Summary
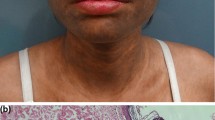
To investigate the role of toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) in the pathogenesis of lichen planus, the expressions of TLR9 and its mRNA in the lesional skin of lichen planus were detected by immunohistochemical technique (SP) and RT-PCR. As control, normal skin of healthy volunteers was also tested. The immunohistochemical study showed that the expression of TLR9 in the lesional skin of lichen planus was significantly higher than that in the normal controls. The results of RT-PCR showed that both skin lesions and normal controls had TLR9 expression. In skin lesions, the expression level of TLR9 mRNA was 1.6075±0.0930, which was significantly higher than that in normal controls (P<0.001). These findings indicated that up-regulated expression of TLR9 and its mRNA might be involved in the pathogenesis of lichen planus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Underhill D M, Ozinsky A. Toll-like receptors: key mediators of microbe detection. Curr Opin Immunol, 2002, 14(1):103–110
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M et al. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature, 1994,342(6248):440–443
Kadowaki N, Ho S, Antonenko S et al. Subsets of human dendritic cell precursors express different toll-like receptors and respond to different microbial antigens. J Exp Med, 2001, 194:863–
De Vries H J, van Marle J, Teunissen M B et al. Lichen planus is associated with human herpesvirus type 7 replica-tion and infiltration of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Br J Dermatol, 2006, 154(2): 361–364
Liu Y J. IPC: professional type I interferon-producing cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors. Annu Rev Immunol, 2005, 23:275–306
Lang, K S, Recher M, Junt T et al. Toll-like receptor en-gagement converts T-cell autoreactivity into overt autoimmune disease. Nat Med, 2005, 11:138–145
Latz E, Schoenemeyer A, Visintin A et al. TLR9 signals after translocating from the ER to CpG DNA in the lysosome. Nat Immunol, 2004, 5(2):190–198
Mbow M L, Sarisky M. Modulating toll-like receptor signalling as a novel antiinfective approach. RT Drug News Perspect, 2005, 18(3): 179–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
LI Jiawen, female, born in 1948, Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Chen, J., Tan, Z. et al. Expression of TLR9 and its mRNA in the lesions of lichen planus. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 203–205 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0226-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0226-7