Summary
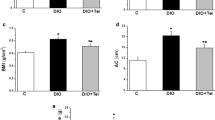
This study investigated the effects of telmisartan on insulin resistance in high-fat diet-treated rats and the possible mechanism. A total of 40 male Sprague-Dawley rats enrolled in the study were divided into 4 groups at random: ND group (n=10) and HD group (n=10), in which the rats were given a normal chow diet or a high-fat diet for 20 weeks following a one-week adaptation; ND+telmisartan (n=10) group and HD+telmisartan group (n=10), in which the rats were initially administered in the same way as the ND or HD group, and then they were orally gavaged with telmisartan (5 mg/kg daily) additionally for 5 weeks. Related inflammatory factors were measured by ELISA. Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), phosphorylated JNK and IκB-α expressions in both adipose and liver were detected by Western blotting. CRP and angiotensin II receptor 1 (AT1) mRNA expressions in both adipose and liver were determined by RT-PCR. The results showed that telmisartan administration in vivo reversed insulin resistance as evidenced by a decrease in plasma fasting glucose levels, plasma fasting insulin levels and homeostasis model of assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). Furthermore, telmisartan administration significantly reduced serum CRP, TNF-α and IL-1β levels, and elevated serum IL-10 levels. It was also found to hamper the high-fat diet-induced increase in CRP mRNA, AT1 mRNA and MCP-1, and decrease in IκB-α in both adipose and liver. It was concluded that telmisartan administration in vivo may improve insulin resistance through attenuated inflammatory response pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurtz TW. Beyond the classic angiotensin-receptorblocker profile. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med, 2008, 5(Suppl 1):S19–26
Andraws R, Brown DL. Effect of inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system on development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (meta-analysis of randomized trials). Am J Cardiol, 2007, 99(7):1006–1012
McMurray JJ, Holman RR, Haffner SM, et al. Effect of valsartan on the incidence of diabetes and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med, 2010,362(16):1477–1490
Sugimoto K, Qi NR, Kazdová L, et al. Telmisartan but not valsartan increases caloric expenditure and protects against weight gain and hepatic steatosis. Hypertension, 2006,47(5):1003–1009
He H, Yang D, Ma L, et al. Telmisartan prevents weight gain and obesity through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta-dependent pathways. Hypertension, 2010,55(4):869–879
Rong X, Li Y, Ebihara K, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-independent beneficial effects of telmisartan on dietary-induced obesity, insulin resistance and fatty liver in mice. Diabetologia, 2010 [PMID: 20390403]
Zanchi A, Dulloo AG, Perregaux C, et al. Telmisartan prevents the glitazone-induced weight gain without interfering with its insulin-sensitizing properties. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2007,293(1):E91–E95
Shimabukuro M, Tanaka H, Shimabukuro T. Effects of telmisartan on fat distribution in individuals with the metabolic syndrome. J Hypertens, 2007,25(4):841–848
Negro R, Formoso G, Hassan H. The effects of irbesartan and telmisartan on metabolic parameters and blood pressure in obese, insulin resistant, hypertensive patients. J Endocrinol Invest, 2006,29(11):957–961
Enjoji M, Kotoh K, Kato M, et al. Therapeutic effect of ARBs on insulin resistance and liver injury in patients with NAFLD and chronic hepatitis C: a pilot study. Int J Mol Med, 2008,22(4):521–527
Liang H, Yin B, Zhang H, et al. Blockade of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type 1-mediated TNF-alpha signaling protected Wistar rats from diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Endocrinology, 2008,149(6): 2943–2951
Xu X, Zhao CX, Wang L, et al. Increased CYP2J3 expression reduces insulin resistance in fructose-treated rats and db/db mice. Diabetes, 2010,59(4):997–1005
Benson SC, Pershadsingh HA, Ho CI, et al. Identification of telmisartan as a unique angiotensin II receptor antagonist with selective PPARgamma-modulating activity. Hypertension, 2004,43(5):993–1002
Zhao C, Wang P, Xiao X, et al. Gene therapy with human tissue kallikrein reduces hypertension and hyperinsulinemia in fructose-induced hypertensive rats. Hypertension, 2003,42(5):1026–1033
Tu L, Xu X, Wan H, et al. Delivery of recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated human tissue kallikrein for therapy of chronic renal failure in rats. Hum Gene Ther, 2008,19(4):318–330
Tam CS, Viardot A, Clément K, et al. Short-term overfeeding may induce peripheral insulin resistance without altering subcutaneous adipose tissue macrophages in humans. Diabetes, 2010,59(9):2164–2170
