(1):36–42
Bubici C, Papa S, Pham CG, et al. NF-κB and JNK. Cell Cycle, 2004,3(12):1524–1529
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by a grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30871036).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Wen, L. et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying the time-dependent autophagy and apoptosis induced by nutrient depletion in multiple myeloma: a pilot study. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 32, 1–8 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-0001-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-0001-2