Abstract
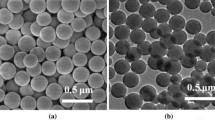
Polystyrene crosslinked microspheres were prepared by soap-free emulsion polymerization using styrene (St) and divinylbenzene (DVB) as monomers; then, the microporous structure was knitted by the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, and the Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) were loaded into the pores through thermal reduction, to obtain AuNPs/hyper-crosslinked microporous polymer composite microspheres. SEM and particle-size test results show that the microspheres show good monodispersity. The micropore analysis indicates that the specific surface area and the pore volume of the microporous polymer microspheres decrease with increasing DVB content, and when the DVB content is 0.1%, the specific surface area reaches a maximum of 1 174.6 m2/g. After loading AuNPs, the specific surface area and the amount of micropores of the composite microspheres decrease obviously. The results of XRD and XPS analyses suggest that HAuCl4 is reduced to AuNPs. The composite microspheres show a good catalytic performance for the reduction catalyst of 4-nitrophenol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawson R, Cooper AI, Adams DJ. Nanoporous Organic Polymer Networks[J]. Prog. Polym. Sci., 2012, 37(4): 530–563
Xu S, Tan B, Parthiban A. Microporous Organic Polymers: Synthesis, Types, and Applications[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2014: 125–164
Hug S, Stegbauer L, Hirscher M, et al. Nitrogen Rich Covalent Triazine Frameworks as High Performance Platforms for Selective Carbon Capture and Storage[J]. Chem. Mater., 2015, 27(23): 8 001–8 010
Yuan S, Liu Z, Ma S. Application Status and Research Progress in the Physical and Chemical Properties, Preparation Methods and Modification Techniques of Gold Nanoparticle[J]. Mater. Rev., 2012, 26(9): 52–58
Schröfel A, Kratošová G, Šafařík I. Applications of Biosynthesized Metallic Nanoparticles-A Review[J]. Acta Biomater., 2014, 10(10): 4 023–4 042
Su D, Zhang Y, Wang Z, et al. Decoration of Graphene Nano Platelets with Gold Nanoparticles for Voltammetry of 4-nonylphenol[J]. Carbon, 2017, 117: 313–321
Mu Z, Zhao X, Xie Z, et al. In Situ Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) in Butterfly Wings for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS)[J]. J. Mater. Chem. B, 2013, 1(11): 1 607–1 613
Hu N, Yin JY, Tang Q, et al. Comparative Study of Amphiphilic Hyperbranched and Linear Polymer Stabilized Organo-soluble Gold Nanoparticles as Efficient Recyclable Catalysts in the Biphasic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol[J]. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem., 2011, 49(17): 3 826–3 834
Zhou DH, Liang CC, Nie J, et al. Construction of a Repairable Fixed Porous Catalytic Bed Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles via Multivalent Host-Guest Interactions[J]. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2017, 5: 7 587–7 593
Fang X, Ma H, Xiao S, et al. Facile Immobilization of Gold Nanoparticles into Electrospun Polyethyleneimine/Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofibers for Catalytic Applications[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(12): 4 493–4 501
Zou XH, Wei ZZ, Du J, et al. Preparation and Properties of Magnetic-fluorescent Microporous Polymer Microspheres[J]. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ., 2018, 34(4): 684–690
Cui J, Wen HE, Liao S, et al. Measuring and Analysing Techniques of Structural Features for Porous Materials Research[J]. Mater. Rev., 2009, 23(13): 82–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51303049)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Zhang, L., Zhao, Y. et al. Preparation and Catalytic Performance of Microporous Polymer/Au Nanoparticles Composite Microspheres. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 35, 464–468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-020-2279-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-020-2279-4