Summary
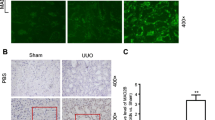
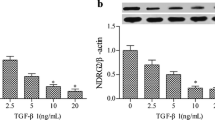
Recently, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) is suggested as a new agent in the fighting against fibrogenesis. In tumor, DJ-1 is identified as a negative regulator of PTEN. But the expression of DJ-1 and the regulation of PTEN in fibrosis are unclear. Renal fibrosis was induced in 5/6 subtotal nephrectomy rat model. Human proximal tubular epithelial cells (HKC) were treated with transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1), or transfected with DJ-1 or PTEN. Confocal microscope was used to investigate the localization of DJ-1 and PTEN. The selective phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, LY294002, was administered to inhibit PI3K pathway. The DJ-1 and PTEN expression, markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and Akt phosphorylation were measured by RT-PCR, Western blotting or immunocytochemistry. In vitro, after HKC cells were stimulated with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 for 72 h, the expression of DJ-1 was increased, and that of PTEN was decreased. In vivo, the same results were identified in 5/6-nephrectomized rats. In normal HKC cells, most of DJ-1 protein localized in cytoplasm, and little in nucleus. TGF-β1 upregulated DJ-1 expression in both cytoplasma and nuclei. In contrary, TGF-β1 emptied cytoplasmic PTEN protein into nucleus. Overexpression of DJ-1 decreased the expression of PTEN, promoted the activation of Akt and the expression of vimentin, and also led to the loss of cytoplasmic PTEN. Contrarily, overexpression of PTEN protected HKC cells from TGF-β1-induced EMT. In conclusion, DJ-1 is upregulated in renal fibrosis and DJ-1 mediates EMT by suppressing cytoplasmic PTEN expression and Akt activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eddy AA. Molecular basis of renal fibrosis. Pediatr Nephrol, 2000,15(34):290–301
Razzaque MS, Taguchi T. Cellular and molecular events leading to renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Med Electron Microsc, 2002,35(2):68–80
Kallui R, Neilson EG. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest, 2003, 112(12):1776–1784
Tamura M, Gu J, Matsumoto K, et al. Inhibition of cell migration, spreading, and focal adhesions by tumor suppressor PTEN. Science, 1998,280(5369):1614–1617
Maehama T, Dixon JE. The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3, 4, 5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem, 1998,273(22):13 375–13 378
Gu J, Tamura M, Pankov R, et al. Shc and FAK differentially regulate cell motility and directionality modulated by PTEN. J Cell Biol, 1999,146(2):389–403
Kwak YG, Song CH, Yi HK, et al. Involvement of PTEN in airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in bronchial asthma. J Clin Invest, 2003,111(7):1083–1092
White ES, Thannickal VJ, Carskadon SL, et al. Integrin α4β1 regulates migration across basement membranes by lung fibroblasts: a role for phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2003,168(4):436–442
White ES, Atrasz RG, Hu B, et al. Negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation by PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10). Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2006,173(1):112–121
Mahimainathan L, Das F, Venkatesan B, et al. Mesangial cell hypertrophy by high glucose is mediated by down-regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN. Diabetes, 2006,55(7):2115–2125
Fu SX, Zhang K, Tan HB, et al. Effect of tumor suppressor PTEN on tubulointerstitial fibrosis (TIF) in IgA. Nephrology, 2008,13:11
Li DM, Sun H. TEP1, encoded by a candidate tumor suppressor locus, is a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase regulated by transforming growth factor beta. Cancer Res, 1997,57(11):2124–2129
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, et al. Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinsonism. Science, 2003,299(5604):256–259
Le Naour F, Misek DE, Krause MC, et al. Proteomics-based identification of RS/DJ-1 as a novel circulating tumor antigen in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2001, 7(11):3328–3335
Mackeigan JP, Clements CM, Lich JD, et al. Proteomic profiling drug-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma: identification of RS/DJ-1 and RhoGDIalpha. Cancer Res, 2003,63(20):6928–6934
Grzmil M, Voigt S, Thelen P, et al. Up-regulated expression of the MAT-8 gene in prostate cancer and its siRNA-mediated inhibition of expression induces a decrease in proliferation of human prostate carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol, 2004,24(1):97–105
Davidson B, Hadar R, Schlossberg R, et al. Expression and clinical role of DJ-1, a negative regulator of PTEN in ovarian carcinoma. Hum Pathol, 2008,39(1):87–95