Haus JM, Solomon TP, Marchetti CM, et al. Free fatty acid-induced hepatic insulin resistance is attenuated following lifestyle intervention in obese individuals with impaired glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2010,95(1):323–327
Tzotzas T, Papadopoulou FG, Tziomalos K, et al. Rising serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels after weight loss in obese women correlate with improvement in insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2010,95(9):4251–4257
Olefsky JM, Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol, 2010,72:219–246
Xu JW, Morita I, Ikeda K, et al. C-reactive protein suppresses insulin signaling in endothelial cells: role of spleen tyrosine kinase. Mol Endocrinol, 2007,21(2):564–573
Solomon SS, Odunusi O, Carrigan D, et al. TNF-alpha inhibits insulin action in liver and adipose tissue: A model of metabolic syndrome. Horm Metab Res, 2010,42(2): 115–121
Jager J, Gremeaux T, Cormont M, et al. Interleukin-1beta-induced insulin resistance in adipocytes through down-regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression. Endocrinology, 2007,148(1):241–251
Osborn O, Brownell SE, Sanchez-Alavez M, et al. treatment with an interleukin 1 beta antibody improves glycemic control in diet-induced obesity. Cytokine, 2008,44(1):141–148
Ehses JA, Lacraz G, Giroix MH, et al. IL-1 antagonism reduces hyperglycemia and tissue inflammation in the type 2 diabetic GK rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009,106(33):13 998–14 003
Owyang AM, Maedler K, Gross L, et al. XOMA 052, an anti-IL-1ta monoclonal antibody, improves glucose control and ta-cell function in the diet-induced obesity mouse model. Endocrinology, 2010,151(6):2515–2527
Cintra DE, Pauli JR, Araújo EP, et al. Interleukin-10 is a protective factor against diet-induced insulin resistance in liver. J Hepatol, 2008,48(4):628–637
Hong EG, Ko HJ, Cho YR, et al. Interleukin-10 prevents diet-induced insulin resistance by attenuating macrophage and cytokine response in skeletal muscle. Diabetes, 2009,58(11):2525–2535
Fernandez-Veledo S, Vila-Bedmar R, Nieto-Vazquez I, et al. c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1/2 activation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces insulin resistance in human visceral but not subcutaneous adipocytes: reversal by liver X receptor agonists. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2009,94(9):3583–3593
Draznin B. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance: serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and increased expression of p85alpha: the two sides of a coin. Diabetes, 2006,55(8):2392–2397
Sartipy P, Loskutoff DJ. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003,100(12):7265–7270
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, et al. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Clin Invest, 2006,116(6):1494–1505
Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med, 1997,336(15):1066–1071
Itani SI, Ruderman NB, Schmieder F, et al. Lipid-induced insulin resistance in human muscle is associated with changes in diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, and IkappaB-alpha. Diabetes, 2002,51(7):2005–2011
Goyal S, Arora S, Bhatt TK, et al. Modulation of PPAR-gamma by telmisartan protects the heart against myocardial infarction in experimental diabetes. Chem Biol Interact, 2010,185(3):271–280
Iwanami J, Mogi M, Tsukuda K, et al. Low dose of telmisartan prevents ischemic brain damage with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation in diabetic mice. J Hypertens, 2010,28(8):1730–1737
Clemenz M, Frost N, Schupp M, et al. Liver-specific peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target gene regulation by the angiotensin type 1 receptor blocker telmisartan. Diabetes, 2008,57(5):1405–1413
Feng X, Luo Z, Ma L, et al. Angiotensin II receptor blocker telmisartan enhances running endurance of skeletal muscle through activation of the PPAR delta/ AMPK pathway. J Cell Mol Med, 2010 [PMID:20477906]
Prasad A, Quyyumi AA. Renin-angiotensin system and angiotensin receptor blockers in the metabolic syndrome. Circulation, 2004,110(11):1507–1512
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was partially supported by a grant from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30971247).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Yin, X., Feng, W. et al. Telmisartan protects against insulin resistance by attenuating inflammatory response in rats. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 317–323 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0374-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0374-7