Summary
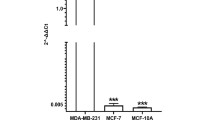
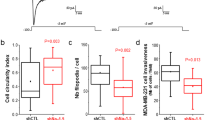
Voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) are known to be involved in the initiation and progression of many malignancies, and the different subtypes of VGSCs play important roles in the metastasis cascade of many tumors. This study investigated the functional expression of Nav1.5 and its effect on invasion behavior of human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. The mRNA and protein expression of Nav1.5 was detected by real time PCR, Western Blot and immunofluorescence. The effects of Nav1.5 on cell proliferation, migration and invasion were respectively assessed by MTT and Transwell. The effects of Nav1.5 on the secretion of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) by MDA-MB-231 were analyzed by RT-PCR. The over-expressed Nav1.5 was present on the membrane of MDA-MB-231 cells. The invasion ability in vitro and the MMP-9 mRNA expression were respectively decreased to (47.82±0.53)% and (43.97±0.64)% (P<0.05) respectively in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with VGSCs specific inhibitor tetrodotoxin (TTX) by blocking Nav1.5 activity. It was concluded that Nav1.5 functional expression potentiated the invasive behavior of human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 by increasing the secretion of MMP-9.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaidya KS, Welch DR. Metastasis suppressors and their roles in breast carcinoma. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia, 2007,12(2–3):175–190
Roger S, Potier M, Vandier C, et al. Voltage-gated sodium channels: new targets in cancer therapy? Curr Pharm Des, 2006,12(28):3681–3695
Jamie L, Victor P, Milton L, et al. Voltage-sensitive ion channels and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2006,25(3):493–500
Goldin A, Barchi R, Caldwell J, et al. Nomenclature of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron, 2000,28(2):365–368
Alami N, Paterson J, Belanger S, et al. Comparative analysis of xanafide cytotoxicity in breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer, 2007,97(1):58–64
Kenneth J, Thomas D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time qantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT mthod. Methods, 2001, 25(4):402–408
Guennec J, Ouadid H, Soriani O, et al. Voltage-gated ion channels, new targets in anti-cancer research. Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov, 007,2(3):189–202
Diss J, Calissano M, Gascoyne D, et al. Identification and characterization of the promoter region of the Nav1.7 voltage-gated sodium channel gene (SCN9A). Mol Cell Neurosci, 2008,37(3):537–547
Monk M, Holding C. Human embryonic genes re-expressed in cancer cells. Oncogene, 2001,20(56):8085–8091
Palmer C, Mycielska M, Burcu H, et al. Single cell adhesion measuring apparatus (SCAMA): application to cancer cell lines of different metastatic potential and voltage- gated Na+ channel expression. Eur Biophys J, 2008,37(4):359–368
Roger S, Rollin J, Barascu A, et al. Voltage-gated sodium channels potentiate the invasive capacities of human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2007,39(4):774–786
Diss J, Stewart D, Pani F, et al. A potential novel marker for human prostate cancer: voltage gated sodium channel expression in vivo. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Disease, 2005,8(3):266–273
Delassus G, Cho H, Park J, et al. New pathway links from cancer-progression determinants to gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases in breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol, 2008,217(3):739–744
Mycielska ME, Fraser SP, Szatkowski M, et al. Contribution of functional voltage-gated Na+ channel expression to cell behaviors involved in the metastatic cascade in rat prostate cancer: II. Secretory membrane activity. J Physiol, 2003,195(3):461–469
Onganer PU, Djamgoz MB. Small cell lung cancer (human): Potentiation of endocytic membrane activity by voltagegated Na(+) channel expression in vitro. J Membr Biol, 2005,204(2):67–75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, R., Wang, J., Shen, Y. et al. Functional expression of voltage-gated sodium channels Nav1.5 in human breast caner cell line MDA-MB-231. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 64–67 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0113-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0113-5