Abstract
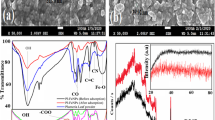
A green and convenient pathway of preparing iron nanoparticles (FeNPs) with pomegranate leaf (PG) extract for highly effective removal of malachite green (MG) was proposed under ambient conditions. The materials were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) techniques. The results show that their surfaces are capped and stabilized by PG extract with amorphous nature and without any detection of zero-valent iron. The size and surface valence state of FeNPs are the key factors that affect the MG removal efficiency. As the reagent volume ratio of PG extract to FeCl3 increases greater than 1, the cross-linked FeNPs become more obvious, having a homogeneous distribution with the size range from 30 to 40 nm, and show an increasing ratio of Fe(II)/Fe(III), which is in proportion to the degradation efficiency of MG, reaching higher than 95% in only 2 min by using 50 mg Fe/L FeNPs and 200 mg/L MG.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas M, Adil M, Ehtisham-ul-Haque S, et al. Vibrio Fischeri Bioluminescence Inhibition Assay for Ecotoxicity Assessment: A Review[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 626: 1295–1309
Iqbal M. Vicia Faba Bioassay for Environmental Toxicity Monitoring: A Review[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144: 785–802
Fu F, Dionysiou D D, Liu H. The Use of Zero-valent Iron for Ground-water Remediation and Wastewater Treatment: A Review[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2014, 267: 194–205
He Y, Gao J F, Feng F Q, et al. The Comparative Study on the Rapid Decolorization of Azo, Anthraquinone and Triphenylmethane Dyes by Zero-valent Iron[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 179: 8–18
Chen K, Wang G H, Li W B. Synthesis of Magnetically Modified Fe-Al Pillared Bentonite and Heterogeneous Fenton-like Degradation of Orange II [J]. J. Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2015, 30: 302–306
Bachheti R K, Konwarh R, Gupta V, et al. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Cutting Edge Technology and Multifaceted Applications[M]. Springer, Cham. Nanomaterials and Plant Potential, 2019: 239–259
Saif S, Tahir A, Chen Y S. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles and Their Environmental Applications and Implications[J]. Nanomaterials, 2016, 6: 209–234
Ting A S Y, Chin J E. Biogenic Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles from Apple Peel Extracts for Decolorization of Malachite Green Dye[J]. Water Air Soil Pollut., 2020, 231: 1–10
Muhammad F, Xia M, Li S, et al. The Reduction of Chromite Ore Processing Residues by Green Tea Synthesized Nano Zerovalent Iron and Its Solidification/Stabilization in Composite Geopolymer[J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2019, 234: 381–391
Ebrahiminezhad A, Zare-Hoseinabadi A, K. Sarmah A, et al. Plant-Mediated Synthesis and Applications of Iron Nanoparticles[J]. Mol. Biotechnol., 2018, 60: 154–168
Ouyang Q, Kou F, Tsang P E, et al. Green Synthesis of Fe-Based Material Using Tea Polyphenols and Its Application as a Heterogeneous Fenton-Like Catalyst for the Degradation of Lincomycin[J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2019, 232: 1492–1498
Seabra A B, Haddad P, Duran N. Biogenic Synthesis of Nanostructured Iron Compounds: Applications and Perspectives[J]. IET Nanobiotechnol., 2013, 7: 90–99
Xiao C Y, Li H Y, Zhao Y, et al. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles by Tea Extract (Polyphenols) and Its Selective Removal of Cationic Dyes[J]. J. Environ. Manage., 2020, 275: 1–11
Plachtová P, Medříková Z, Zbořil R, et al. Iron and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized with Green Tea Extract: Differences in Ecotoxicological Profile and Ability to Degrade Malachite Green[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2018, 6: 8679–8687
Dash A, Ahmed M T, Selvaraj R. Mesoporous Magnetite Nanoparticles Synthesis Using the Peltophorum Pterocarpum Pod Extract, Their Antibacterial Efficacy Against Pathogens and Ability to Remove a Pollutant Dye[J]. J. Mol. Struct., 2019, 1178: 268–273