Kim RH, Peters M, Jang YJ, et al. DJ-1, a novel regulator of the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cancer Cell, 2005,7(3): 263–273
Ge S, Zeng R, Luo Y, et al. Role of protein kinase C in advanced glycation end products-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2009, 29(3):281–285
Luo XU, Yang Q, Zhang Q, et al. Differential analysis of associated proteome in hepatic fibrosis tissue. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese), 2007,87(48):3411–3414
Fan JM, Ng YY, Hill PA, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta regulated tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vitro. Kidney Int, 1999,56(4):1455–1467
Wang X, Trotman LC, Koppie T, et al. NEDD4-1 is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN. Cell, 2007, 128(1):129–139
Gimm O, Perren A, Weng LP, et al. Differential nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of PTEN in normal thyroid tissue, and benign and malignant epithelial thyroid tumors. Am J Pathol, 2000,156(5):1693–1700
Perren A, Weng LP, Boag AH, et al. Immunohistochemical evidence of loss of PTEN expression in primary ductal adenocarcinomas of the breast. Am J Pathol, 1999,155(4):1253–1260
Virolle T, Adamson ED, Baron V, et al. The Egr-1 transcription factor directly activates PTEN during irradiation-induced signaling. Nat Cell Biol, 2001,3(12):1124–1128
Stambolic V, MacPherson D, Sas D, et al. Regulation of PTEN transcription by p53. Mol Cell, 2001,8(2):317–325
Patel L, Pass I, Coxon P, et al. Tumor suppressor and anti-inflammatory actions of PPARgamma agonists are mediated via upregulation of PTEN. Curr Biol, 2001,11(10):764–768
Xia D, Srinivas H, Ahn YH, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-4 promotes cell survival by decreasing PTEN expression through an NF kappa B-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem, 2007,282(6):3507–3519
Quiroz Y, Bravo J, Herrera-Acosta J, et al. Apoptosis and NFkappaB activation are simultaneously induced in renal tubulointerstitium in experimental hypertension. Kidney Int Suppl, 2003,86:S27–32
Burgering BM, Coffer PJ. Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phospha-tidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature, 1995,376(6541):599–602
Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC. Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem, 1998,67:481–507
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase. Balpha Curr Biol, 1997,7(4):261–269
Sun H, Lesche R, Li DM, et al. PTEN modulates cell cycle progression and cell survival by regulating phosphatidylinositol 3, 4, 5,-trisphosphate and Akt/protein kinase B signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999,96(11):6199–6204
Chung JH, Eng C. Nuclear-cytoplasmic partitioning of phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) differentially regulates the cell cycle and apoptosis. Cancer Res, 2005,65(18):8096–8100
Roura S, Miravet S, Piedra J, et al. Regulation of E-cadherin/catenin association by tyosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem, 1999,274(51):36 734–36 740
Han M, Xu G, Zeng R, et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of β-catenin modulates the expression of E-cadhein in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-β. Chin J Nephrol, 2006,22(8):494–498
Kattla JJ, Carew RM, Heljic M, et al. Protein kinase B/Akt activity is involved in renal TGFta-1 driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2008,295(1):F215–225
Kuwano K. PTEN as a new agent in the fight against fibrogenesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2006,173(1):5–6
Tan EK, Tan C, Zhao Y, et al. Genetic analysis of DJ-1 in cohort Parkinson’s disease patients of different ethnicity. Neurosci Lett, 2004,367(1):109–112
Sekito A, Taira T, Niki T, et al. Stimulation of transforming activity of DJ-1 by Abstrakt, a DJ-1-binding protein. Int J Oncol, 2005,26(3):685–689
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV. Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: A review. Ann Bot (Lond), 2003,91:179–194
Nangaku M. Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: A final common pathway to end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2006,17(1):17–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported by a grant from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30800525).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Wei, H., Liu, L. et al. Upregulated DJ-1 promotes renal tubular EMT by suppressing cytoplasmic PTEN expression and Akt activation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 469–475 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0475-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0475-3