Elkady M, Shokry H, El-Sharkawy A, et al. New Insights into the Activity of Green Supported Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron Composites for Enhanced Acid Blue-25 Dye Synergistic Decolorization from Aqueous Medium[J]. J. Mol. Liq., 2019, 294: 1–18
Ozkan Z Y, Cakirgoz M, Kaymak E S, et al. Rapid Decolorization of Textile Wastewater by Green Synthesized Iron Nanoparticles[J]. Water Sci. Technol., 2018, 77(2): 511–517
Machado S, Pinto S L, Grosso J P, et al. Green Production of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles Using Tree Leaf Extracts[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2013, 445–446: 1–8
Bibi I, Nazar N, Ata S, et al. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Pomegranate Seeds Extract and Photocatalytic Activity Evaluation for the Degradation of Textile Dye[J]. J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2019, 8: 6115–6124
Nadagouda M N, Castle A B, Murdock R C, et al. In Vitro Biocompatibility of Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron Particles (NZVI) Synthesized Using Tea Polyphenols[J]. Green Chem., 2010, 12: 114–122
Huang L L, Luo F, Chen Z, et al. Green Synthesized Conditions Impacting on the Reactivity of Fe NPs for the Degradation of Malachite Green[J]. Spectrochim. Acta. A, 2015, 137: 154–159
Chen Z X, Jin X Y, Chen Z L, et al. Removal of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solution Using Bentonite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron[J]. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 363: 601–607
Weng X L, Huang L L, Chen Z L, et al. Synthesis of Iron-Based Nanoparticles by Green Tea Extract and Their Degradation of Malachite[J]. Ind. Crop. Prod., 2013, 51: 342–347
Wang X, Wang A, Ma J, et al. Facile Green Synthesis of Functional Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Studies of Its Activity Toward Ultrasound-Enhanced Decolorization of Cationic Dyes[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 166: 80–88
Markova Z, Novak P, Kaslik J, et al. Iron(II, III)-Polyphenol Complex Nanoparticles Derived from Green Tea with Remarkable Ecotoxicological Impact[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2014, 2: 1674–1680
Wang Z. Iron Complex Nanoparticles Synthesized by Eucalyptus Leaves[J]. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2013, 1: 1551–1554
Huang L L, Weng X L, Chen Z L, et al. Synthesis of Iron-Based Nanoparticles Using Oolong Tea Extract for the Degradation of Malachite Green[J]. Spectrochim. Acta. A, 2014, 117: 801–804
Wang Z, Fang C, Megharaj M. Characterization of Iron-Polyphenol Nanoparticles Synthesized by Three Plant Extracts and Their Fenton Oxidation of Azo Dye[J]. ACS Sustain Chem. Eng., 2014, 2: 1022–1025
Wang Z, Fang C, Megharaj M. Characterization of Iron-Polyphenol Complex Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sage (Salvia officinalis) Leaves[J]. Environ. Technol. Inno., 2015, 4: 92–97
Ebrahiminezhad A, Taghizadeh S, Ghasemi Y, et al. Green Synthesized Nanoclusters of Ultra-Small Zero Valent Iron Nanoparticles as a Novel Dye Removing Material[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 621: 1527–1532
Yu L, Qiu Y W, Yu Y, et al. Reductive Decolorization of Azo Dyes Via in situ Generation of Green Tea Extract-Iron Chelate[J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2018, 25: 17300–17309
Biesinger M C, Payne B P, Grosvenor A P, et al. Resolving Surface Chemical States in XPS Analysis of First Row Transition Metals, Oxides and Hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257: 2717–2730
Huang L L, Weng X L, Chen Z L, et al. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles by Various Tea Extracts: Comparative Study of the Reactivity[J]. Spectrochim. Acta. A, 2014, 130: 295–301
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21407050), and the Excellent Young and Middle-aged Science and Technology Innovation Team Plan of Hubei Colleges (No. T201824)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Zhou, S., Pan, X. et al. Fe Nanoparticles Synthesized by Pomegranate Leaves for Treatment of Malachite Green. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 37, 350–354 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-022-2538-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-022-2538-7